|
Real-Time Quaking-Induced Conversion
Real-time quaking-induced conversion (RT-QuIC) is a highly sensitive assay for prion detection. __TOC__ Technique The "quaking" in the name of the technique refers to the fact that samples in the RT-QuIC assay are literally subjected to shaking. This action breaks apart aggregates of prion protein (PrP) that are then further incubated, amplifying the amount of misfolded PrP to detectable levels. It is "an early, rapid and specific assay for prion diseases". It can sample multiple sample types, such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), brain, lymph nodes, blood, muscle, and skin, and so it is applicable to scrapie in sheep, chronic wasting disease (CWD) in cervids, bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) in cows and sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease in humans, amongst others. The RT-QuIC assay uses in excess recombinantly produced normally folded prions, often a truncated Syrian Hamster protein, amino acids 90-231. Samples suspected of containing misfolded prions are added, leading to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prion
Prions are misfolded proteins that have the ability to transmit their misfolded shape onto normal variants of the same protein. They characterize several fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases in humans and many other animals. It is not known what causes a normal protein to misfold, but the resulting abnormal three-dimensional structure confers infectious properties by collapsing nearby protein molecules into the same shape. The word ''prion'' is derived from the term, "proteinaceous infectious particle". In comparison to all other known infectious agents such as viroids, viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites, all of which contain nucleic acids ( DNA, RNA, or both), the hypothesized role of a protein as an infectious agent stands in contrast. Prion isoforms of the prion protein (PrP), whose specific function is uncertain, are hypothesized as the cause of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), including scrapie in sheep, chronic wasting disease (CWD) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence Detection
A fluorometer, fluorimeter or fluormeter is a device used to measure parameters of visible spectrum fluorescence: its intensity and wavelength distribution of emission spectrum after excitation by a certain spectrum of light. These parameters are used to identify the presence and the amount of specific molecules in a medium. Modern fluorometers are capable of detecting fluorescent molecule concentrations as low as 1 part per trillion. Fluorescence analysis can be orders of magnitude more sensitive than other techniques. Applications include chemistry/biochemistry, medicine, environmental monitoring. For instance, they are used to measure chlorophyll fluorescence to investigate plant physiology. Components and Design Typically fluorometers utilize a double beam. These two beams work in tandem to decrease the noise created from radiant power fluctuations. The upper beam is passed through a filter or monochromator and passes through the sample. The lower beam is passed through an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rare Diseases
A rare disease is any disease that affects a small percentage of the population. In some parts of the world, an orphan disease is a rare disease whose rarity means there is a lack of a market large enough to gain support and resources for discovering treatments for it, except by the government granting economically advantageous conditions to creating and selling such treatments. Orphan drugs are ones so created or sold. Most rare diseases are genetic and thus are present throughout the person's entire life, even if symptoms do not immediately appear. Many rare diseases appear early in life, and about 30% of children with rare diseases will die before reaching their fifth birthdays. With only four diagnosed patients in 27 years, ribose-5-phosphate isomerase deficiency is considered the rarest known genetic disease. No single cut-off number has been agreed upon for which a disease is considered rare. A disease may be considered rare in one part of the world, or in a particular gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wikipedia Neurology Articles Ready To Translate
Wikipedia is a multilingual free online encyclopedia written and maintained by a community of volunteers, known as Wikipedians, through open collaboration and using a wiki-based editing system. Wikipedia is the largest and most-read reference work in history. It is consistently one of the 10 most popular websites ranked by Similarweb and formerly Alexa; Wikipedia was ranked the 5th most popular site in the world. It is hosted by the Wikimedia Foundation, an American non-profit organization funded mainly through donations. Wikipedia was launched by Jimmy Wales and Larry Sanger on January 15, 2001. Sanger coined its name as a blend of ''wiki'' and ''encyclopedia''. Wales was influenced by the "spontaneous order" ideas associated with Friedrich Hayek and the Austrian School of economics after being exposed to these ideas by the libertarian economist Mark Thornton. Initially available only in English, versions in other languages were quickly developed. Its combined editions com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurodegenerative Disorders
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, multiple system atrophy, and prion diseases. Neurodegeneration can be found in the brain at many different levels of neuronal circuitry, ranging from molecular to systemic. Because there is no known way to reverse the progressive degeneration of neurons, these diseases are considered to be incurable; however research has shown that the two major contributing factors to neurodegeneration are oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomedical research has revealed many similarities between these diseases at the subcellular level, including atypical protein assemblies (like proteinopathy) and induced cell death. These similarities suggest that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies
Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) are a group of progressive and fatal conditions that are associated with prions and affect the brain and nervous system of many animals, including humans, cattle, and sheep. According to the most widespread hypothesis, they are transmitted by prions, though some other data suggest an involvement of a ''Spiroplasma'' infection. Mental and physical abilities deteriorate and many tiny holes appear in the cortex causing it to appear like a sponge when brain tissue obtained at autopsy is examined under a microscope. The disorders cause impairment of brain function, including memory changes, personality changes and problems with movement that worsen chronically. TSEs of humans include Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease, Gerstmann–Sträussler–Scheinker syndrome, fatal familial insomnia, and kuru, as well as the recently discovered variably protease-sensitive prionopathy and familial spongiform encephalopathy. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease itsel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prions
Prions are misfolded proteins that have the ability to transmit their misfolded shape onto normal variants of the same protein. They characterize several fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases in humans and many other animals. It is not known what causes a normal protein to misfold, but the resulting abnormal three-dimensional structure confers infectious properties by collapsing nearby protein molecules into the same shape. The word ''prion'' is derived from the term, "proteinaceous infectious particle". In comparison to all other known infectious agents such as viroids, viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites, all of which contain nucleic acids ( DNA, RNA, or both), the hypothesized role of a protein as an infectious agent stands in contrast. Prion isoforms of the prion protein (PrP), whose specific function is uncertain, are hypothesized as the cause of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), including scrapie in sheep, chronic wasting disease (C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
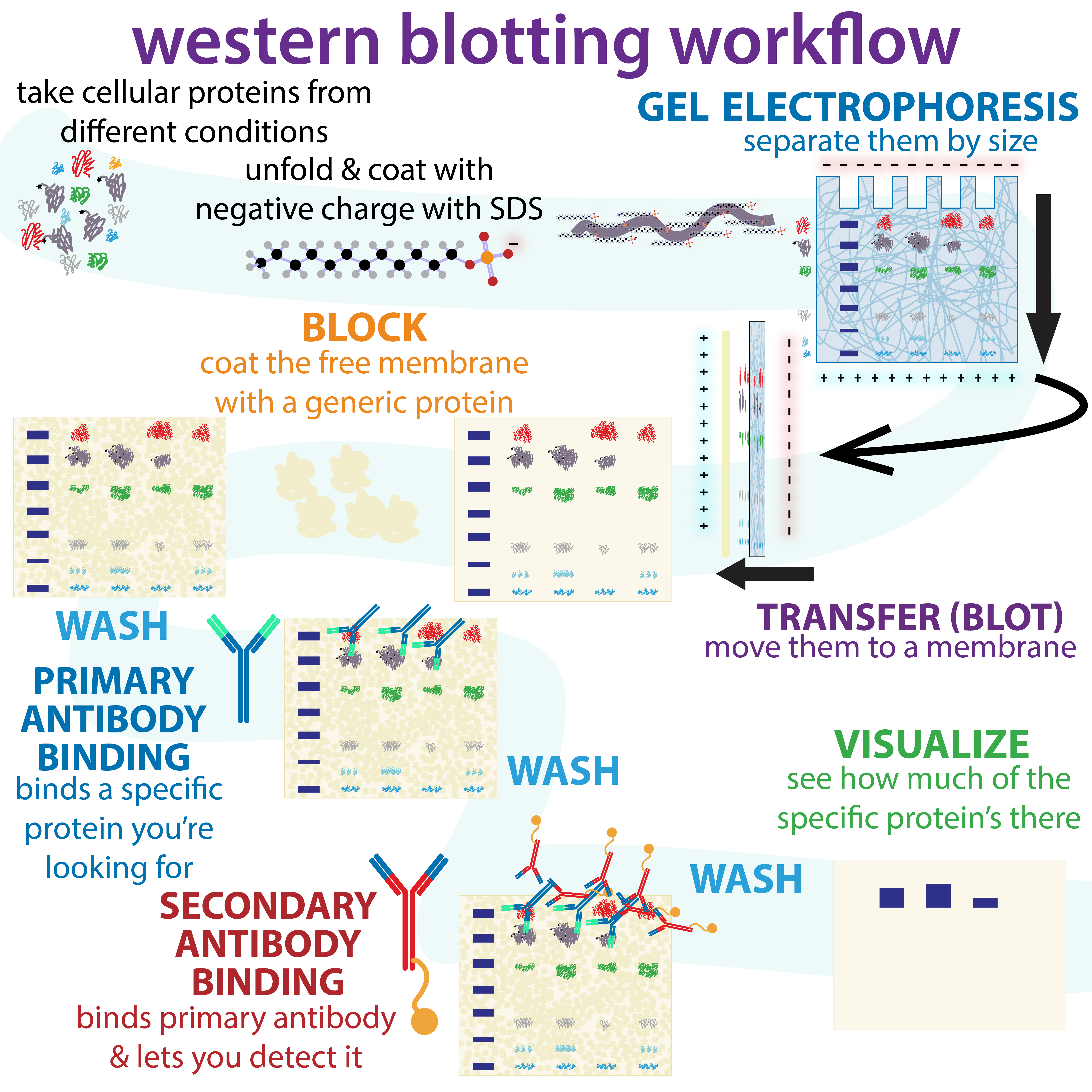
Western Blot
The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot), or western blotting, is a widely used analytical technique in molecular biology and immunogenetics to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. Besides detecting the proteins, this technique is also utilized to visualize, distinguish, and quantify the different proteins in a complicated protein combination. Western blot technique uses three elements to achieve its task of separating a specific protein from a complex: separation by size, transfer of protein to a solid support, and marking target protein using a primary and secondary antibody to visualize. A synthetic or animal-derived antibody (known as the primary antibody) is created that recognizes and binds to a specific target protein. The electrophoresis membrane is washed in a solution containing the primary antibody, before excess antibody is washed off. A secondary antibody is added which recognizes and binds to the primary antibody ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Misfolding Cyclic Amplification
Protein misfolding cyclic amplification (PMCA) is an amplification technique (conceptually like PCR but not involving nucleotides) to multiply misfolded prions originally developed by Soto and colleagues.Saborio, G.P., Permanne, B. and Soto, C. (2001) Sensitive detection of pathological prion protein by cyclic amplification of protein misfolding. Nature, 411, 810-813. It is a test for spongiform encephalopathies like CWD or BSE. Technique The technique initially incubates a small amount of abnormal prion with an excess of normal protein, so that some conversion takes place. The growing chain of misfolded protein is then blasted with ultrasound, breaking it down into smaller chains and so rapidly increasing the amount of abnormal protein available to cause conversions. By repeating the cycle, the mass of normal protein is rapidly changed into the prion being tested for. Development PMCA was originally developed to, in vitro, mimic prion replication with a similar efficiency to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centers For Disease Control And Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The agency's main goal is the protection of public health and safety through the control and prevention of disease, injury, and disability in the US and worldwide. The CDC focuses national attention on developing and applying disease control and prevention. It especially focuses its attention on infectious disease, food borne pathogens, environmental health, occupational safety and health, health promotion, injury prevention and educational activities designed to improve the health of United States citizens. The CDC also conducts research and provides information on non-infectious diseases, such as obesity and diabetes, and is a founding member of the International Association of National Public Health Institutes. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thioflavin T
Thioflavins are fluorescent dyes that are available as at least two compounds, namely Thioflavin T and Thioflavin S. Both are used for histology staining and biophysical studies of protein aggregation. In particular, these dyes have been used since 1989 to investigate amyloid formation. They are also used in biophysical studies of the electrophysiology of bacteria. Thioflavins are corrosive, irritants, and are acutely toxic, causing serious eye damage. Thioflavin T has been used in research into Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Thioflavin T Thioflavin T (Basic Yellow 1, Methylene yellow, CI 49005, or ThT) is a benzothiazole salt obtained by the methylation of dehydrothiotoluidine with methanol in the presence of hydrochloric acid. The dye is widely used to visualize and quantify the presence of misfolded protein aggregates called amyloid, both ''in vitro'' and ''in vivo'' (e.g., plaques composed of amyloid beta found in the brains of Alzheimer's disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |