|
Regelia (brachiopod)
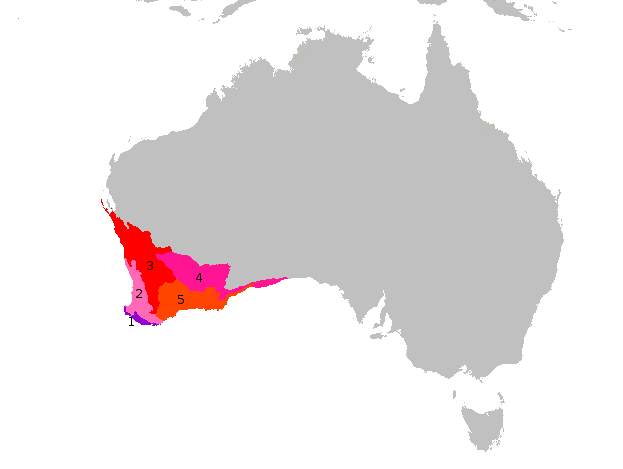
''Regelia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. The genus is composed of five species of small leaved, evergreen shrubs which have heads of flowers on the ends of branches which continue to grow after flowering. Another species, previously known as ''Regelia punicea'' and which is endemic to Kakadu National Park in the Northern Territory, has been transferred to ''Melaleuca punicea''. Description Plants in the genus ''Regelia'' are woody, evergreen shrubs ranging in height from . Their leaves are small, arranged in opposite pairs or spirally and are noted for bearing essential oils. Their flowers are pinkish purple, rarely red, and are arranged in heads on the ends of branches which continue to grow after flowering. The flowers have 5 sepals, 5 petals and numerous stamens arranged in 5 bundles around the edge of the flower. In many respects, they are similar to plants in the genera ''Melaleuca'', ''Calot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regelia Megacephala
''Regelia megacephala'' is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a taller shrub than others in its genus, with small, rounded leaves and clusters of purplish-red flowers from October to December. Description ''Regelia megacephala'' is an erect, straggly shrub which grows to a height of . Its leaves are small and are arranged in alternating pairs (decussate) so that they make four rows along its long stems. The flowers are mauve and arranged in dense heads across on the ends of long stems which continue to grow after flowering. There are 5 sepals, 5 petals and 5 bundles of stamens. Flowering occurs from September to December and is followed by fruit which are woody capsules. Taxonomy and naming ''Regelia megacephala'' was first formally described in 1964 by the Australian botanist, Charles Gardner in ''Journal of the Royal Society of Western Australia''. The specific epithet (''megacephala'') means "large-headed". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamen
The stamen (plural ''stamina'' or ''stamens'') is the pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. Collectively the stamens form the androecium., p. 10 Morphology and terminology A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament and an anther which contains ''sporangium, microsporangia''. Most commonly anthers are two-lobed and are attached to the filament either at the base or in the middle area of the anther. The sterile tissue between the lobes is called the connective, an extension of the filament containing conducting strands. It can be seen as an extension on the dorsal side of the anther. A pollen grain develops from a microspore in the microsporangium and contains the male gametophyte. The stamens in a flower are collectively called the androecium. The androecium can consist of as few as one-half stamen (i.e. a single locule) as in ''Canna (plant), Canna'' species or as many as 3,482 stamens which have been counted in the saguaro (''Carnegiea gigantea'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regelia Cymbifolia
''Regelia cymbifolia'' is a plant in the myrtle Family (biology), family, Myrtaceae and is Endemism, endemic to the South West (Western Australia), south-west of Western Australia. It is a much branched shrub bearing tiny, wedge shaped leaves and clusters of deep pink to purple flowers on the ends of its branches in spring. Description ''Regelia cymbifolia'' is much branched shrub which grows to a height of . The leaves are arranged in alternating pairs (Phyllotaxy, decussate), so that they make four rows along the stems. They are egg-shaped, usually less than long, curved with their lower half pressed against the stem and have a prominent mid-vein. The flowers are deep pink to purple and arranged in small clusters on the ends of branches that continue to grow after flowering. There are 5 sepals, 5 petals and 5 bundles of stamens. Flowering occurs between August and November and is followed by fruit which are woody Capsule (botany), capsules. Taxonomy and naming ''Regelia cym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Australia
Southwest Australia is a biogeographic region in Western Australia. It includes the Mediterranean-climate area of southwestern Australia, which is home to a diverse and distinctive flora and fauna. The region is also known as the Southwest Australia Global Diversity Hotspot, as well as Kwongan. Geography The region includes the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregions of Western Australia. The region covers 356,717 km2, consisting of a broad coastal plain 20-120 kilometres wide, transitioning to gently undulating uplands made up of weathered granite, gneiss and laterite. Bluff Knoll in the Stirling Range is the highest peak in the region, at 1,099 metres (3,606 ft) elevation. Desert and xeric shrublands lie to the north and east across the centre of Australia, separating Southwest Australia from the other Mediterranean and humid-climate regions of the continent. Climate The region has a wet-winter, dry-summer Mediterranean climate, one of five such regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard August Von Regel
Eduard August von Regel (sometimes Edward von Regel or Edward de Regel or Édouard von Regel), Russian: Эдуард Август Фон Регель; (born 13 August 1815 in Gotha; died 15 April 1892 in St. Petersburg) was a German horticulturalist and botanist. He ended his career serving as the Director of the Russian Imperial Botanical Garden of St. Petersburg. As a result of naturalists and explorers sending back biological collections, Regel was able to describe and name many previously unknown species from frontiers around the world. History Regel was the son of the teacher and garrison-preacher Ludwig A. Regel. Already as a child he liked growing fruits and learnt to prune apple trees from a gardener of his grandfather Döring and cultivated the garden of his parents. He visited the Gymnasium at Gotha but left without Abitur Regel earned a degree from the University of Bonn. At 15, Regel began his career as an apprentice at the Royal Garden Limonaia in Gotha in 1830 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanist
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek word (''botanē'') meaning "pasture", " herbs" "grass", or " fodder"; is in turn derived from (), "to feed" or "to graze". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists (in the strict sense) study approximately 410,000 species of land plants of which some 391,000 species are vascular plants (including approximately 369,000 species of flowering plants), and approximately 20,000 are bryophytes. Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germans
, native_name_lang = de , region1 = , pop1 = 72,650,269 , region2 = , pop2 = 534,000 , region3 = , pop3 = 157,000 3,322,405 , region4 = , pop4 = 21,000 3,000,000 , region5 = , pop5 = 125,000 982,226 , region6 = , pop6 = 900,000 , region7 = , pop7 = 142,000 840,000 , region8 = , pop8 = 9,000 500,000 , region9 = , pop9 = 357,000 , region10 = , pop10 = 310,000 , region11 = , pop11 = 36,000 250,000 , region12 = , pop12 = 25,000 200,000 , region13 = , pop13 = 233,000 , region14 = , pop14 = 211,000 , region15 = , pop15 = 203,000 , region16 = , pop16 = 201,000 , region17 = , pop17 = 101,000 148,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regelia Ciliata
''Regelia ciliata'' is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a rigid, spreading shrub with paper-like bark on the stems, tiny wedge shaped leaves and dense heads of mauve flowers in spring and summer. Description ''Regelia ciliata'' is rigid, spreading shrub which grows to a height of . The leaves are arranged in alternating pairs (decussate) so that they make four rows along the stems. They are broadly egg-shaped, about long and wide and fringed with short hairs. The flowers are mauve and arranged in dense heads across on the ends of branches which continue to grow after flowering. There are 5 sepals, 5 petals and 5 bundles of stamens. Flowering occurs over an extended period in spring and summer and is followed by fruit which are woody capsules in small, almost spherical clusters around the stem. Taxonomy and naming ''Regelia ciliata'' was the first of its genus to be formally described. The description was wri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary (botany)
In the flowering plants, an ovary is a part of the female reproductive organ of the flower or gynoecium. Specifically, it is the part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. The pistil may be made up of one carpel or of several fused carpels (e.g. dicarpel or tricarpel), and therefore the ovary can contain part of one carpel or parts of several fused carpels. Above the ovary is the style and the stigma, which is where the pollen lands and germinates to grow down through the style to the ovary, and, for each individual pollen grain, to fertilize one individual ovule. Some wind pollinated flowers have much reduced and modified ovaries. Fruits A fruit is the mature, ripened ovary of a flower following double fertilization in an angiosperm. Because gymnosperms do not have an ovary but reproduce through double fertilization of unprotected ovules, they produce naked seeds that do not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capsule (botany)
In botany a capsule is a type of simple, dry, though rarely fleshy dehiscent fruit produced by many species of angiosperms (flowering plants). Origins and structure The capsule (Latin: ''capsula'', small box) is derived from a compound (multicarpeled) ovary. A capsule is a structure composed of two or more carpels. In (flowering plants), the term locule (or cell) is used to refer to a chamber within the fruit. Depending on the number of locules in the ovary, fruit can be classified as uni-locular (unilocular), bi-locular, tri-locular or multi-locular. The number of locules present in a gynoecium may be equal to or less than the number of carpels. The locules contain the ovules or seeds and are separated by septa. Dehiscence In most cases the capsule is dehiscent, i.e. at maturity, it splits apart (dehisces) to release the seeds within. A few capsules are indehiscent, for example those of ''Adansonia digitata'', ''Alphitonia'', and '' Merciera''. Capsules are often classifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male cone to the female cone of gymnosperms. If pollen lands on a compatible pistil or female cone, it germinates, producing a pollen tube that transfers the sperm to the ovule containing the female gametophyte. Individual pollen grains are small enough to require magnification to see detail. The study of pollen is called palynology and is highly useful in paleoecology, paleontology, archaeology, and forensics. Pollen in plants is used for transferring haploid male genetic material from the anther of a single flower to the stigma of another in cross-pollination. In a case of self-pollination, this process takes place from the anth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phymatocarpus
''Phymatocarpus'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. All three species are shrubs with pink to purple flowers. Description Plants in the genus ''Phymatocarpus'' are shrubs which grow to a height of . Their leaves are small and are dotted with oil glands. The flowers are arranged in almost spherical heads on the ends of the branches and have 5 oval sepals, 5 petals and up to 75 stamens. The stamens are in a ring around the hypanthium, but above the ring are joined in 5 bundles. The stamens are all longer than the petals and give the flowers their pink to purple colour. The fruit is a woody capsule. Taxonomy and naming The genus was first described in 1862 by the Victorian government botanist, Ferdinand von Mueller in '' Fragmenta Phytographiae Australiae''. The first species he described was '' Phymatocarpus porphyrocephalus''. The name ''Phymatocarpus'' is derived from the Ancient Greek ''phymatos'' (plu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(255_30)_Tulip;_cross-section.jpg)
.png)
