|
Regiment Of Light Dragoons (United States)
Under the designation Regiment of Light Dragoons existed two different units of the U.S. Army in the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, respectively. A first unit of its name was short lived, established just prior the Quasi-War with France, in 1798 and discharged in 1800.Heitman pp. 79—80 The second unit under this designation was activated in 1808. During the War of 1812, it was temporarily designated as the 1st Regiment of Light Dragoons when the War Department created an additional similar regiment. On May 12, 1814, the additional regiment was consolidated with the 1st Regiment, which reverted to its unnumbered designation. The regiment was consolidated with the Corps of Artillery on May 17, 1815.Heitman pp. 79—80 The very first unit of the U.S. Army designed as Light Dragoons was a single ''Squadron of Light Dragoons'', assigned to the Legion of the United States, by September 1792. All these units followed the model of the british Regiments of Light Drago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragoons
Dragoons were originally a class of mounted infantry, who used horses for mobility, but dismounted to fight on foot. From the early 17th century onward, dragoons were increasingly also employed as conventional cavalry and trained for combat with swords and firearms from horseback. While their use goes back to the late 16th century, dragoon regiments were established in most European armies during the 17th and early 18th centuries; they provided greater mobility than regular infantry but were far less expensive than cavalry. The name reputedly derives from a type of firearm, called a '' dragon'', which was a handgun version of a blunderbuss, carried by dragoons of the French Army. The title has been retained in modern times by a number of armoured or ceremonial mounted regiments. Origins and name The establishment of dragoons evolved from the practice of sometimes transporting infantry by horse when speed of movement was needed. In 1552, Alexander Farnese, Duke of Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chesapeake–Leopard Affair
The ''Chesapeake''–''Leopard'' affair was a naval engagement off the coast of Norfolk, Virginia, on June 22, 1807, between the British fourth-rate and the American frigate . The crew of ''Leopard'' pursued, attacked, and boarded the American frigate, looking for deserters from the Royal Navy. ''Chesapeake'' was caught unprepared and after a short battle involving broadsides received from ''Leopard'', the commander of ''Chesapeake'', James Barron, surrendered his vessel to the British. ''Chesapeake'' had fired only one shot. Four crew members were removed from the American vessel and were tried for desertion, one of whom was subsequently hanged. ''Chesapeake'' was allowed to return home, where James Barron was court martialed and relieved of command. The ''Chesapeake''–''Leopard'' affair created an uproar among Americans. There were strident calls for war with Great Britain, but these quickly subsided. President Thomas Jefferson initially attempted to use this widespread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Established In 1808
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragoon Regiments Of The United States Army
Dragoons were originally a class of mounted infantry, who used horses for mobility, but dismounted to fight on foot. From the early 17th century onward, dragoons were increasingly also employed as conventional cavalry and trained for combat with swords and firearms from horseback. While their use goes back to the late 16th century, dragoon regiments were established in most European armies during the 17th and early 18th centuries; they provided greater mobility than regular infantry but were far less expensive than cavalry. The name reputedly derives from a type of firearm, called a '' dragon'', which was a handgun version of a blunderbuss, carried by dragoons of the French Army. The title has been retained in modern times by a number of armoured or ceremonial mounted regiments. Origins and name The establishment of dragoons evolved from the practice of sometimes transporting infantry by horse when speed of movement was needed. In 1552, Alexander Farnese, Duke of Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
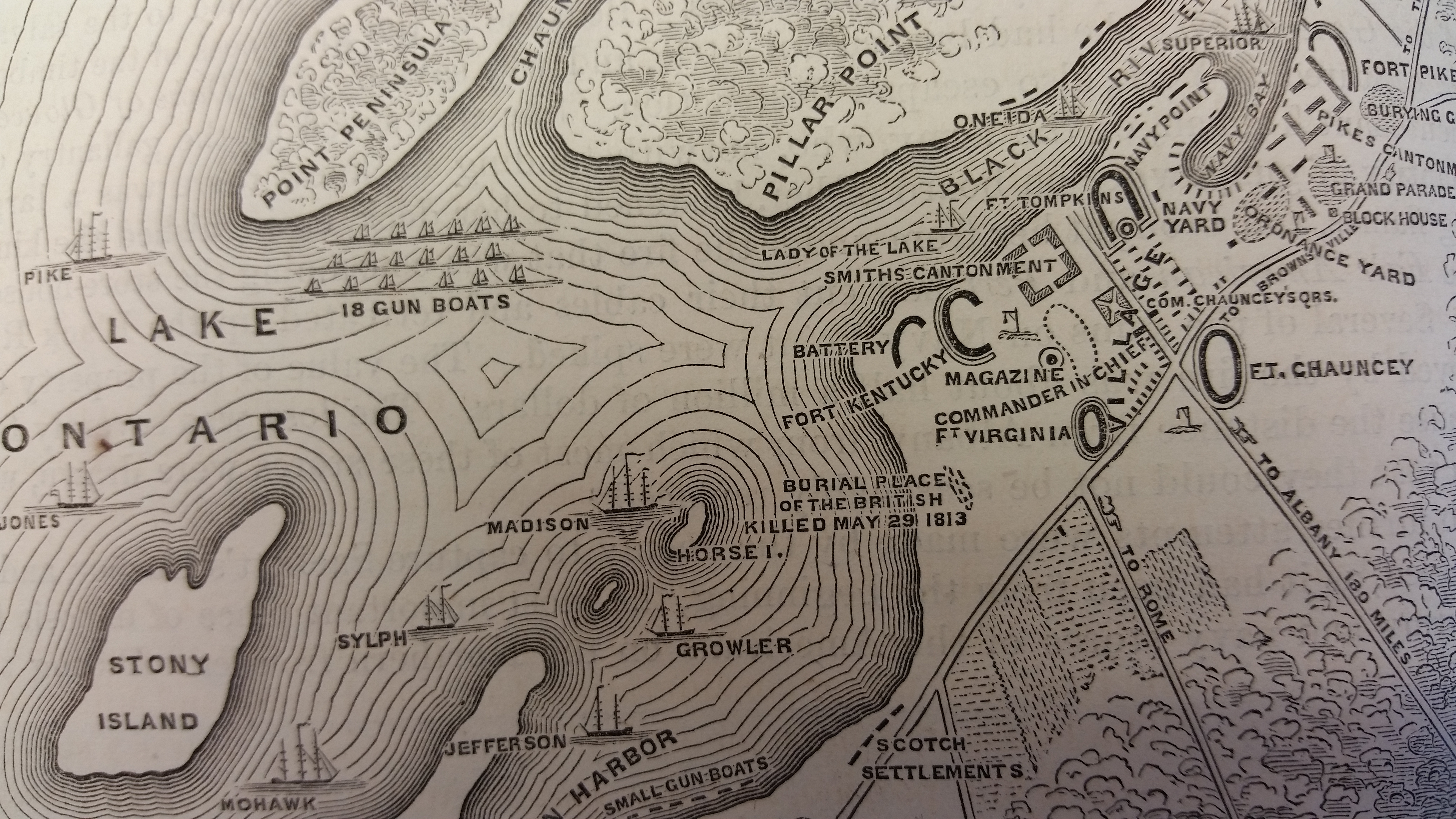
Second Battle Of Sacket's Harbor
The Second Battle of Sacket's Harbor or simply the Battle of Sacket's Harbor, took place on 29 May 1813, during the War of 1812. A British force was transported across Lake Ontario and attempted to capture the town, which was the principal dockyard and base for the American naval squadron on the lake. Twelve warships were built here. The British were repulsed by American regulars, militia, marines and sailors. Background In the early weeks of the War, the British had seized control of the Great Lakes. In September 1812 U.S. Navy Captain Isaac Chauncey was ordered to assume command of naval forces on Lakes Ontario and Erie with the directive to "...use every exertion to obtain control of them this fall." Within three weeks he had directed and brought 149 ships' carpenters, 700 Seamen and Marines, and some 100 cannon, along with a good quantity of muskets and other supplies, to Sacket's Harbor on Lake Ontario where there was already a small navy yard. At the start of the campaig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Regiment Of Light Dragoons (United States)
The 2nd Regiment of Light Dragoons was a unit of the U.S. Army in the early nineteenth century. It was first activated in 1812. The regiment was consolidated with the 1st Regiment of Light Dragoons on May 12, 1814, forming the Regiment of Light Dragoons. Background An act of Congress on January 11, 1812 authorized an additional regiment of light Dragoons.Heitman pp. 80 By June 1812, the regiment had been activated.Rauch p. 8 Organization Although the regiment was organized on January 11, 1812 the regimental colonel, James Burn, was not appointed until April 25. Secretary of War William Eustis delayed recruiting for almost a month, then allowed recruitment of only three out of twelve companies. No clothing or equipment was supplied until September and October. The regiment was not fully equipped until December. Purchase of horses had been ordered in March but by September only half the regiment was mounted; many of its mounts were unfit for service. Eustis scattered the regiment f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragoon
Dragoons were originally a class of mounted infantry, who used horses for mobility, but dismounted to fight on foot. From the early 17th century onward, dragoons were increasingly also employed as conventional cavalry and trained for combat with swords and firearms from horseback. While their use goes back to the late 16th century, dragoon regiments were established in most European armies during the 17th and early 18th centuries; they provided greater mobility than regular infantry but were far less expensive than cavalry. The name reputedly derives from a type of firearm, called a ''dragon'', which was a handgun version of a blunderbuss, carried by dragoons of the French Army. The title has been retained in modern times by a number of armoured or ceremonial mounted regiments. Origins and name The establishment of dragoons evolved from the practice of sometimes transporting infantry by horse when speed of movement was needed. In 1552, Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of Congress
An Act of Congress is a statute enacted by the United States Congress. Acts may apply only to individual entities (called Public and private bills, private laws), or to the general public (Public and private bills, public laws). For a Bill (law), bill to become an act, the text must pass through both houses with a majority, then be either signed into law by the president of the United States, be left unsigned for ten days (excluding Sundays) while Congress remains in session, or, if vetoed by the president, receive a congressional override from of both houses. Public law, private law, designation In the United States, Acts of Congress are designated as either public laws, relating to the general public, or private laws, relating to specific institutions or individuals. Since 1957, all Acts of Congress have been designated as "Public Law X–Y" or "Private Law X–Y", where X is the number of the Congress and Y refers to the sequential order of the bill (when it was enacted). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XYZ Affair
The XYZ Affair was a political and diplomatic episode in 1797 and 1798, early in the presidency of John Adams, involving a confrontation between the United States and Republican France that led to the Quasi-War. The name derives from the substitution of the letters X, Y, and Z for the names of French diplomats Jean-Conrad Hottinguer (X), Pierre Bellamy (Y), and Lucien Hauteval (Z) in documents released by the Adams administration. An American diplomatic commission was sent to France in July 1797 to negotiate a solution to problems that were threatening to break out into war. The diplomats, Charles Cotesworth Pinckney, John Marshall, and Elbridge Gerry, were approached through informal channels by agents of the French foreign minister, Talleyrand, who demanded bribes and a loan before formal negotiations could begin. Although it was widely known that diplomats from other nations had paid bribes to deal with Talleyrand at the time, the Americans were offended by the demands, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasi-War
The Quasi-War (french: Quasi-guerre) was an undeclared naval war fought from 1798 to 1800 between the United States and the French First Republic, primarily in the Caribbean and off the East Coast of the United States. The ability of Congress to authorize military action without a formal declaration of war was later confirmed by the Supreme Court and formed the basis of many similar actions since, including American participation in the Vietnam War and the 1991 Gulf War. In 1793, Congress suspended repayments of French loans incurred during the American Revolutionary War. The dispute escalated further due to different interpretations of the 1778 treaties of Alliance and Commerce between the two countries. France, then engaged in the 1792–1797 War of the First Coalition, which included Great Britain, viewed the 1794 Jay Treaty between the United States and Britain as incompatible with those treaties, and retaliated by seizing American ships trading with Britain. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


