|
Reichstag (German Empire)
The Reichstag () of the German Empire was Germany's lower house of parliament from 1871 to 1918. Within the governmental structure of the Reich, it represented the national and democratic element alongside the federalism of the Bundesrat and the monarchic and bureaucratic element of the executive, embodied in the Reich chancellor. Together with the Bundesrat, the Reichstag had legislative power and shared in decision-making on the Reich budget. It also had certain rights of control over the executive branch and could engage the public through its debates. The emperor had little political power, and over time the position of the Reichstag strengthened with respect to the Bundesrat. Reichstag members were elected for three year terms from 1871 to 1888 and following that for five years. It had one of the most progressive electoral laws of its time: with only a few restrictions, all men 25 and older were allowed to vote, secretly and equally. The Reichstag met throughout the First Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary empire led by an emperor, although has been used in German to denote the Roman Empire because it had a weak hereditary tradition. In the case of the German Empire, the official name was , which is properly translated as "German Empire" because the official position of head of state in the constitution of the German Empire was officially a "presidency" of a confederation of German states led by the King of Prussia who would assume "the title of German Emperor" as referring to the German people, but was not emperor of Germany as in an emperor of a state. –The German Empire" ''Harper's New Monthly Magazine''. vol. 63, issue 376, pp. 591–603; here p. 593. also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich, as well as simply Germany, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1871 German Federal Election
The first federal elections were held in Germany on 3 March 1871.Dieter Nohlen & Philip Stöver (2010) ''Elections in Europe: A data handbook'', p762 The National Liberal Party emerged as the largest party in the Reichstag, with 117 of the 382 seats.Nohlen & Stöver, p788 Voter turnout was just 51.0%. Results References {{Authority control Federal elections in Germany Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ... 1871 elections in Germany Elections in the German Empire March 1871 events ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Saxony
The Kingdom of Saxony (german: Königreich Sachsen), lasting from 1806 to 1918, was an independent member of a number of historical confederacies in Napoleonic through post-Napoleonic Germany. The kingdom was formed from the Electorate of Saxony. From 1871, it was part of the German Empire. It became a free state in the era of Weimar Republic in 1918 after the end of World War I and the abdication of King Frederick Augustus III of Saxony. Its capital was the city of Dresden, and its modern successor state is the Free State of Saxony. History Napoleonic era and the German Confederation Before 1806, Saxony was part of the Holy Roman Empire, a thousand-year-old entity that had become highly decentralised over the centuries. The rulers of the Electorate of Saxony of the House of Wettin had held the title of elector for several centuries. When the Holy Roman Empire was dissolved in August 1806 following the defeat of Emperor Francis II by Napoleon at the Battle of Austerlitz, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Bavaria
The Kingdom of Bavaria (german: Königreich Bayern; ; spelled ''Baiern'' until 1825) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1805 and continued to exist until 1918. With the unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the kingdom became a federated state of the new empire and was second in size, power, and wealth only to the leading state, the Kingdom of Prussia. The polity's foundation dates back to the ascension of prince-elector Maximilian IV Joseph of the House of Wittelsbach as King of Bavaria in 1805. The crown would go on being held by the Wittelsbachs until the kingdom came to an end in 1918. Most of the border of modern Germany's Free State of Bavaria were established after 1814 with the Treaty of Paris, in which the Kingdom of Bavaria ceded Tyrol and Vorarlberg to the Austrian Empire while receiving Aschaffenburg and Würzburg. In 1918, Bavaria became a republic after the German Revolution, and the kingdom was thus succeeded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick II, more commonly known as Frederick the Great, who was the third son of Frederick William I.Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Frederick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffrage
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise, is the right to vote in representative democracy, public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally in English, the right to vote is called active suffrage, as distinct from passive suffrage, which is the right to stand for election. The combination of active and passive suffrage is sometimes called ''full suffrage''. In most democracies, eligible voters can vote in elections of representatives. Voting on issues by referendum may also be available. For example, in Switzerland, this is permitted at all levels of government. In the United States, some U.S. state, states such as California, Washington, and Wisconsin have exercised their shared sovereignty to offer citizens the opportunity to write, propose, and vote on referendums; other states and the United States federal government, federal government have not. Referendums in the United K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North German Constitution
The North German Constitution was the constitution of the North German Confederation, which existed as a country from 1 July 1867 to 31 December 1870. The Constitution of the German Empire (1871) was closely based on it. A constituent Reichstag was elected on 12 February 1867. Its only task was to discuss, amend and adopt the proposal for a constitution which had been largely written by Otto von Bismarck, the Prussian minister president and first and only federal chancellor (), the sole minister of the Confederation. The constituent Reichstag was dominated by national liberals and moderate conservatives. The highest body of the country was the Bundesrat (Federal Council). It represented the governments of the North German states. Prussia had 17 of 43 votes in the Bundesrat. Decisions were based on a simple majority (Article 7), but Prussia's great size and influence often gave it what amounted to a veto. Under the constitution, the king of Prussia (William I), was the holder of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
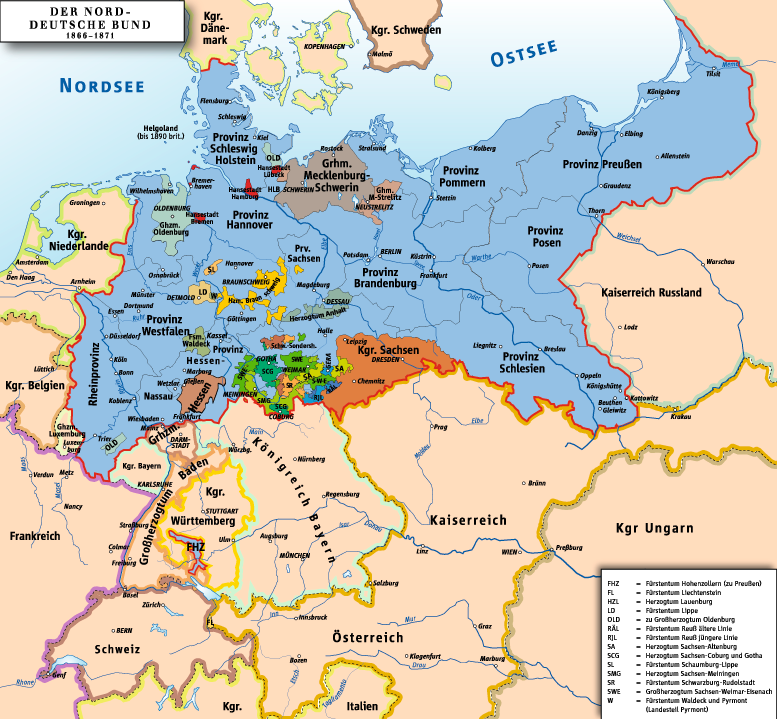
North German Confederation
The North German Confederation (german: Norddeutscher Bund) was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated state (a ''de facto'' federal state) that existed from July 1867 to December 1870. A milestone of the German Unification, it was the earliest continual legal predecessor of the modern German nation-state known today as the Federal Republic of Germany. The Confederation came into existence following the Prussian victory in the Austro-Prussian War of 1866 over the lordship of two small Danish duchies (Schleswig-Holstein) resulting in the Peace of Prague, where Prussia pressured Austria and its allies into accepting the dissolution of the existing German Confederation (an association of German states under the leadership of the Austrian Empire), thus paving the way for the Lesser German version of German unification in the form of a federal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichstag Of The North German Confederation
The Reichstag () of the North German Confederation was the federal state's lower house of parliament. The popularly elected Reichstag was responsible for federal legislation together with the Bundesrat, the upper house whose members were appointed by the governments of the individual states to represent their interests. Executive power lay with the Bundesrat and the king of Prussia acting as ''Bundespräsidium'', or head of state. The Reichstag debated and approved or rejected taxes and expenditures and could propose laws in its own right. To become effective, all laws required the approval of both the Bundesrat and the Reichstag. Voting rights in Reichstag elections were advanced for the time, granting universal, equal, and secret suffrage to men above the age of 25. When the German Empire was established in 1871, the North German Reichstag formed the basis of the new Reichstag of the German Empire. Background The draft constitution Following Prussia's victory in the 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichstag Of The Weimar Republic
The Reichstag of the Weimar Republic (1919–1933) was the lower house of Germany's parliament; the upper house was the Reichsrat, which represented the states. The Reichstag convened for the first time on 24 June 1920, taking over from the Weimar National Assembly, which had served as an interim parliament following the collapse of the German Empire in November 1918. Under the Weimar Constitution of 1919, the Reichstag was elected every four years by universal, equal, secret and direct suffrage, using a system of party-list proportional representation. All citizens who had reached the age of 20 were allowed to vote, including women for the first time, but excluding soldiers on active duty. The Reichstag voted on the laws of the Reich and was responsible for the budget, questions of war and peace, and confirmation of state treaties. Oversight of the Reich government (the ministers responsible for executing the laws) also resided with the Reichstag. It could force individual m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Revolution Of 1918–1919
The German Revolution or November Revolution (german: Novemberrevolution) was a civil conflict in the German Empire at the end of the First World War that resulted in the replacement of the German federal constitutional monarchy with a democratic parliamentary republic that later became known as the Weimar Republic. The revolutionary period lasted from November 1918 until the adoption of the Weimar Constitution in August 1919. Among the factors leading to the revolution were the extreme burdens suffered by the German population during the four years of war, the economic and psychological impacts of the German Empire's defeat by the Allies, and growing social tensions between the general population and the aristocratic and bourgeois elite. The first acts of the revolution were triggered by the policies of the Supreme Command () of the German Army and its lack of coordination with the Naval Command (). In the face of defeat, the Naval Command insisted on trying to precipita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |