|
Rayleigh Theorem For Eigenvalues
In mathematics, the Rayleigh theorem for eigenvalues pertains to the behavior of the solutions of an eigenvalue equation as the number of basis functions employed in its resolution increases. Rayleigh, Lord Rayleigh, and 3rd Baron Rayleigh are the titles of John William Strutt, after the death of his father, the 2nd Baron Rayleigh. Lord Rayleigh made contributions not just to both theoretical and experimental physics, but also to applied mathematics. The Rayleigh theorem for eigenvalues, as discussed below, enables the energy minimization that is required in many self-consistent calculations of electronic and related properties of materials, from atoms, molecules, and nanostructures to semiconductors, insulators, and metals. Except for metals, most of these other materials have an energy or a band gap, i.e., the difference between the lowest, unoccupied energy and the highest, occupied energy. For crystals, the energy spectrum is in bands and there is a band gap, if any, as opposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eigenvalue Equation
In linear algebra, linear transformations can be represented by matrices. If T is a linear transformation mapping \mathbb^n to \mathbb^m and \mathbf x is a column vector with n entries, then T( \mathbf x ) = A \mathbf x for some m \times n matrix A, called the transformation matrix of T. Note that A has m rows and n columns, whereas the transformation T is from \mathbb^n to \mathbb^m. There are alternative expressions of transformation matrices involving row vectors that are preferred by some authors. Uses Matrices allow arbitrary linear transformations to be displayed in a consistent format, suitable for computation. This also allows transformations to be composed easily (by multiplying their matrices). Linear transformations are not the only ones that can be represented by matrices. Some transformations that are non-linear on an n-dimensional Euclidean space R''n'' can be represented as linear transformations on the ''n''+1-dimensional space R''n''+1. These include both affi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent of quantum mechanics, describes many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at small (atomic and subatomic) scales. Most theories in classical physics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation valid at large (macroscopic) scale. Quantum mechanics differs from classical physics in that energy, momentum, angular momentum, and other quantities of a bound system are restricted to discrete values ( quantization); objects have characteristics of both particles and waves (wave–particle duality); and there are limits to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overcompleteness
Overcompleteness is a concept from linear algebra that is widely used in mathematics, computer science, engineering, and statistics (usually in the form of overcomplete frames). It was introduced by R. J. Duffin and A. C. Schaeffer in 1952. Formally, a subset of the vectors \_ of a Banach space X, sometimes called a "system", is complete if every element in X can be approximated arbitrarily well in norm by finite linear combinations of elements in \_.C. Heil, A Basis Theory Primer: Expanded Edition. Boston, MA: Birkhauser, 2010. A complete system is additionally overcomplete if there exists a \phi_j which can be removed from the system while maintaining completeness (i.e., \exists j : \_ \text). In this sense, the system contains more vectors than necessary to be complete, hence "''over''complete". In research areas such as signal processing and function approximation, overcompleteness can help researchers to achieve a more stable, more robust, or more compact decomposition th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground State
The ground state of a quantum-mechanical system is its stationary state of lowest energy; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state. In quantum field theory, the ground state is usually called the vacuum state or the vacuum. If more than one ground state exists, they are said to be degenerate. Many systems have degenerate ground states. Degeneracy occurs whenever there exists a unitary operator that acts non-trivially on a ground state and commutes with the Hamiltonian of the system. According to the third law of thermodynamics, a system at absolute zero temperature exists in its ground state; thus, its entropy is determined by the degeneracy of the ground state. Many systems, such as a perfect crystal lattice, have a unique ground state and therefore have zero entropy at absolute zero. It is also possible for the highest excited state to have absolute zero temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hohenberg–Kohn Theorem
Density-functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics, chemistry and materials science to investigate the electronic structure (or nuclear structure) (principally the ground state) of many-body systems, in particular atoms, molecules, and the condensed phases. Using this theory, the properties of a many-electron system can be determined by using functionals, i.e. functions of another function. In the case of DFT, these are functionals of the spatially dependent electron density. DFT is among the most popular and versatile methods available in condensed-matter physics, computational physics, and computational chemistry. DFT has been very popular for calculations in solid-state physics since the 1970s. However, DFT was not considered accurate enough for calculations in quantum chemistry until the 1990s, when the approximations used in the theory were greatly refined to better model the exchange and correlation interactions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basis Set (chemistry)
In theoretical and computational chemistry, a basis set is a set of functions (called basis functions) that is used to represent the electronic wave function in the Hartree–Fock method or density-functional theory in order to turn the partial differential equations of the model into algebraic equations suitable for efficient implementation on a computer. The use of basis sets is equivalent to the use of an approximate resolution of the identity: the orbitals , \psi_i\rangle are expanded within the basis set as a linear combination of the basis functions , \psi_i\rangle \approx \sum_\mu c_ , \mu\rangle, where the expansion coefficients c_ are given by c_ = \sum_\nu \langle \mu, \nu \rangle^ \langle \nu , \psi_i \rangle. The basis set can either be composed of atomic orbitals (yielding the linear combination of atomic orbitals approach), which is the usual choice within the quantum chemistry community; plane waves which are typically used within the solid state community, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self Consistent
In classical deductive logic, a consistent theory is one that does not lead to a logical contradiction. The lack of contradiction can be defined in either semantic or syntactic terms. The semantic definition states that a theory is consistent if it has a model, i.e., there exists an interpretation under which all formulas in the theory are true. This is the sense used in traditional Aristotelian logic, although in contemporary mathematical logic the term ''satisfiable'' is used instead. The syntactic definition states a theory T is consistent if there is no formula \varphi such that both \varphi and its negation \lnot\varphi are elements of the set of consequences of T. Let A be a set of closed sentences (informally "axioms") and \langle A\rangle the set of closed sentences provable from A under some (specified, possibly implicitly) formal deductive system. The set of axioms A is consistent when \varphi, \lnot \varphi \in \langle A \rangle for no formula \varphi. If there e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground State
The ground state of a quantum-mechanical system is its stationary state of lowest energy; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state. In quantum field theory, the ground state is usually called the vacuum state or the vacuum. If more than one ground state exists, they are said to be degenerate. Many systems have degenerate ground states. Degeneracy occurs whenever there exists a unitary operator that acts non-trivially on a ground state and commutes with the Hamiltonian of the system. According to the third law of thermodynamics, a system at absolute zero temperature exists in its ground state; thus, its entropy is determined by the degeneracy of the ground state. Many systems, such as a perfect crystal lattice, have a unique ground state and therefore have zero entropy at absolute zero. It is also possible for the highest excited state to have absolute zero temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-consistent
In classical deductive logic, a consistent theory is one that does not lead to a logical contradiction. The lack of contradiction can be defined in either semantic or syntactic terms. The semantic definition states that a theory is consistent if it has a model, i.e., there exists an interpretation under which all formulas in the theory are true. This is the sense used in traditional Aristotelian logic, although in contemporary mathematical logic the term ''satisfiable'' is used instead. The syntactic definition states a theory T is consistent if there is no formula \varphi such that both \varphi and its negation \lnot\varphi are elements of the set of consequences of T. Let A be a set of closed sentences (informally "axioms") and \langle A\rangle the set of closed sentences provable from A under some (specified, possibly implicitly) formal deductive system. The set of axioms A is consistent when \varphi, \lnot \varphi \in \langle A \rangle for no formula \varphi. If there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
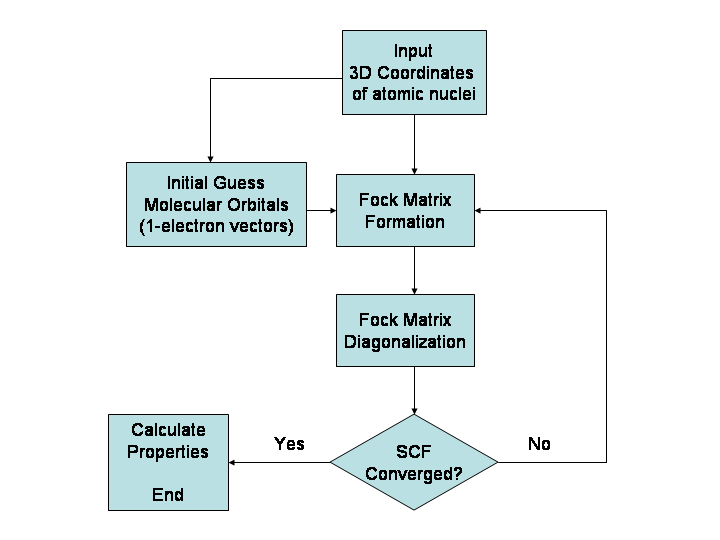
Hartree–Fock Method
In computational physics and chemistry, the Hartree–Fock (HF) method is a method of approximation for the determination of the wave function and the energy of a quantum many-body system in a stationary state. The Hartree–Fock method often assumes that the exact ''N''-body wave function of the system can be approximated by a single Slater determinant (in the case where the particles are fermions) or by a single permanent (in the case of bosons) of ''N'' spin-orbitals. By invoking the variational method, one can derive a set of ''N''-coupled equations for the ''N'' spin orbitals. A solution of these equations yields the Hartree–Fock wave function and energy of the system. Especially in the older literature, the Hartree–Fock method is also called the self-consistent field method (SCF). In deriving what is now called the Hartree equation as an approximate solution of the Schrödinger equation, Hartree required the final field as computed from the charge distribution to be "s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Function
A wave function in quantum physics is a mathematical description of the quantum state of an isolated quantum system. The wave function is a complex-valued probability amplitude, and the probabilities for the possible results of measurements made on the system can be derived from it. The most common symbols for a wave function are the Greek letters and (lower-case and capital psi, respectively). The wave function is a function of the degrees of freedom corresponding to some maximal set of commuting observables. Once such a representation is chosen, the wave function can be derived from the quantum state. For a given system, the choice of which commuting degrees of freedom to use is not unique, and correspondingly the domain of the wave function is also not unique. For instance, it may be taken to be a function of all the position coordinates of the particles over position space, or the momenta of all the particles over momentum space; the two are related by a Fourier tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |