|
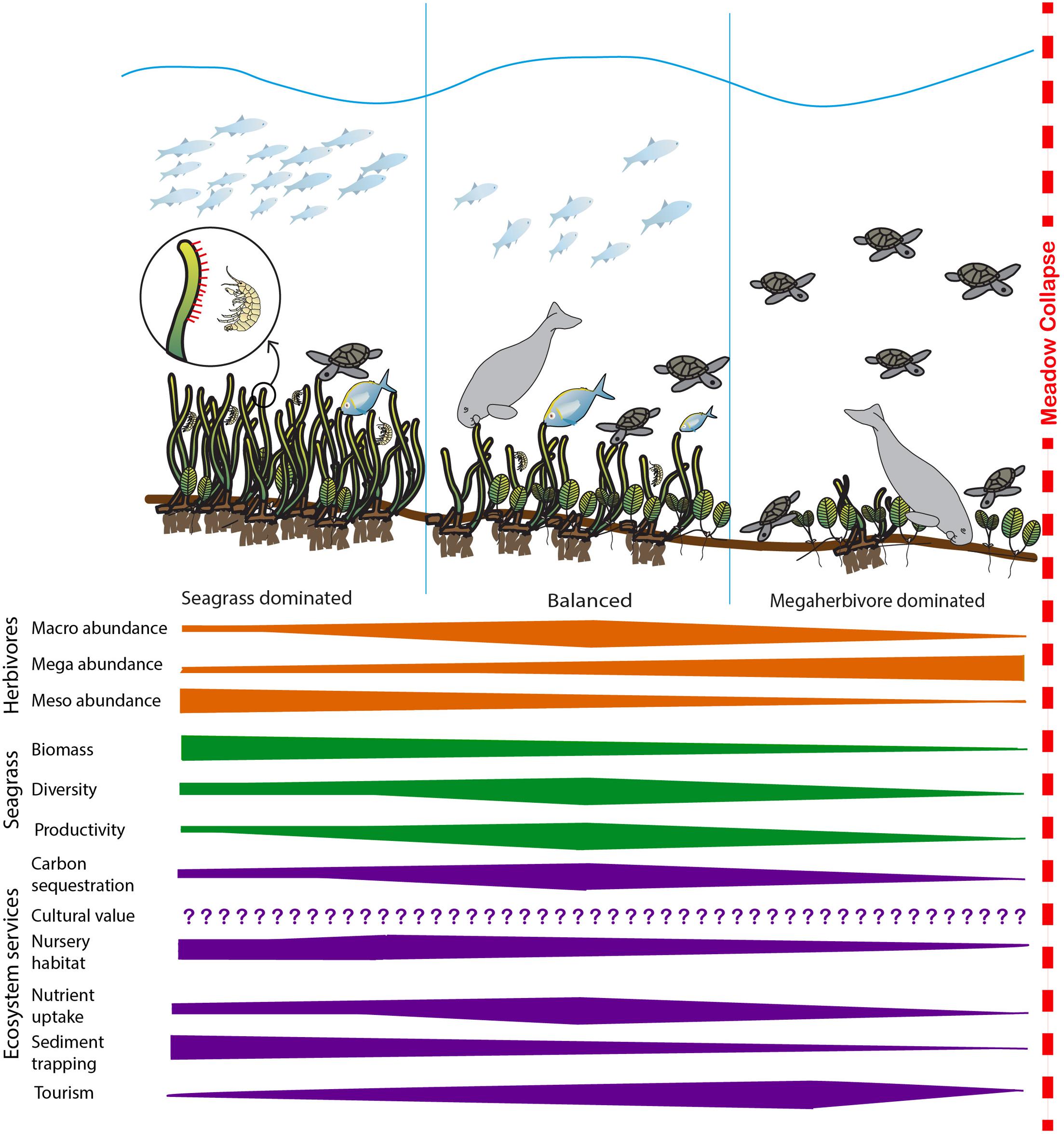
Relative Abundance Distribution
In the field of ecology, the relative abundance distribution (RAD) or species abundance distribution describes the relationship between the number of species observed in a field study as a function of their observed abundance. The graphs obtained in this manner are typically fitted to a Zipf–Mandelbrot law, the exponent of which serves as an index of biodiversity Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ... in the ecosystem under study. Notes and references Ecological metrics {{ecology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and it is not synonymous with environmentalism. Among other things, ecology is the study of: * The abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment * Life processes, antifragility, interactions, and adaptations * The movement of materials and energy through living communities * The successional development of ecosystems * Cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species * Patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes Ecology has practical applications in conservation biology, wetland management, natural res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abundance (ecology)
In ecology, local abundance is the relative representation of a species in a particular ecosystem. It is usually measured as the number of individuals found per sample. The ratio of abundance of one species to one or multiple other species living in an ecosystem is referred to as relative species abundances. Both indicators are relevant for computing biodiversity. A variety of sampling methods are used to measure abundance. For larger animals, these may include spotlight counts, track counts and roadkill counts, as well as presence at monitoring stations. In many plant communities the abundances of plant species are measured by plant cover, i.e. the relative area covered by different plant species in a small plot. Abundance is in simplest terms usually measured by identifying and counting every individual of every species in a given sector. It is common for the distribution of species to be skewed so that a few species take up the bulk of individuals collected. Relative spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zipf–Mandelbrot Law
In probability theory and statistics, the Zipf–Mandelbrot law is a discrete probability distribution. Also known as the Pareto–Zipf law, it is a power-law distribution on ranked data, named after the linguist George Kingsley Zipf who suggested a simpler distribution called Zipf's law, and the mathematician Benoit Mandelbrot, who subsequently generalized it. The probability mass function is given by: :f(k;N,q,s)=\frac where H_ is given by: :H_=\sum_^N \frac which may be thought of as a generalization of a harmonic number. In the formula, k is the rank of the data, and q and s are parameters of the distribution. In the limit as N approaches infinity, this becomes the Hurwitz zeta function \zeta(s,q). For finite N and q=0 the Zipf–Mandelbrot law becomes Zipf's law. For infinite N and q=0 it becomes a Zeta distribution. Applications The distribution of words ranked by their frequency Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') level. Biodiversity is not distributed evenly on Earth; it is usually greater in the tropics as a result of the warm climate and high primary productivity in the region near the equator. Tropical forest ecosystems cover less than 10% of earth's surface and contain about 90% of the world's species. Marine biodiversity is usually higher along coasts in the Western Pacific, where sea surface temperature is highest, and in the mid-latitudinal band in all oceans. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity. Biodiversity generally tends to cluster in hotspots, and has been increasing through time, but will be likely to slow in the future as a primary result of deforestation. It encompasses the evolutionary, ecological, and cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)