|
Rancho Little Temecula
Rancho Little Temecula was a Mexican land grant in present-day Riverside County, California given in 1845 by Governor Pío Pico to Pablo Apis. The grant was one of the few held by indigenous people. The grant is south of present-day Temecula and is bordered on the north by Temecula Creek. At the time of the US patent, Rancho Little Temecula was a part of San Diego County. Riverside County was created by the California Legislature in 1893 by taking land from both San Bernardino and San Diego Counties. History Pablo Apis (1792–1854) was born a Luiseño and at age six was among the first indigenous people baptized at the Mission San Luis Rey. Apis learned to read and write in Spanish and eventually rose to a position of leadership in which he was the principal spokesman for the local Luiseños. After the missions became secularized in the 1830s, more indigenous people came to live in Temecula, an outpost of Mission San Luis Rey. Apis was one of the Luiseño leaders who fought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranchos Of California
The Spanish and Mexican governments made many concessions and land grants in Alta California (now known as California) and Baja California from 1775 to 1846. The Spanish Concessions of land were made to retired soldiers as an inducement for them to remain in the frontier. These Concessions reverted to the Spanish crown upon the death of the recipient. The Mexican government later encouraged settlement by issuing much larger land grants to both native-born and naturalized Mexican citizens. The grants were usually two or more square leagues, or in size. Unlike Spanish Concessions, Mexican land grants provided permanent, unencumbered ownership rights. Most ranchos granted by Mexico were located along the California coast around San Francisco Bay, inland along the Sacramento River, and within the San Joaquin Valley. When the government secularized the Mission churches in 1833, they required that land be set aside for each Neophyte family. But the Native Americans were quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1845 American annexation of Texas, which Mexico still considered its territory. Mexico refused to recognize the Velasco treaty, because it was signed by President Antonio López de Santa Anna while he was captured by the Texan Army during the 1836 Texas Revolution. The Republic of Texas was ''de facto'' an independent country, but most of its Anglo-American citizens wanted to be annexed by the United States. Sectional politics over slavery in the United States were preventing annexation because Texas would have been admitted as a slave state, upsetting the balance of power between Northern free states and Southern slave states. In the 1844 United States presidential election, Democrat James K. Polk was elected on a platform of expand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
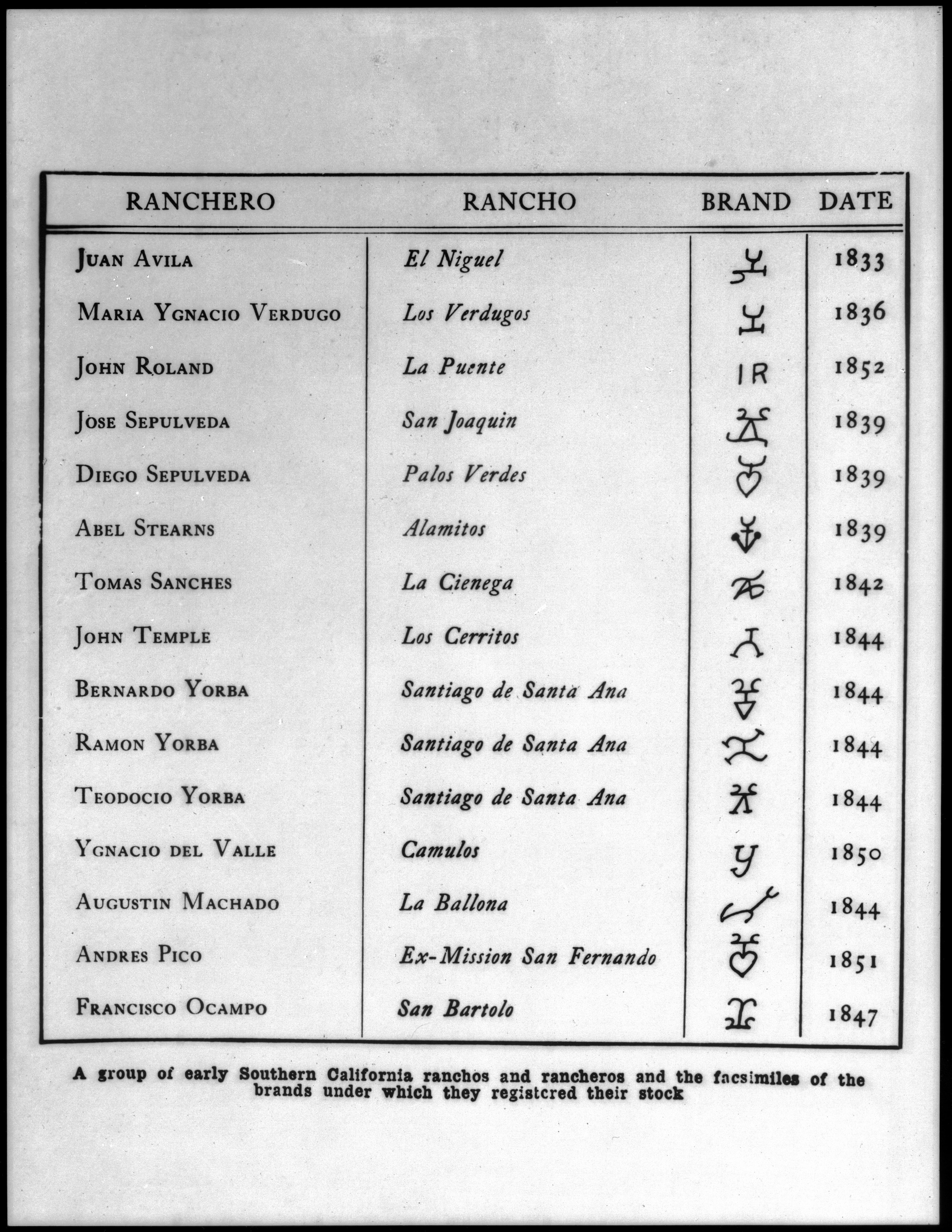
List Of Ranchos Of California
These California land grants were made by Spanish (1784–1821) and Mexican (1822–1846) authorities of Las Californias and Alta California to private individuals before California became part of the United States of America.Shumway, Burgess M.,1988, ''California Ranchos: Patented Private Land Grants Listed by County'', The Borgo Press, San Bernardino, CA, Under Spain, no private land ownership was allowed, so the grants were more akin to free leases. After Mexico achieved independence, the Spanish grants became actual land ownership grants. Following the Mexican–American War, the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo provided that the land grants would be honored. Alta California ranchos in Mexico From 1773 to 1836, the border between Alta California and Baja California was about 30 miles south of the Mexico–United States border drawn by the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo that ended the Mexican–American War in 1848. Under the Siete Leyes constitutional reforms of 1836, the Alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temecula
Temecula (; es, Temécula, ; Luiseño: ''Temeekunga'') is a city in southwestern Riverside County, California, United States. The city had a population of 110,003 as of the 2020 census and was incorporated on December 1, 1989. The city is a tourist and resort destination, with the Temecula Valley Wine Country, Old Town Temecula, the Temecula Valley Balloon & Wine Festival, the Temecula Valley International Film Festival, championship golf courses, and resort accommodations contributing to the city's economic profile. The city of Temecula, forming the southwestern anchor of the Inland Empire region, is approximately north of downtown San Diego and southeast of downtown Los Angeles. Although Temecula is geographically closer to downtown San Diego than downtown Los Angeles, it is considered part of the Greater Los Angeles area. Temecula is bordered by the city of Murrieta to the north and the Pechanga Indian Reservation and San Diego County to the south. History Pre-1800 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Yuma
Fort Yuma was a fort in California located in Imperial County, across the Colorado River from Yuma, Arizona. It was on the Butterfield Overland Mail route from 1858 until 1861 and was abandoned May 16, 1883, and transferred to the Department of the Interior. The Fort Yuma Indian School and the Saint Thomas Yuma Indian Mission now occupy the site. It is one of the "associated sites" listed as Yuma Crossing and Associated Sites on the National Register of Historic Places in the Yuma Crossing National Heritage Area. In addition, it is registered as California Historical Landmark #806. History Pre-Civil War First established after the end of the Mexican–American War (1848), the fort was originally located in the bottoms near the Colorado River, less than a mile below the mouth of the Gila River. It was constructed to defend the newly settled community of Yuma, New Mexico Territory, located on the other side of the Colorado River, and the nearby Mexican border. In March 1851 the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world's most populous megacities. Los Angeles is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Southern California. With a population of roughly 3.9 million residents within the city limits , Los Angeles is known for its Mediterranean climate, ethnic and cultural diversity, being the home of the Hollywood film industry, and its sprawling metropolitan area. The city of Los Angeles lies in a basin in Southern California adjacent to the Pacific Ocean in the west and extending through the Santa Monica Mountains and north into the San Fernando Valley, with the city bordering the San Gabriel Valley to it's east. It covers about , and is the county seat of Los Angeles County, which is the most populous county in the United States with an estim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterfield Overland Mail
Butterfield Overland Mail (officially the Overland Mail Company)Waterman L. Ormsby, edited by Lyle H. Wright and Josephine M. Bynum, "The Butterfield Overland Mail", The Huntington Library, San Marino, California, 1991. was a stagecoach service in the United States operating from 1858 to 1861. It carried passengers and U.S. Mail from two eastern termini, Memphis, Tennessee, and St. Louis, Missouri, to San Francisco, California. The routes from each eastern terminus met at Fort Smith, Arkansas, and then continued through Indian Territory (Oklahoma), Texas, New Mexico, Arizona, Mexico, and California ending in San Francisco.Goddard Bailey, Special Agent to Hon. A.V. Brown. P.M., Washington, D.C., The Senate of the United States, Second Session, Thirty-Fifth Congress, 1858–'59, Postmaster General, Appendix, "Great Overland Mail", Washington, D. C., October 18, 1858.https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uc1.c109481050;view=1up;seq=745 On March 3, 1857, Congress authorized the U.S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Emigrant Trail
:''The Southern Emigrant Trail should not be confused with the Applegate Trail, which is part of the Northern Emigrant Trails.'' Southern Emigrant Trail, also known as the Gila Trail, the Kearny Trail, Southern Trail and the Butterfield Stage Trail, was a major land route for immigration into California from the eastern United States that followed the Santa Fe Trail to New Mexico during the California Gold Rush. Unlike the more northern routes, pioneer wagons could travel year round, mountain passes not being blocked by snows, however it had the disadvantage of summer heat and lack of water in the desert regions through which it passed in New Mexico Territory and the Colorado Desert of California. Subsequently, it was a route of travel and commerce between the eastern United States and California. Many herds of cattle and sheep were driven along this route and it was followed by the San Antonio-San Diego Mail Line in 1857–1858 and then the Butterfield Overland Mail from 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rancho Pauba
Rancho Pauba was a Ranchos of California, Mexican land grant in present-day Riverside County, California given in 1844 by Governor Manuel Micheltorena to Vicente Moraga and Luis Arenas. The grant was just east of present-day Temecula, California, Temecula. At the time of the Land patent, US patent, Rancho Pauba was a part of San Diego County, California, San Diego County. Riverside County was created by the California Legislature in 1893 by taking land from both San Bernardino County, California, San Bernardino and San Diego Counties. History Vincent Moraga and Luis Arenas, both officials in Pueblo de Los Angeles, were granted six square leagues in the Temecula Valley that was formerly part of the lands of the Mission San Luis Rey de Francia, Mission San Luis Rey. Frenchman Jean-Louis Vignes (Juan Luis Vignes) acquired Rancho Pauba in 1848. Vignes owned both Rancho Pauba and the adjacent Rancho Temecula. With the Mexican Cession, cession of California to the United States fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rancho Temecula
Rancho Temecula was a Mexican land grant in present-day Riverside County, California given on December 14, 1844 by Governor Manuel Micheltorena to Feliz Valdez. The grant extended south along the east bank Murrieta Creek to Temecula Creek and encompassed present-day Temecula, Murrieta and Murrieta Hot Springs. At the time of the US patent, Rancho Temecula was a part of San Diego County. Riverside County was created by the California Legislature in 1893 by taking land from both San Bernardino and San Diego Counties. History Felix Valdes, a Mexican army officer, was granted Rancho Temecula, six square leagues (18,500 hectares or 45,800 acres) in the Temecula Valley that was formerly part of the lands of the Mission San Luis Rey. In 1846, Felix Valdes sold Rancho Temecula to Frenchman Jean-Louis Vignes (Juan Luis Vignes). Vignes owned both Rancho Temecula and the adjacent Rancho Pauba. With the cession of California to the United States following the Mexican–American War, the 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rancho Santa Rosa (Moreno)
Rancho Santa Rosa was a Mexican land grant in present day Riverside County, California given in 1846 by Governor Pio Pico to Juan Moreno. At the time of the US patent, Rancho Santa Rosa was a part of San Diego County. Riverside County was created by the California Legislature in 1893 by taking land from both San Bernardino and San Diego Counties. The site is now registered as a California Historical Landmark. History The Santa Rosa Plateau became Rancho Santa Rosa under an 1846 Mexican land grant to cattle and sheep rancher Juan Moreno. With the cession of California to the United States following the Mexican-American War, the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo provided that the land grants would be honored. As required by the Land Act of 1851, a claim for Rancho Santa Rosa was filed with the Public Land Commission in 1852, and the grant was patented to Juan Moreno in 1872. Moreno sold the rancho to Augustin Machado in 1855. Machado subsequently purchased neighboring Rancho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pechanga Indian Reservation
The Pechanga Band of Indians is a federally recognized tribe of Luiseño Indians based in Riverside County, California, where their reservation is located. As of 2006, there were 1,370 members of the nation. The tribe owns the Pechanga Resort & Casino in Temecula and the naming rights to the San Diego sports arena now known as the Pechanga Arena. The tribe was formerly named the Pechanga Band of Luiseno Mission Indians of the Pechanga Reservation. There are five other federally recognized tribes of Luiseño bands based in Southern California, and an organized band that has not received federal recognition as a tribe. Government The Pechanga Band is headquartered in Temecula, California, part of the historic territory associated with their historic ancestors. Today the tribe has a constitution, adopted in 1978, and is governed by a democratically elected, seven-person council, including the Tribal Chairperson. In the event of a voting tie, they would be the deciding vote. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |