|
Rekolok
{{unreferenced, date=December 2014 The German term Rekonstruktionslokomotive (abbreviated to: Rekolokomotive or Rekolok) meant 'reconstruction locomotive' and was introduced in 1957 by the Deutsche Reichsbahn in the GDR. The term was used for classes of steam locomotive that underwent considerable rebuilding in order to improve performance, rectify design faults and redress wartime austerity features. At the same time, repairs were carried out. The 'reconstruction' included, as a minimum, the installation of a new high performance steam generation system. Consequently, a characteristic feature of these ''Rekoloks'' is a combustion chamber boiler with rectangular mixing chamber (''Mischkasten'') in front of the chimney. On individual classes (Class 58.30), completely new driver's cabs were built, instead of just fitting the new end walls needed after the boiler had been replaced. The worn cast cylinder blocks were sometimes replaced by welded cylinders. Unlike the Deutsche Bundesb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRG Class 41
The German Class 41 steam locomotives were standard goods train engines ('' Einheitslokomotiven'') operated by the Deutsche Reichsbahn (DRB) and built from 1937 to 1941. History In the search for a new, fast, goods train locomotive, the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft (DRG) in 1934 was attracted by the proposal from the Berliner Maschinenbau (BMAG, formerly Louis Schwartzkopff) for a 2-8-2 (1'D1'h2) engine. The design, produced by Friedrich Wilhelm Eckhardt (1892–1961), differed from the DRG's original requirement for a 2-8-0 (1'D) engine, because the required performance with an 18-ton axle load was easier to generate on a 2-8-2 engine rather than one with a 2-8-0 wheel configuration. Continued adherence to this instruction would in the end have given the new engine no significant advantage over the Prussian goods train locomotives which were to be withdrawn. The Reichsbahn Central Office Engineering Works (RZM) eventually agreed to this proposal; the BMAG was taske ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRG Class 50
The DRB Class 50Wartime locomotives classes are prefixed DRB (Deutsche Reichsbahn) to distinguish them from those introduced by the DRG (prefixed DRG), which became defunct in 1937, and those introduced later by the East German Deutsche Reichsbahn (prefixed DR). is a German class of 2-10-0 locomotive, built from 1939 as a standard locomotive (''Einheitsdampflokomotive'') for hauling goods trains. It had one leading axle and five coupled axles and was one of the most successful designs produced for the Deutsche Reichsbahn. This class was procured as part of the German Nazi party's preparations for war that led into the Second World War. Up to 1948, 3,164 Class 50 engines were built by almost all the European locomotive factories – towards the end as so-called provisional war locomotives (''Übergangskriegslokomotiven'') and classified as 50 ÜK. At the end of the steam locomotive era, they became virtually a universal class of mixed-traffic steam engine that, thanks to their low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DR Class 22
The steam locomotives of DR Class 22 were reconstructed passenger train locomotives in service with the Deutsche Reichsbahn in East Germany after the Second World War. These engines were rebuilt from DRG Class 39.0-2 locomotives and appeared between 1958 and 1962 as part of the reconstruction programme. The latter had a significant problem: the boiler did not generate enough steam and the steam pipes were too winding, which considerably reduced the maximum power of the engine. A total of 85 examples were equipped with a new combustion-chambered boiler with an ''IfS'' mixer-preheater. The locomotive frame had to be extended to accommodate the new engine. The wider outer firebox meant that the driver's cab needed a modified rear wall. The locomotives were given operating numbers 22 001–085 and were mainly homed in the Reichsbahn divisions of Dresden and Erfurt. The DR employed the locomotives on heavy express train duties in the schedules for the DRG Class 01, which led to ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRG Class 23
The German Class 23 (''Baureihe 23'' or ''BR 23'') engines of the Deutsche Reichsbahn (''DRG'') were standard ('' Einheitslokomotiven'') steam engines that were conceived as a replacement for the Prussian P 8 by the Schichau Works. They were given the same boiler as the Class 50s which were developed in parallel and, like them, the newly developed 2'2' T 26 tender with its front wall that protected train crews during reverse running. In 1941 the two prototypes were built and delivered. The procurement of 800 locomotives had been planned, however the constraints of the Second World War meant that they never entered full production. After the war the two locomotives, with operating numbers 23 001 and 23 002, went to the DR in East Germany and were variously stabled in Berlin, Brandenburg an der Havel, Jüterbog and Halle. In 1961, number 23 001 was given a '' Reko'' boiler with combustion chamber, developed for the Class 50. In 1970 the locomotive was given EDP number 35 2001 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian P 10
The Prussian state railways' Class P 10 were 2-8-2 "Mikado" type passenger-hauling steam locomotives built for hauling heavy express trains in the hilly terrain of the ''Mittelgebirge''. They were the last Prussian passenger train steam locomotives to be developed in Prussia before the state railways were merged into the Deutsche Reichsbahn (German Imperial Railway), who eventually designated them as DRG Class 39. The design by Borsig, under the supervision of chief engineer August Meister, was ready in 1919 but, due to material shortages, no locomotives were produced until 1922. They were three-cylinder locomotives, all cylinders driving the second coupled axle. Three sets of Walschaerts valve gear were used, the one for the inside cylinder being mainly located inside the frame, but driven from the same eccentric crank as the valve gear on the left-hand side; two eccentric rods of different lengths being attached to the same crank. The locomotives' heavy axle-load exceeded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian G 12
The Prussian G 12 is a 1'E 2-10-0 goods train locomotive built for the Prussian state railways (''Preußische Staatseisenbahnen''). It had been shown during the First World War that, from a servicing and maintenance point of view, it was a great disadvantage for each state railway to have its own locomotive classes with no standardization. Even spare parts for locos of the same class often did not fit their sister locos. In addition, the military railways needed a fast, powerful, goods locomotive that did not have a high axle load. ''Einheitslokomotive'' G 12 In the advertisements placed by locomotive factories, G 12 engines were described as ''Einheitslokomotiven'' (standard locomotives). That caused a lot of confusion, because the term ''Einheitslokomotive'' had become synonymous with the ''Einheitslokomotive 1925'', designed in that year by the DRG ( „Kunibald“ Wagner). The Deutsche Bundesbahn (DB) also called its steam locomotives ''Einheitslokomotive 1950'' according ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRG Class 01
The Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft's BR 01 steam locomotives were the first standardised (''Einheitsdampflokomotive'') steam express passenger locomotives built by the unified German railway system. They were of 4-6-2 "Pacific" wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or 2′C1′ h2 in the UIC classification. The idea of standardisation was that it would reduce maintenance costs; i.e. if a BR 01 whose engine shop was in, say, Berlin broke down in Dresden, instead of having to ship the necessary part from Berlin and take the locomotive out of service, a part from the Dresden shop could be used as all of the engines, parts, and workings were exactly the same and produced nationwide. Thus it was a "standard" product for engine shops. History The firms of AEG and Borsig, who were the main manufacturers of these engines, together with Henschel, Hohenzollern, Krupp and BMAG previously Schwartzkopff, delivered a total of 231 examples of this ''Einheitsdampflokomotive'' between 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Bundesbahn
The Deutsche Bundesbahn or DB (German Federal Railway) was formed as the state railway of the newly established Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) on 7 September 1949 as a successor of the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft (DRG). The DB remained the state railway of West Germany until after German reunification, when it was merged with the former East German Deutsche Reichsbahn (DR) to form Deutsche Bahn, which came into existence on 1 January 1994. Background After World War II, each of the military governments of the Allied Occupation Zones in Germany were ''de facto'' in charge of the German railways in their respective territories. On 10 October 1946, the railways in the British and American occupation zones formed the ''Deutsche Reichsbahn im Vereinigten Wirtschaftsgebiet'' (German Imperial Railway in the united economic area), while on 25 June 1947, the provinces under French occupation formed the Südwestdeutsche Eisenbahn. With the formation of the FRG these succe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
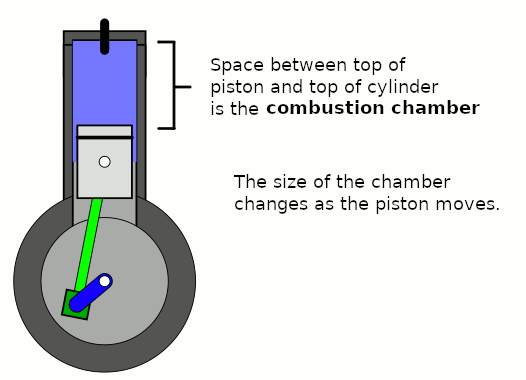
Combustion Chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process. Internal combustion engines In an internal combustion engine, the pressure caused by the burning air/fuel mixture applies direct force to part of the engine (e.g. for a piston engine, the force is applied to the top of the piston), which converts the gas pressure into mechanical energy (often in the form of a rotating output shaft). This contrasts an external combustion engine, where the combustion takes place in a separate part of the engine to where the gas pressure is converted into mechanical energy. Spark-ignition engines In spark ignition engines, such as petrol (gasoline) engines, the combustion chamber is usually located in the cylinder head. The engines are often designed such that the bottom of combustion chamber is roughly in li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxon XX HV (Reko)
The Saxon Class XX \textstyle \mathfrak\textstyle \mathfrak were German eight-coupled express train, tender locomotives built for the Royal Saxon State Railways (''Königlich Sächsische Staatseisenbahnen'') just after the First World War. The locomotives, which became known as the 'Pride of Saxony' (''Sachsenstolz'') were the first and only German express locomotives with a 2-8-2 wheel arrangement and, at the time of their appearance, were the largest express engines in the whole of Europe. In 1925, the Deutsche Reichsbahn grouped these locomotive into their DRG Class 19.0. History The XX HVs were the last Saxon express train locomotives and were the pinnacle of Saxon locomotive engineering. They were conceived primarily for heavy express train duties on the winding and hilly Dresden to Hof trunk route through the ''Mittelgebirge''. Its design was related to the simultaneously developed 4-6-2 express locomotive Saxon XVIII H, but unlike the latter, it had a fourth coupled axle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baden IV H (DR) (18 314)
The class IV h (four-h) locomotives of the Grand Duchy of Baden State Railway (German: ''Großherzoglich Badische Staatseisenbahnen, G.Bad.St.E.'') were express locomotives with a 4-6-2 (Pacific) wheel arrangement. They later passed to the Deutsche Reichsbahn, who classified them as class 183. Construction features The twenty class IV h locomotives built by Maffei for the Grand Duchy of Baden State Railway were intended to replace the class IV f locomotives, which were overburdened on the Rhine Valley railway line between Basel and Mannheim due to their driving wheels being too small. Accordingly, the IV h with a drive wheel diameter of was designed uncompromisingly as a flatland express train locomotive. Nevertheless, the IV h were initially only approved for for braking reasons. The IV h has a four-cylinder compound engine with divided drive. In contrast to earlier Maffei designs, the inner cylinders are driven on the first coupled wheelset, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DR 18 201
The German express locomotive, number 18 201 of the Deutsche Reichsbahn in East Germany, appeared in 1960–61 at Meiningen Steam Locomotive Works as a conversion of the Henschel-Wegmann train locomotive 61 002, the tender from 44 468 and parts of H 45 024 and Class 41. It is the fastest operational steam locomotive in the world. Origin The motivation for the conversion was firstly that, as a one-off, locomotive 61 002 could not really be used for scheduled services, and secondly that the research institute at VES-M Halle urgently needed locomotives that could do at least 160 km/h in order to test passenger coaches. For the conversion a DR Class 22 new-design boiler, parts of the unsuccessful high pressure locomotive, H 45 024, (outside cylinders, trailing wheels and rear section of the locomotive frame) as well as the tender of locomotive 44 468 were used. The inside cylinder of the three-cylinder engine was not however taken from 61 002, rather a new one was made. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)