|
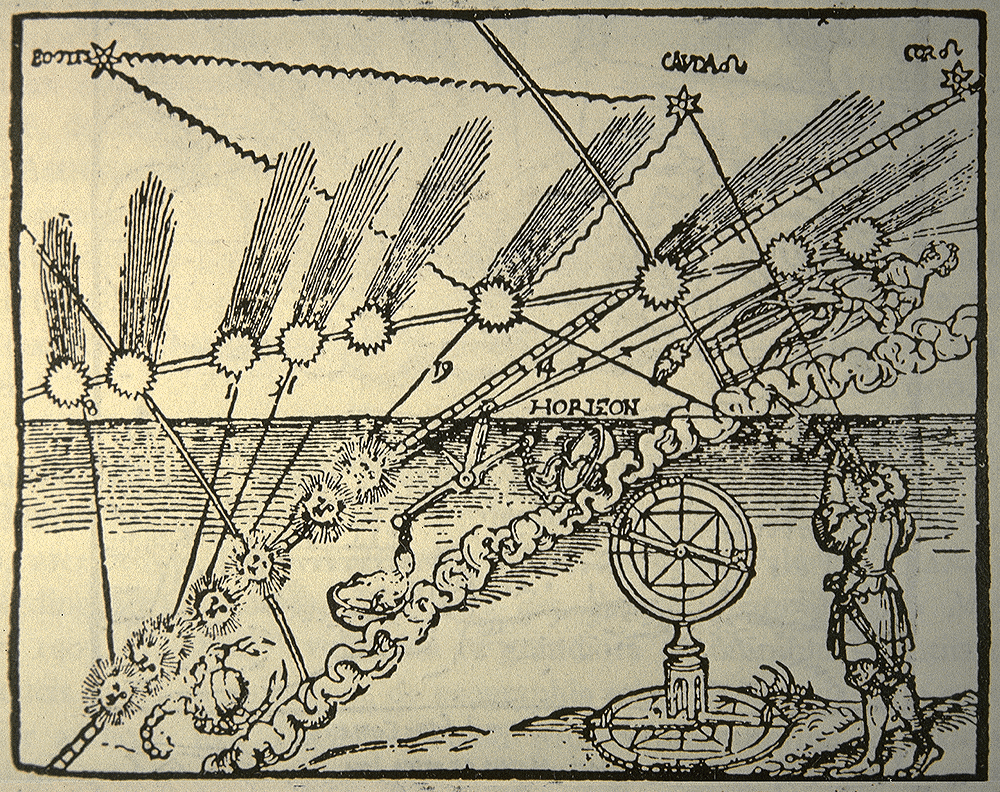
Rectangulus
The rectangulus was an astronomical instrument made by Richard of Wallingford around 1326. Dissatisfied with the limitations of existing astrolabes, Richard developed the rectangulus as an instrument for spherical trigonometry and to measure the angles between planets and other astronomical bodies. This was one of a number of instruments he created, including the '' Albion'', a form of equatorium, and a famously complicated and expensive horologium (astronomical clock). His ''Tractus Rectanguli'', describing the rectangulus, was an influential text in medieval astronomy and at least thirty copies were known to survive. His ''Quadripartitum'' was the first text on spherical trigonometry to be published in Western Europe. The rectangulus was a form of skeleton torquetum. This was a series of nested angular scales, so that measurements in azimuth and elevation could be made directly in polar coordinates, relative to the ecliptic. Conversion from these coordinates though was difficu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Of Wallingford
Richard of Wallingford (1292–1336) was an English mathematician, astronomer, horologist, and cleric who made major contributions to astronomy and horology while serving as abbot of St Albans Abbey in Hertfordshire. Biography Richard was born, the son of a blacksmith, at Wallingford in Berkshire (now Oxfordshire) in England in 1292. When he was orphaned he was taken to William de Kirkeby the Prior of Wallingford Priory and dedicated to the Holy Trinity. (Wallingford was a dependant priory to S Albans Abbey) Richard subsequently spent six years studying at Oxford University before becoming a monk at St Albans. He later studied for nine more years at Oxford. In 1327 he became abbot of St Albans. Richard of Wallingford is best known for the astronomical clock he designed, while he was abbot, which is described in the ''Tractatus Horologii Astronomici'' (1327). The clock was completed about 20 years after Richard's death by William of Walsham but was apparently destroyed during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbot Richard Wallingford
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a monastery. The female equivalent is abbess. Origins The title had its origin in the monasteries of Egypt and Syria, spread through the eastern Mediterranean, and soon became accepted generally in all languages as the designation of the head of a monastery. The word is derived from the Aramaic ' meaning "father" or ', meaning "my father" (it still has this meaning in contemporary Hebrew: אבא and Aramaic: ܐܒܐ) In the Septuagint, it was written as "abbas". At first it was employed as a respectful title for any monk, but it was soon restricted by canon law to certain priestly superiors. At times it was applied to various priests, e.g. at the court of the Frankish monarchy the ' ("of the palace"') and ' ("of the camp") were chaplains to the Merovingian an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartesian Coordinate System
A Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, measured in the same unit of length. Each reference coordinate line is called a ''coordinate axis'' or just ''axis'' (plural ''axes'') of the system, and the point where they meet is its ''origin'', at ordered pair . The coordinates can also be defined as the positions of the perpendicular projections of the point onto the two axes, expressed as signed distances from the origin. One can use the same principle to specify the position of any point in three-dimensional space by three Cartesian coordinates, its signed distances to three mutually perpendicular planes (or, equivalently, by its perpendicular projection onto three mutually perpendicular lines). In general, ''n'' Cartesian coordinates (an element of real ''n''-space) specify the point in an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Instruments
Astronomical instruments include: *Alidade *Armillary sphere * Astrarium *Astrolabe *Astronomical clock *the Antikythera mechanism, an astronomical clock *Blink comparator * Bolometer *the Canterbury Astrolabe Quadrant *Celatone *Celestial sphere *Charge-coupled device *Computers *CMOS sensor * Coronagraph * Cosmolabe *Dioptra *Equatorial ring *Equatorium *Gnomon *Inclinometer *Interferometer * Kamal * Meridian circle * Microchannel plate detector *Mural instrument *Nebra sky disk *Nocturnal * Octant *Optical spectrometer, a.k.a., Spectrograph *Orrery *Photographic plate *Photometer * Planisphere *the Prague astronomical clock * Quadrant *Reticle * Radio plate *Retroreflector * Scaphe *Sextant *Starshade *Space telescope *Spectrometers *Sundial *Telescope *Torquetum * Triquetrum *Zenith telescope See also *Astronomy Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 '' Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Chicago Press
The University of Chicago Press is the largest and one of the oldest university presses in the United States. It is operated by the University of Chicago and publishes a wide variety of academic titles, including ''The Chicago Manual of Style'', numerous academic journals, and advanced monographs in the academic fields. One of its quasi-independent projects is the BiblioVault, a digital repository for scholarly books. The Press building is located just south of the Midway Plaisance on the University of Chicago campus. History The University of Chicago Press was founded in 1890, making it one of the oldest continuously operating university presses in the United States. Its first published book was Robert F. Harper's ''Assyrian and Babylonian Letters Belonging to the Kouyunjik Collections of the British Museum''. The book sold five copies during its first two years, but by 1900 the University of Chicago Press had published 127 books and pamphlets and 11 scholarly journals, inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museum Of The History Of Science
The History of Science Museum in Broad Street, Oxford, England, holds a leading collection of scientific instruments from Middle Ages to the 19th century. The museum building is also known as the Old Ashmolean Building to distinguish it from the newer Ashmolean Museum building completed in 1894. The museum was built in 1683, and it is the world's oldest surviving purpose-built museum. History Built in 1683 to house Elias Ashmole's collection, the building was the world's first purpose-built museum building and was also open to the public. The original concept of the museum was to institutionalize the new learning about nature that appeared in the 17th century and experiments concerning natural philosophy were undertaken in a chemical laboratory in the basement, while lectures and demonstration took place in the School of Natural History, on the middle floor. Ashmole's collection was expanded to include a broad range of activities associated with the history of natural knowled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museum Of The History Of Science, Oxford
The History of Science Museum in Broad Street, Oxford, England, holds a leading collection of scientific instruments from Middle Ages to the 19th century. The museum building is also known as the Old Ashmolean Building to distinguish it from the newer Ashmolean Museum building completed in 1894. The museum was built in 1683, and it is the world's oldest surviving purpose-built museum. History Built in 1683 to house Elias Ashmole's collection, the building was the world's first purpose-built museum building and was also open to the public. The original concept of the museum was to institutionalize the new learning about nature that appeared in the 17th century and experiments concerning natural philosophy were undertaken in a chemical laboratory in the basement, while lectures and demonstration took place in the School of Natural History, on the middle floor. Ashmole's collection was expanded to include a broad range of activities associated with the history of natural kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plumb Bob
A plumb bob, plumb bob level, or plummet, is a weight, usually with a pointed tip on the bottom, suspended from a string and used as a vertical reference line, or plumb-line. It is a precursor to the spirit level and used to establish a vertical datum. It is typically made of stone, wood, or lead, but can also be made of other metals. If it is used for decoration, it may be made of bone or ivory. The instrument has been used since at least the time of ancient EgyptDenys A. Stocks. Experiments in Egyptian archaeology: stoneworking technology in ncient Egypt'. Routledge; 2003. . p. 180. to ensure that constructions are "plumb", or vertical. It is also used in surveying, to establish the nadir with respect to gravity of a point in space. It is used with a variety of instruments (including levels, theodolites, and steel tapes) to set the instrument exactly over a fixed survey marker or to transcribe positions onto the ground for placing a marker. Etymology The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the background of stars. The ecliptic is an important reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system. Sun's apparent motion The ecliptic is the apparent path of the Sun throughout the course of a year. Because Earth takes one year to orbit the Sun, the apparent position of the Sun takes one year to make a complete circuit of the ecliptic. With slightly more than 365 days in one year, the Sun moves a little less than 1° eastward every day. This small difference in the Sun's position against the stars causes any particular spot on Earth's surface to catch up with (and stand directly north or south of) the Sun about four minutes later each day than it would if Earth did not orbit; a day on Earth is therefore 24 hours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Instrument
Astronomical instruments include: *Alidade * Armillary sphere *Astrarium * Astrolabe *Astronomical clock *the Antikythera mechanism, an astronomical clock *Blink comparator *Bolometer *the Canterbury Astrolabe Quadrant * Celatone * Celestial sphere *Charge-coupled device * Computers *CMOS sensor *Coronagraph * Cosmolabe *Dioptra *Equatorial ring *Equatorium * Gnomon * Inclinometer * Interferometer * Kamal *Meridian circle * Microchannel plate detector *Mural instrument *Nebra sky disk * Nocturnal * Octant *Optical spectrometer, a.k.a., Spectrograph *Orrery * Photographic plate *Photometer *Planisphere *the Prague astronomical clock * Quadrant *Reticle *Radio plate *Retroreflector * Scaphe * Sextant * Starshade *Space telescope *Spectrometers * Sundial *Telescope *Torquetum * Triquetrum * Zenith telescope See also *Astronomy *Outline of astronomy *Surveying instrument *Measurement instrument {{DEFAULTSORT:Astronomical instruments Instruments Instrument may refer to: Scienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torquetum
The ''torquetum'' or turquet is a medieval astronomical instrument designed to take and convert measurements made in three sets of coordinates: Horizon, equatorial, and ecliptic. It is said to be a combination of Ptolemy's astrolabon and the plane astrolabe. In a sense, the ''torquetum'' is an analog computer. Invention The origins of the ''torquetum'' are unclear. The earliest account of the ''torquetum'' appear in the writings of Bernard of Verdun and Franco of Poland. Franco of Poland's work was published in 1284; however, Bernard of Verdun's work does not contain a date. Therefore, it is impossible to know which work was written first. Franco's work was more widely known and is credited with the distribution of knowledge about the ''torquetum''. The first ''torquetum'' is thought to have been built by Jabir ibn Aflah (more commonly known as Geber). However, there is conflicting evidence that suggests that Jabir simply inspired the invention of the torquetum. One of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |