|
Rancho Temecula
Rancho Temecula was a Mexican land grant in present-day Riverside County, California given on December 14, 1844 by Governor Manuel Micheltorena to Feliz Valdez. The grant extended south along the east bank Murrieta Creek to Temecula Creek and encompassed present-day Temecula, Murrieta and Murrieta Hot Springs. At the time of the US patent, Rancho Temecula was a part of San Diego County. Riverside County was created by the California Legislature in 1893 by taking land from both San Bernardino and San Diego Counties. History Felix Valdes, a Mexican army officer, was granted Rancho Temecula, six square leagues (18,500 hectares or 45,800 acres) in the Temecula Valley that was formerly part of the lands of the Mission San Luis Rey. In 1846, Felix Valdes sold Rancho Temecula to Frenchman Jean-Louis Vignes (Juan Luis Vignes). Vignes owned both Rancho Temecula and the adjacent Rancho Pauba. With the cession of California to the United States following the Mexican–American War, the 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
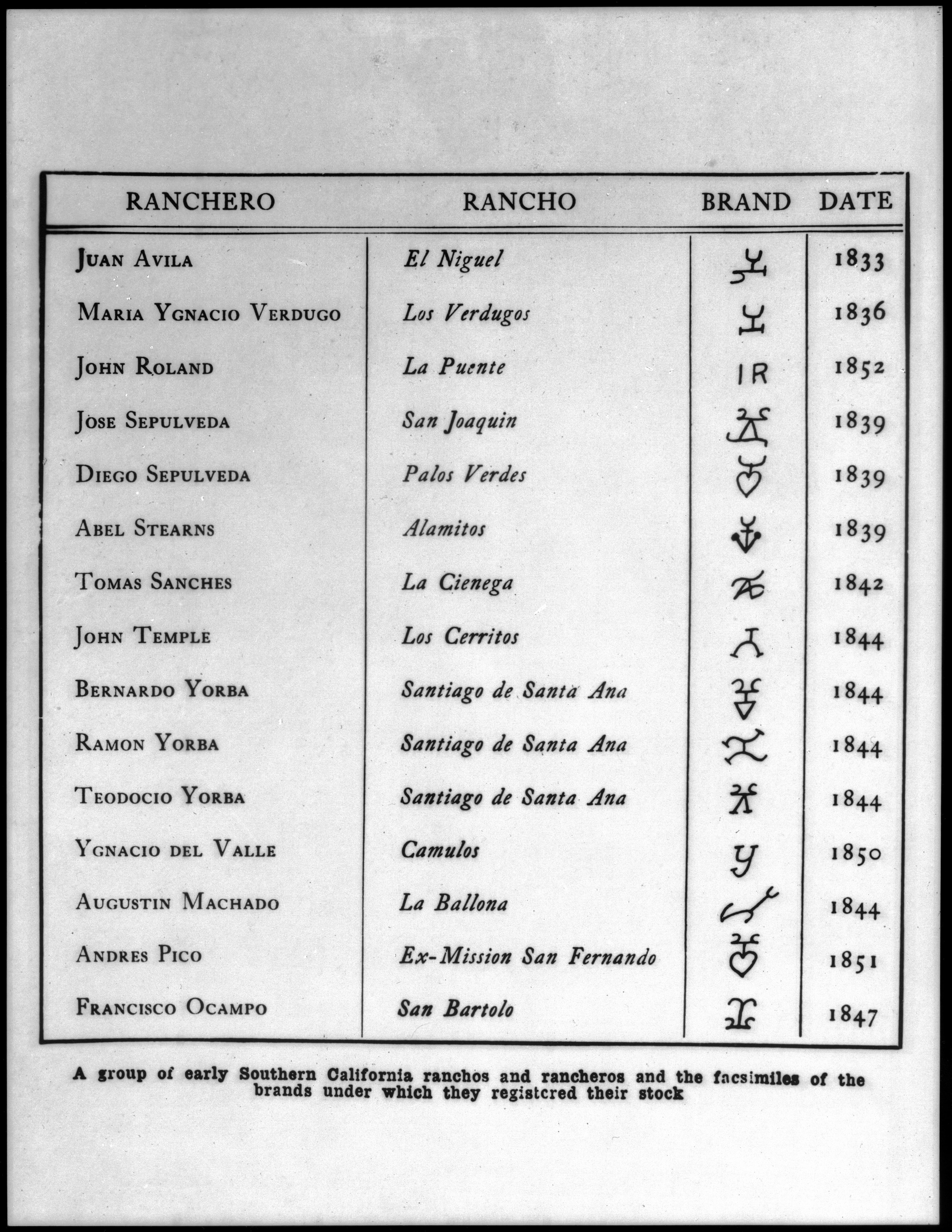
Ranchos Of California
The Spanish and Mexican governments made many concessions and land grants in Alta California (now known as California) and Baja California from 1775 to 1846. The Spanish Concessions of land were made to retired soldiers as an inducement for them to remain in the frontier. These Concessions reverted to the Spanish crown upon the death of the recipient. The Mexican government later encouraged settlement by issuing much larger land grants to both native-born and naturalized Mexican citizens. The grants were usually two or more square leagues, or in size. Unlike Spanish Concessions, Mexican land grants provided permanent, unencumbered ownership rights. Most ranchos granted by Mexico were located along the California coast around San Francisco Bay, inland along the Sacramento River, and within the San Joaquin Valley. When the government secularized the Mission churches in 1833, they required that land be set aside for each Neophyte family. But the Native Americans were quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squatters
Squatting is the action of occupying an abandoned or unoccupied area of land or a building, usually residential, that the squatter does not own, rent or otherwise have lawful permission to use. The United Nations estimated in 2003 that there were one billion slum residents and squatters globally. Squatting occurs worldwide and tends to occur when people who are poor and homeless find empty buildings or land to occupy for housing. It has a long history, broken down by country below. In developing countries and least developed countries, shanty towns often begin as squatted settlements. In African cities such as Lagos much of the population lives in slums. There are pavement dwellers in India and in Hong Kong as well as rooftop slums. Informal settlements in Latin America are known by names such as villa miseria (Argentina), pueblos jóvenes (Peru) and asentamientos irregulares (Guatemala, Uruguay). In Brazil, there are favelas in the major cities and land-based movements. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Ranchos
The Spanish and Mexican governments made many concessions and land grants in Alta California (now known as California) and Baja California from 1775 to 1846. The Spanish Concessions of land were made to retired soldiers as an inducement for them to remain in the frontier. These Concessions reverted to the Spanish crown upon the death of the recipient. The Mexican government later encouraged settlement by issuing much larger land grants to both native-born and naturalized Mexican citizens. The grants were usually two or more square leagues, or in size. Unlike Spanish Concessions, Mexican land grants provided permanent, unencumbered ownership rights. Most ranchos granted by Mexico were located along the California coast around San Francisco Bay, inland along the Sacramento River, and within the San Joaquin Valley. When the government secularized the Mission churches in 1833, they required that land be set aside for each Neophyte family. But the Native Americans were quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ranchos Of California
