|
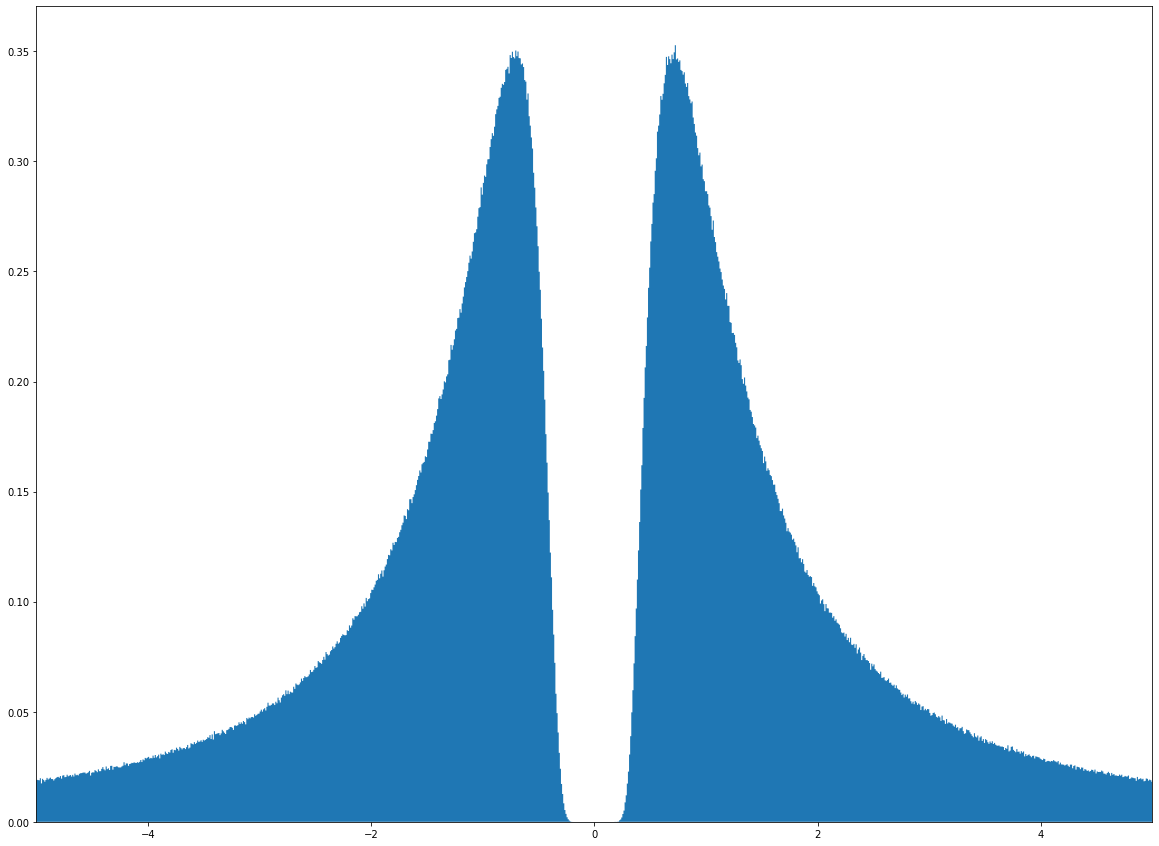
Reciprocal Normal Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, an inverse distribution is the distribution of the reciprocal of a random variable. Inverse distributions arise in particular in the Bayesian context of prior distributions and posterior distributions for scale parameters. In the algebra of random variables, inverse distributions are special cases of the class of ratio distributions, in which the numerator random variable has a degenerate distribution. Relation to original distribution In general, given the probability distribution of a random variable ''X'' with strictly positive support, it is possible to find the distribution of the reciprocal, ''Y'' = 1 / ''X''. If the distribution of ''X'' is continuous with density function ''f''(''x'') and cumulative distribution function ''F''(''x''), then the cumulative distribution function, ''G''(''y''), of the reciprocal is found by noting that : G(y) = \Pr(Y \leq y) = \Pr\left(X \geq \frac\right) = 1-\Pr\left(X<\frac\right) = 1 - F\left( \ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expressing it through a set of axioms. Typically these axioms formalise probability in terms of a probability space, which assigns a measure taking values between 0 and 1, termed the probability measure, to a set of outcomes called the sample space. Any specified subset of the sample space is called an event. Central subjects in probability theory include discrete and continuous random variables, probability distributions, and stochastic processes (which provide mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic or uncertain processes or measured quantities that may either be single occurrences or evolve over time in a random fashion). Although it is not possible to perfectly predict random events, much can be said about their behavior. Two major results in probability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |