|
Reginald Bosworth Smith
Reginald Bosworth Smith (1839–1908) was an English academic, schoolmaster, man of letters and author. Background and early life Born on 28 June 1839 at West Stafford rectory, Dorset, he was the second son in the large family of Reginald Southwell Smith (1809–1896); his mother was Emily Genevieve Simpson, daughter of Henry Hanson Simpson of Bitterne Manor House, Hampshire, and 12 Camden Place, Bath. His was an invalid suffering from tuberculosis. Bosworth Smith was brought up mostly by his mother, in a rectory family of 12 children, most of whom were infected by tuberculosis with some dying young. From Milton Abbas school, near Blandford, Bosworth Smith went on in August 1855 to Marlborough College, where he was head boy under successive headmasters—George Edward Lynch Cotton, and George Granville Bradley. Oxford and Harrow At Michaelmas 1858 Bosworth Smith matriculated with an open classical scholarship at Corpus Christi College, Oxford, and he graduated B.A. in 1862 with fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schoolmaster
The word schoolmaster, or simply master, refers to a male school teacher. This usage survives in British independent schools, both secondary and preparatory, and a few Indian boarding schools (such as The Doon School) that were modelled after British public schools, but is generally obsolete elsewhere. Origins The word “master” in this context translates the Latin word magister. In England, a schoolmaster was usually a university graduate, and until the 19th century the only universities were Oxford and Cambridge. Their graduates in almost all subjects graduated as Bachelors of Arts and were then promoted to Masters of Arts (''magister artium'') simply by seniority. The core subject in an English grammar school was Latin. Usage Where a school has more than one schoolmaster, a man in charge of the school is the headmaster, sometimes spelt as two words, "head master". This name survives in British independent schools, but it has been replaced by ''head teacher'' in most Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winwood Reade
William Winwood Reade (26 December 1838 – 24 April 1875) was a British historian, explorer, novelist and philosopher. His two best-known books, the universal history ''The Martyrdom of Man'' (1872) and the novel ''The Outcast'' (1875), were included in the Thinker's Library. Reade published one novel under the pseudonym, Francesco Abati. Biography Early life Born in Perthshire, Scotland, in 1838, William Winwood Reade was a "scion of a wealthy landed family". Having failed at Oxford University and, despite having composed two novels, "failed in any conventional sense as a novelist", Reade decided to begin geographical exploration. Travels to Africa Thus, at age 25, using his private funds and with sponsorship from the Royal Geographical Society, he departed for Africa, arriving in Cape Town by paddle steamer during 1862. After several months of observing gorillas and travelling through Angola, Reade returned home and published his first travel account, ''Savage Africa''. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Penrhyn Stanley
Arthur Penrhyn Stanley, (13 December 1815 – 18 July 1881), known as Dean Stanley, was an English Anglican priest and ecclesiastical historian. He was Dean of Westminster from 1864 to 1881. His position was that of a Broad Churchman and he was the author of a number of works on Church History. He was a co-founder of the Palestine Exploration Fund. Early life Stanley was born in Alderley Edge, in Cheshire, where his father, Edward Stanley, later Bishop of Norwich, was then rector. A brother was Owen Stanley, and his sister was Mary Stanley. The middle-name 'Penrhyn' suggests Welsh lineage. He was educated at Rugby School under Thomas Arnold and in 1834 went up to Balliol College, Oxford. He is generally considered to be the source for the character of George Arthur in Thomas Hughes's well-known book ''Tom Brown's Schooldays'', which is based on Rugby. After winning the Ireland scholarship and the Newdigate Prize for an English poem (''The Gypsies''), he was in 1839 elected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Wilmot Blyden
Edward Wilmot Blyden (3 August 1832 – 7 February 1912) was a Liberian educator, writer, diplomat, and politician who was primarily active in West Africa. Born in the Danish West Indies, he joined the waves of black immigrants from the Americas who migrated to the country. Blyden became a teacher for five years in the British West African colony of Sierra Leone in the early twentieth century. His writings on pan-Africanism became influential throughout West Africa, attracting attention in countries such as the United States as well. He believed that Zionism was a model for what he termed Ethiopianism, and that African Americans could return to Africa and help in the rebuilding of the continent. Blyden was recognised in his youth for his talents and drive; he was educated and mentored by John Knox, an American Protestant minister in Sankt Thomas who encouraged him to continue his education in the United States. In 1850 Blyden was refused admission to three Northern theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Pope Hennessy
Sir John Pope Hennessy (; 8 August 1834 – 7 October 1891), was an Irish and British politician and colonial administrator who served as the eighth Governor of Hong Kong and the fifteenth Governor of Mauritius. Early life John Pope Hennessy was born in County Cork in 1834, the son of John Hennessy of Ballyhennessy and his wife Elizabeth Casey. He was one of eight children. The family were middle class with his father working as a hide merchant. He suffered from bronchitis as a child and was therefore initially privately tutored. In 1850 he entered Queen's College, Cork, initially studying in the science division of the faculty of arts. During his first year he was awarded a scholarship as he was one of the top three students, and this allowed him to transfer to medicine. He proved to be a gifted student scoring honours in five out of six subjects in his finals, came first in surgery and second in medicine. In May 1855 he went to London to further his studies at Charing C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Waitz
Theodor Waitz (17 March 182121 May 1864) was a German psychologist and anthropologist. His research in psychology brought him into touch with anthropology, and he will be best remembered by his monumental work in six volumes, ''Die Anthropologie der Naturvölker'' ("The anthropology of peoples that live close to nature"). Biography Waitz was born at Gotha and educated at the universities of Leipzig and Jena. He made philosophy, philology and mathematics his chief studies, and in 1848 he was appointed associate professor of philosophy at the University of Marburg (full professor, 1862). He was a severe critic of the philosophy of Fichte, Schelling and Hegel, and considered psychology to be the basis of all philosophy. He died in Marburg. Theorizing boredom Theodor Waitz contributed significantly as an affective psychologist, particularly in the field of conceptualizing boredom.According to Waitz, boredom was about flow of thoughts. As one thought begets another, expectations o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
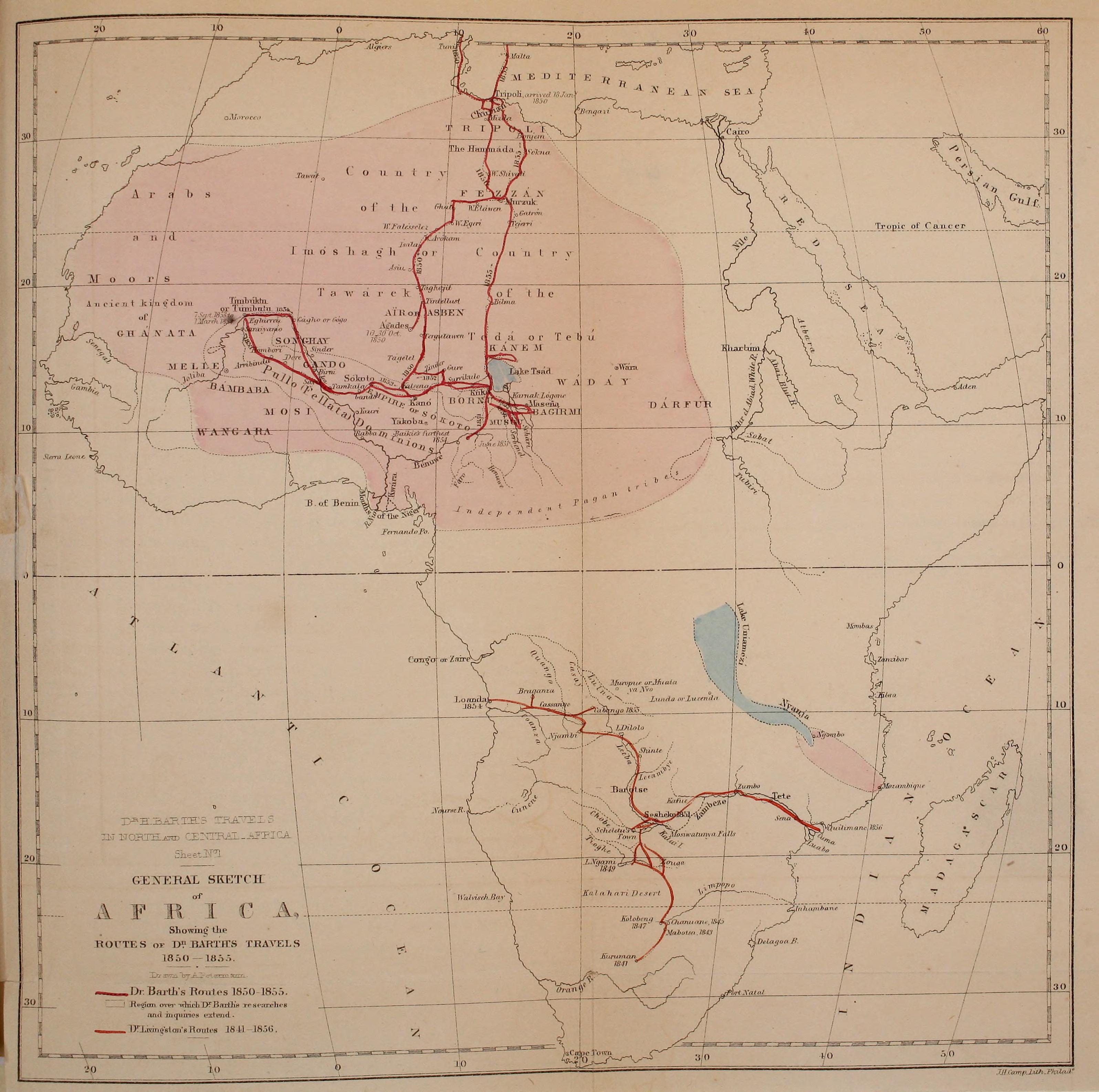
Heinrich Barth
Johann Heinrich Barth (; ; 16 February 1821 – 25 November 1865) was a German explorer of Africa and scholar. Barth is thought to be one of the greatest of the European explorers of Africa, as his scholarly preparation, ability to speak and write Arabic, learning African languages, and character meant that he carefully documented the details of the cultures he visited. He was among the first to comprehend the uses of oral history of peoples, and collected many. He established friendships with African rulers and scholars during his five years of travel (1850–1855). After the deaths of two European companions, he completed his travels with the aid of Africans. Afterwards, he wrote and published a five-volume account of his travels in both English and German. It has been invaluable for scholars of his time and since. Early life and education Heinrich Barth was born in Hamburg on 16 February 1821. He was the third child of Johann Christoph Heinrich Barth and his wife Charlotte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity And Islam
Christianity and Islam are the two largest religions in the world, with 2.8 billion and 1.9 billion adherents, respectively. Both religions are considered as Abrahamic, and are monotheistic, originating in the Middle East. Christianity developed out of Second Temple Judaism in the 1st century CE. It is founded on the life, teachings, death, and resurrection of Jesus Christ, and those who follow it are called Christians. Islam developed in the 7th century CE. Islam is founded on the teachings of Muhammad, as an expression of surrender to the will of God. Those who follow it are called Muslims which means "submitter to God". Muslims view Christians to be People of the Book, and also regard them as kafirs (unbelievers) committing shirk (polytheism) because of the Trinity, and thus, contend that they must be dhimmis (religious taxpayers) under Sharia law. Christians similarly possess a wide range of views about Islam. The majority of Christians view Islam as a false reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reredos
A reredos ( , , ) is a large altarpiece, a screen, or decoration placed behind the altar in a church. It often includes religious images. The term ''reredos'' may also be used for similar structures, if elaborate, in secular architecture, for example very grand carved chimneypieces. It also refers to a simple, low stone wall placed behind a hearth. Description A reredos can be made of stone, wood, metal, ivory, or a combination of materials. The images may be painted, carved, gilded, composed of mosaics, and/or embedded with niches for statues. Sometimes a tapestry or another fabric such as silk or velvet is used. Derivation and history of the term ''Reredos'' is derived through Middle English from the 14th-century Anglo-Norman ''areredos'', which in turn is from''arere'' 'behind' +''dos'' 'back', from Latin ''dorsum''. (Despite its appearance, the first part of the word is not formed by doubling the prefix "re-", but by an archaic spelling of "rear".) In the 14th and 15th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fine Arts Society
Fine may refer to: Characters * Sylvia Fine (''The Nanny''), Fran's mother on ''The Nanny'' * Officer Fine, a character in ''Tales from the Crypt'', played by Vincent Spano Legal terms * Fine (penalty), money to be paid as punishment for an offence * Fine on alienation, a sum of money paid to a feudal lord when a tenant had occasion to make over his land to another * Fine of lands, an obsolete type of land conveyance to a new owner * Fine, a dated term for a premium on a lease of land Music * Fine (band), a late 1990s American band * ''Fine'' (album), a 1994 album by Snailhouse * "Fine" (Taeyeon song), 2017 * "Fine" (Whitney Houston song), 2000 * " F.I.N.E.*", a 1993 song by Aerosmith * "Fine", a song by James from the 2001 album '' Pleased to Meet You'' * "Fine", a song by Kylie Minogue from the 2014 album ''Kiss Me Once'' * "Fine", a song by Prism from the 1983 album ''Beat Street'' * "fine", a 2019 song by Mike Shinoda Brands and enterprises * Fine (brandy), a term for s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Goldwin Rivière
Hugh Goldwin Rivière (1869–1956) was a noted British portraitist. He was one of seven children of Briton Rivière and was of Huguenot descent. Examples of his work are held in a very wide variety of public collections, including the Victoria Art Gallery in Bath, Guildhall Art Gallery and Victoria and Albert Museum in London, the Royal Shakespeare Company, Cheltenham Art Gallery, Gloucestershire County Council, and the Royal Albert Memorial Museum, Exeter. His portrait painting of Sir Squire Bancroft and several drawings and prints are in the National Portrait Gallery collection. National Portrait Gallery. Retrieved 2014-01-06. One of his best portraits is that of |
_headshot.jpg)

.jpg)