These California land grants were made by Spanish (1784–1821) and Mexican (1822–1846) authorities of Las Californias and Alta California to private individuals before California became part of the United States of America.Shumway, Burgess M.,1988, ''California Ranchos: Patented Private Land Grants Listed by County'', The Borgo Press, San Bernardino, CA, Under Spain, no private land ownership was allowed, so the grants were more akin to free leases. After Mexico achieved independence, the Spanish grants became actual land ownership grants. Following the Mexican–American War, the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo provided that the land grants would be honored. Alta California ranchos in Mexico From 1773 to 1836, the border between Alta California and Baja California was about 30 miles south of the Mexico–United States border drawn by the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo that ended the Mexican–American War in 1848. Under the Siete Leyes constitutional reforms of 1836, the Alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaiser Steel
Kaiser Steel was a steel mill near Fontana, California, founded by Henry J. Kaiser on December 1, 1941. The plant's first blast furnace, "Bess No. 1" (named after Kaiser's wife) was fired up on December 30, 1942, and the first steel plate was produced in August 1943 for the Pacific Coast shipbuilding industry amid World War II. The facility was fully integrated, taking ore and producing steel at a single site, the only such steel plant on the West Coast. The Fontana facility produced about 75 million tons of steel over its history. The mill was part of Kaiser's vertically-integrated business: iron ore was supplied by Kaiser's mine in Eagle Mountain, California using Kaiser's Eagle Mountain Railroad, coal was supplied by Kaiser's mines in New Mexico and Utah and limestone was from a Kaiser mine in Cushenbury, California, the steel produced was used by the Kaiser Shipyards and other Kaiser owned businesses (among other customers), and the Kaiser Permanente health maintenance organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Angeles, California
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world's most populous megacities. Los Angeles is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Southern California. With a population of roughly 3.9 million residents within the city limits , Los Angeles is known for its Mediterranean climate, ethnic and cultural diversity, being the home of the Hollywood film industry, and its sprawling metropolitan area. The city of Los Angeles lies in a basin in Southern California adjacent to the Pacific Ocean in the west and extending through the Santa Monica Mountains and north into the San Fernando Valley, with the city bordering the San Gabriel Valley to it's east. It covers about , and is the county seat of Los Angeles County, which is the most populous county in the United States with an estim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rancho Little Temecula
Rancho Little Temecula was a Mexican land grant in present-day Riverside County, California given in 1845 by Governor Pío Pico to Pablo Apis. The grant was one of the few held by indigenous people. The grant is south of present-day Temecula and is bordered on the north by Temecula Creek. At the time of the US patent, Rancho Little Temecula was a part of San Diego County. Riverside County was created by the California Legislature in 1893 by taking land from both San Bernardino and San Diego Counties. History Pablo Apis (1792–1854) was born a Luiseño and at age six was among the first indigenous people baptized at the Mission San Luis Rey. Apis learned to read and write in Spanish and eventually rose to a position of leadership in which he was the principal spokesman for the local Luiseños. After the missions became secularized in the 1830s, more indigenous people came to live in Temecula, an outpost of Mission San Luis Rey. Apis was one of the Luiseño leaders who fought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rancho Santa Rosa (Moreno)
Rancho Santa Rosa was a Mexican land grant in present day Riverside County, California given in 1846 by Governor Pio Pico to Juan Moreno. At the time of the US patent, Rancho Santa Rosa was a part of San Diego County. Riverside County was created by the California Legislature in 1893 by taking land from both San Bernardino and San Diego Counties. The site is now registered as a California Historical Landmark. History The Santa Rosa Plateau became Rancho Santa Rosa under an 1846 Mexican land grant to cattle and sheep rancher Juan Moreno. With the cession of California to the United States following the Mexican-American War, the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo provided that the land grants would be honored. As required by the Land Act of 1851, a claim for Rancho Santa Rosa was filed with the Public Land Commission in 1852, and the grant was patented to Juan Moreno in 1872. Moreno sold the rancho to Augustin Machado in 1855. Machado subsequently purchased neighboring Rancho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Mexico Territory
The Territory of New Mexico was an organized incorporated territory of the United States from September 9, 1850, until January 6, 1912. It was created from the U.S. provisional government of New Mexico, as a result of ''Santa Fe de Nuevo México, Nuevo México'' becoming part of the American frontier after the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. It existed with varying boundaries until the territory was admitted to the Union as the U.S. state of New Mexico. This jurisdiction was an organized, incorporated territory of the US for nearly 62 years, the longest period of any territory in the contiguous United States. Before the territory was organized In 1846, during the Mexican–American War, the United States established U.S. provisional government of New Mexico, a provisional government of New Mexico. Territorial boundaries were somewhat ambiguous. After the Mexican Republic formally ceded the region to the United States in 1848, this temporary wartime/military government operated u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Column
The California Column was a force of Union volunteers sent to Arizona and New Mexico during the American Civil War. The command marched over from California through Arizona and New Mexico Territory to the Rio Grande and as far east as El Paso, Texas, between April and August 1862. Formation The "California Column" originally consisted of ten companies of the 1st California Infantry, all five companies of the 1st Regiment California Volunteer Cavalry, Company B, 2nd Regiment California Volunteer Cavalry and Light Battery A of the Third U.S. Artillery. This command contained 1500 well drilled and disciplined men. Later on, Lieutenant Colonel George W. Bowie's 5th California Infantry was added, bringing the total strength of the Column to 2350 men. Expedition The objective of California Column commander, Colonel James Henry Carleton (promoted to brigadier general while the column was en route) was to drive Confederate troops out of the Federal New Mexico Territory. In 1861 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Yuma
Fort Yuma was a fort in California located in Imperial County, across the Colorado River from Yuma, Arizona. It was on the Butterfield Overland Mail route from 1858 until 1861 and was abandoned May 16, 1883, and transferred to the Department of the Interior. The Fort Yuma Indian School and the Saint Thomas Yuma Indian Mission now occupy the site. It is one of the "associated sites" listed as Yuma Crossing and Associated Sites on the National Register of Historic Places in the Yuma Crossing National Heritage Area. In addition, it is registered as California Historical Landmark #806. History Pre-Civil War First established after the end of the Mexican–American War (1848), the fort was originally located in the bottoms near the Colorado River, less than a mile below the mouth of the Gila River. It was constructed to defend the newly settled community of Yuma, New Mexico Territory, located on the other side of the Colorado River, and the nearby Mexican border. In March 1851 the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union (American Civil War), Union of the collective U.S. state, states. It proved essential to the preservation of the United States as a working, viable republic. The Union Army was made up of the permanent Regular Army (United States), regular army of the United States, but further fortified, augmented, and strengthened by the many temporary units of dedicated United States Volunteers, volunteers, as well as including those who were drafted in to service as Conscription in the United States, conscripts. To this end, the Union Army fought and ultimately triumphed over the efforts of the Confederate States Army in the American Civil War. Over the course of the war, 2,128,948 men enlisted in the Union Army, including 178,895 United States Colored Troops, colored troops; 25% of the white men who s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |