|
Randolph W. Thrower
Randolph William Thrower (September 5, 1913 – March 8, 2014) was an American attorney. He served as Commissioner of Internal Revenue under President Richard Nixon from 1969 to 1971. Early life and education Thrower was born in Tampa, Florida. He graduated from Georgia Military Academy in 1930. He received an undergraduate degree from Emory University in 1934 and received his law degree from the Emory University School of Law in 1936. Career Following graduation from law school he joined the firm of Sutherland Asbill & Brennan LLP, a law firm with principal offices in Atlanta and Washington, D.C. He became a partner and remained one until his death. Many of his early cases involved handling appeals for death row inmates in Georgia prisons. According to the New York Times, Thrower was haunted for the rest of his life by the case of his client Will Coxson, a black teenager who had been convicted for rape. Thrower was convinced he was innocent. Thrower had just joined the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commissioner Of Internal Revenue
The Commissioner of Internal Revenue is the head of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), an agency within the United States Department of the Treasury. The office of Commissioner was created by Congress as part of the Revenue Act of 1862. Section 7803 of the Internal Revenue Code provides for the appointment of a Commissioner of Internal Revenue to administer and supervise the execution and application of the internal revenue laws. The Commissioner is appointed by the President of the United States, with the consent of the U.S. Senate, for a five-year term. Douglas O’Donnell became the current and Acting Commissioner of Internal Revenue after Charles P. Rettig's term as Commissioner ended on November 12, 2022. Responsibilities The Commissioner's duties include administering, managing, conducting, directing, and supervising "the execution and application of the internal revenue laws or related statutes and tax conventions to which the United States is a party" and advising the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawyers' Committee For Civil Rights Under Law
The Lawyers' Committee for Civil Rights Under Law, or simply the Lawyers' Committee, is a civil rights organization founded in 1963 at the request of President John F. Kennedy. At the time, Alabama Governor George Wallace had vowed to resist court-ordered desegregation of the University of Alabama. Voting rights activist Medgar Evers was assassinated inside his home in Mississippi on June 11. These events galvanized private lawyers to call for officials to commit to the rule of law. These events also prompted President Kennedy to call for private lawyers to do more to defend the civil rights of Black citizens, with Evers' assassination amounting to the last straw. The organization's long-standing mission is to secure equal justice for all through the rule of law by enlisting the leadership of the private bar. While the Lawyers' Committee works to stop all civil rights violations, the majority of its work targets the inequities that primarily confront African Americans, and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Bar Association Medal
The American Bar Association Medal (or ABA Medal) is the highest award given by the American Bar Association for "exceptionally distinguished service by a lawyer or lawyers to the cause of American jurisprudence." The ABA Board of Governors chooses the medal's recipient. The medal was authorized at the 50th anniversary meeting of the ABA in 1928. The first medal was given in 1929 and it has been given most, but not all, years since. The medal itself was designed by Laura Gardin Fraser. It is four inches in diameter, made of 24K gold, later reduced to 14K gold. On the obverse is a profile of John Marshall with the inscription "To the end it may be a government of laws and not of men," from the Constitution of Massachusetts. On the reverse is "Justitia" with a likeness of Lady Justice. List of recipients :''Source:Recipients of the American Bar Association Medal at the American Bar Association website'' * 1929 Samuel Williston * 1930 Elihu Root * 1931 Oliver Wendel Holmes * 1932 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John D
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Reform Act Of 1969
The Tax Reform Act of 1969 () was a United States federal tax law signed by President Richard Nixon in 1969. Its largest impact was creating the Alternative Minimum Tax, which was intended to tax high-income earners who had previously avoided incurring tax liability due to various exemptions and deductions. It also established individual and corporate minimum taxes and a new tax schedule for single taxpayers. The Act slightly increased standard deductions and personal exemptions and created more stringent requirements on nonprofit organizations, which many argue drove them to professionalization. Summary The Office of Tax Analysis of the United States Department of the Treasury summarized the tax changes as follows. * phased-in increase in personal exemption amount from $600 to $750 * repealed investment tax credit * increased minimum standard deduction from $300 plus $100 per capita (total max $1,000) to $1,000 * phased-in increase in percentage standard deduction from 10% to 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segregation Academies
Segregation academies are private schools in the Southern United States that were founded in the mid-20th century by white parents to avoid having their children attend desegregated public schools. They were founded between 1954, when the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that segregated public schools were unconstitutional, and 1976, when the court ruled similarly about private schools. While many of these schools still existmost with low percentages of minority students even todaythey may not legally discriminate against students or prospective students based on any considerations of religion, race or ethnicity that serve to exclude non-white students. The laws that permitted their racially-discriminatory operation, including government subsidies and tax exemption, were invalidated by U.S. Supreme Court decisions. After ''Runyon v. McCrary'' (1976), all of these private schools were forced to accept African-American students. As a result, segregation academies changed their admission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washington, D.C. Senators and representatives are chosen through direct election, though vacancies in the Senate may be filled by a governor's appointment. Congress has 535 voting members: 100 senators and 435 representatives. The U.S. vice president has a vote in the Senate only when senators are evenly divided. The House of Representatives has six non-voting members. The sitting of a Congress is for a two-year term, at present, beginning every other January. Elections are held every even-numbered year on Election Day. The members of the House of Representatives are elected for the two-year term of a Congress. The Reapportionment Act of 1929 establishes that there be 435 representatives and the Uniform Congressional Redistricting Act requires ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia's 5th Congressional District
Georgia's 5th congressional district is a congressional district in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. The district was represented by Democratic Party (United States), Democrat John Lewis from January 3, 1987 until his death on July 17, 2020. Kwanza Hall was elected to replace Lewis on December 1, 2020 and served until January 3, 2021 when Nikema Williams took his place. Hall was elected in a 2020 Georgia's 5th congressional district special election, special election for the balance of Lewis' 17th term. He chose not to run in the general election for a full two-year term, which was won by Williams. The district's boundaries were redrawn following the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census, which granted an additional congressional seat to Georgia.Justice Department appro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James C
James is a common English language surname and given name: *James (name), the typically masculine first name James * James (surname), various people with the last name James James or James City may also refer to: People * King James (other), various kings named James * Saint James (other) * James (musician) * James, brother of Jesus James the Just, or a variation of James, brother of the Lord ( la, Iacobus from he, יעקב, and grc-gre, Ἰάκωβος, , can also be Anglicized as " Jacob"), was "a brother of Jesus", according to the New Testament. He was an early le ... Places Canada * James Bay, a large body of water * James, Ontario United Kingdom * James College, York, James College, a college of the University of York United States * James, Georgia, an unincorporated community * James, Iowa, an unincorporated community * James City, North Carolina * James City County, Virginia ** James City (Virginia Company) ** James City Shire * James City, Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racial Segregation
Racial segregation is the systematic separation of people into race (human classification), racial or other Ethnicity, ethnic groups in daily life. Racial segregation can amount to the international crime of apartheid and a crimes against humanity, crime against humanity under the Statute of the International Criminal Court. Segregation can involve the wikt:spatial, spatial separation of the races, and mandatory use of different institutions, such as schools and hospitals by people of different races. Specifically, it may be applied to activities such as eating in restaurants, drinking from water fountains, using public toilets, attending schools, going to films, riding buses, renting or purchasing homes or renting hotel rooms. In addition, segregation often allows close contact between members of different racial or ethnic groups in social hierarchy, hierarchical situations, such as allowing a person of one race to work as a servant for a member of another race. Segregation i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
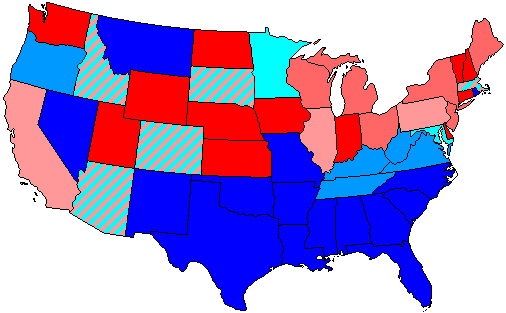
1956 United States House Of Representatives Elections
The 1956 United States House of Representatives elections was an election for the United States House of Representatives in 1956 which coincided with the re-election of President Dwight D. Eisenhower. With no major national issues and the economic upswing of the 1950s in full force, voters generally chose to uphold the status quo, keeping the Republican president and the Democratic Congress. Overall results Special elections In these special elections, the winner was seated during 1956 or before January 3, 1957; ordered by election date. Alabama Arizona Arkansas California Colorado Connecticut Delaware Florida Georgia Idaho Illinois Indiana Iowa Kansas Kentucky Louisiana Maine Maryland Massachusetts Michigan Minnesota Mississippi Missouri Montana Nebraska Nevada New Hampshire New Jersey New Mexico New York North Carolina North Dakota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)