|
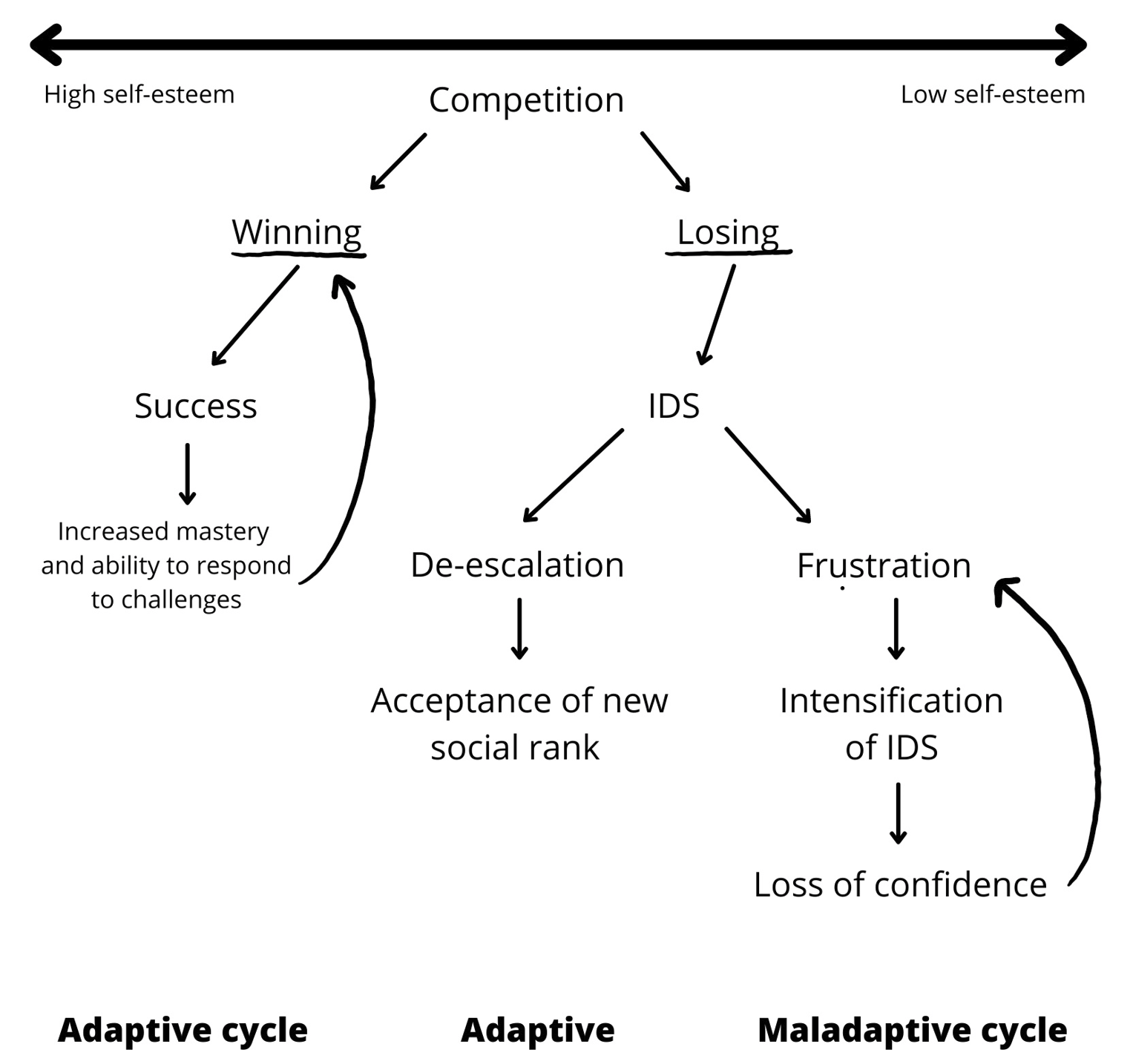
Rank Theory Of Depression
Rank theory is an evolutionary theory of depression, developed by Anthony Stevens and John Price, and proposes that depression promotes the survival of genes. Depression is an adaptive response to losing status (rank) and losing confidence in the ability to regain it. The adaptive function of the depression is to change behaviour to promote survival for someone who has been defeated. According to rank theory, depression was naturally selected to allow us to accept a subordinate role. The function of this depressive adaptation is to prevent the loser from suffering further defeat in a conflict. In the face of defeat, a behavioural process swings into action which causes the individual to cease competing and reduce their ambitions. This process is involuntary and results in the loss of energy, depressed mood, sleep disturbance, poor appetite, and loss of confidence, which are typical characteristics of depression. The outward symptoms of depression (facial expressions, constant cryin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Approaches To Depression
Evolutionary approaches to depression are attempts by evolutionary psychologists to use the theory of evolution to shed light on the problem of mood disorders within the perspective of evolutionary psychiatry. Depression is generally thought of as dysfunction or a mental disorder, but its prevalence does not increase with age the way dementia and other organic dysfunction commonly does. Some researchers have surmised that the disorder may have evolutionary roots, in the same way that others suggest evolutionary contributions to schizophrenia, sickle cell anemia, psychopathy and other disorders. Psychology and psychiatry have not generally embraced evolutionary explanations for behaviors, and the proposed explanations for the evolution of depression remain controversial. Background Major depression (also called "major depressive disorder", "clinical depression" or often simply "depression") is a leading cause of disability worldwide, and in 2000 was the fourth leading contributor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Approaches To Depression
Evolutionary approaches to depression are attempts by evolutionary psychologists to use the theory of evolution to shed light on the problem of mood disorders within the perspective of evolutionary psychiatry. Depression is generally thought of as dysfunction or a mental disorder, but its prevalence does not increase with age the way dementia and other organic dysfunction commonly does. Some researchers have surmised that the disorder may have evolutionary roots, in the same way that others suggest evolutionary contributions to schizophrenia, sickle cell anemia, psychopathy and other disorders. Psychology and psychiatry have not generally embraced evolutionary explanations for behaviors, and the proposed explanations for the evolution of depression remain controversial. Background Major depression (also called "major depressive disorder", "clinical depression" or often simply "depression") is a leading cause of disability worldwide, and in 2000 was the fourth leading contributor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychodynamics
Psychodynamics, also known as psychodynamic psychology, in its broadest sense, is an approach to psychology that emphasizes systematic study of the psychological forces underlying human behavior, feelings, and emotions and how they might relate to early experience. It is especially interested in the dynamic relations between conscious motivation and unconscious motivation. The term psychodynamics is also used to refer specifically to the psychoanalytical approach developed by Sigmund Freud (1856–1939) and his followers. Freud was inspired by the theory of thermodynamics and used the term psychodynamics to describe the processes of the mind as flows of psychological energy (libido or psi) in an organically complex brain. There are four major schools of thought regarding psychological treatment: psychodynamic, cognitive-behavioral, biological, and humanistic treatment. In the treatment of psychological distress, psychodynamic psychotherapy tends to be a less intensive (once- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a psycho-social intervention that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression and anxiety disorders. CBT focuses on challenging and changing cognitive distortions (such as thoughts, beliefs, and attitudes) and their associated behaviors to improve emotional regulation and develop personal coping strategies that target solving current problems. Though it was originally designed to treat depression, its uses have been expanded to include the treatment of many mental health conditions, including anxiety, substance use disorders, marital problems, and eating disorders. CBT includes a number of cognitive or behavioral psychotherapies that treat defined psychopathologies using evidence-based techniques and strategies. CBT is a common form of talk therapy based on the combination of the basic principles from behavioral and cognitive psychology. It is different from historical approaches to psychotherapy, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Comparison Theory
Social comparison theory, initially proposed by social psychologist Leon Festinger in 1954, centers on the belief that there is a drive within individuals to gain accurate self-evaluations. The theory explains how individuals evaluate their own opinions and abilities by comparing themselves to others in order to reduce uncertainty in these domains, and learn how to define the self. Comparing oneself to others socially is a form of measurement and self assessment to identify where an individual stands according to their own set of standards and emotions about themselves. Following the initial theory, research began to focus on social comparison as a way of self-enhancement, introducing the concepts of downward and upward comparisons and expanding the motivations of social comparisons.Schachter, S. (1959). The psychology of affiliation: Experimental studies of the sources of gregariousness (Vol. 1). Stanford University Press. Social comparison can be traced back to the pivotal paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attachment Theory
Attachment theory is a psychological, evolutionary and ethological theory concerning relationships between humans. The most important tenet is that young children need to develop a relationship with at least one primary caregiver for normal social and emotional development. The theory was formulated by psychiatrist and psychoanalyst John Bowlby. Within attachment theory, infant behaviour associated with attachment is primarily the seeking of proximity to an attachment figure in stressful situations. Infants become attached to adults who are sensitive and responsive in social interactions with them, and who remain as consistent caregivers for some months during the period from about six months to two years of age. During the latter part of this period, children begin to use attachment figures (familiar people) as a secure base to explore from and return to. Parental responses lead to the development of patterns of attachment; these, in turn, lead to internal working models ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Anxiety
Social anxiety is the anxiety and fear specifically linked to being in social settings (i.e., interacting with others). Some categories of disorders associated with social anxiety include anxiety disorders, mood disorders, autism spectrum disorders, eating disorders, and substance use disorders. Individuals with higher levels of social anxiety often avert their gazes, show fewer facial expressions, and show difficulty with initiating and maintaining a conversation. Social anxiety commonly manifests itself in the teenage years and can be persistent throughout life, however, people who experience problems in their daily functioning for an extended period of time can develop social anxiety disorder. Trait social anxiety, the stable tendency to experience this anxiety, can be distinguished from state anxiety, the momentary response to a particular social stimulus. Half of the individuals with any social fears meet the criteria for social anxiety disorder. Age, culture, and gender im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rumination (psychology)
Rumination is the focused attention on the symptoms of one's distress, and on its possible causes and consequences, as opposed to its solutions, according to the ''Response Styles Theory'' proposed by Nolen-Hoeksema (1998). Because the Response Styles Theory has been empirically supported, this model of rumination is the most widely used conceptualization. Other theories, however, have proposed different definitions for rumination. For example, in the ''Goal Progress Theory'', rumination is conceptualized not as a reaction to a mood state, but as a "response to failure to progress satisfactorily towards a goal". As such, both rumination and worry are associated with anxiety and other negative emotional states; however, its measures have not been unified. Multiple tools exist to measure ruminative thoughts. Treatments specifically addressing ruminative thought patterns are still in the early stages of development. Theories Response styles theory Response styles theory (RST) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Depressive Disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introduced by a group of US clinicians in the mid-1970s, the term was adopted by the American Psychiatric Association for this symptom cluster under mood disorders in the 1980 version of the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM-III), and has become widely used since. The diagnosis of major depressive disorder is based on the person's reported experiences, behavior reported by relatives or friends, and a mental status examination. There is no laboratory test for the disorder, but testing may be done to rule out physical conditions that can cause similar symptoms. The most common time of onset is in a person's 20s, with females affected about twice as often as males. The course of the disorder varies widely, from one epis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Gilbert (psychologist)
Paul Raymond Gilbert (born 20 July 1951) is a British clinical psychologist. Gilbert is the founder of compassion focused therapy (CFT), compassionate mind training (CMT) and author of books such as ''The Compassionate Mind: A New Approach to Life's Challenges'' and ''Overcoming Depression''. Before retirement Gilbert was head of the Mental Health Research Unit, Derbyshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust. He remains Professor at the University of Derby. In 2011 Gilbert was awarded the Order of the British Empire (OBE) for his continued contribution in mental healthcare. Early life and education Gilbert was born in The Gambia and went to a British boarding school in 1962. In early life he considered being a rock guitarist but "unfortunately I was a very average sort of player and I recognized that this wasn't going to take me very far". He went to the University of Wolverhampton to study economics, graduating in 1973 before pursuing a career as a psychologist. In 1975 G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhedonia
Anhedonia is a diverse array of deficits in hedonic function, including reduced motivation or ability to experience pleasure. While earlier definitions emphasized the inability to experience pleasure, anhedonia is currently used by researchers to refer to reduced motivation, reduced anticipatory pleasure (wanting), reduced consummatory pleasure (liking), and deficits in reinforcement learning. In the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition'' (DSM-5), anhedonia is a component of depressive disorders, substance-related disorders, psychotic disorders, and personality disorders, where it is defined by either a reduced ability to experience pleasure, or a diminished interest in engaging in pleasurable activities. While the ''International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision'' (ICD-10) does not explicitly mention anhedonia, the depressive symptom analogous to anhedonia as described in the DSM-5 is a loss of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Distortion
A cognitive distortion is an exaggerated or irrational thought pattern involved in the onset or perpetuation of psychopathological states, such as depression and anxiety. Cognitive distortions are thoughts that cause individuals to perceive reality inaccurately. According to Aaron Beck's cognitive model, a negative outlook on reality, sometimes called ''negative schemas'' (or ''schemata''), is a factor in symptoms of emotional dysfunction and poorer subjective well-being. Specifically, negative thinking patterns reinforce negative emotions and thoughts. During difficult circumstances, these distorted thoughts can contribute to an overall negative outlook on the world and a depressive or anxious mental state. According to hopelessness theory and Beck's theory, the meaning or interpretation that people give to their experience importantly influences whether they will become depressed and whether they will experience severe, repeated, or long-duration episodes of depression. Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |