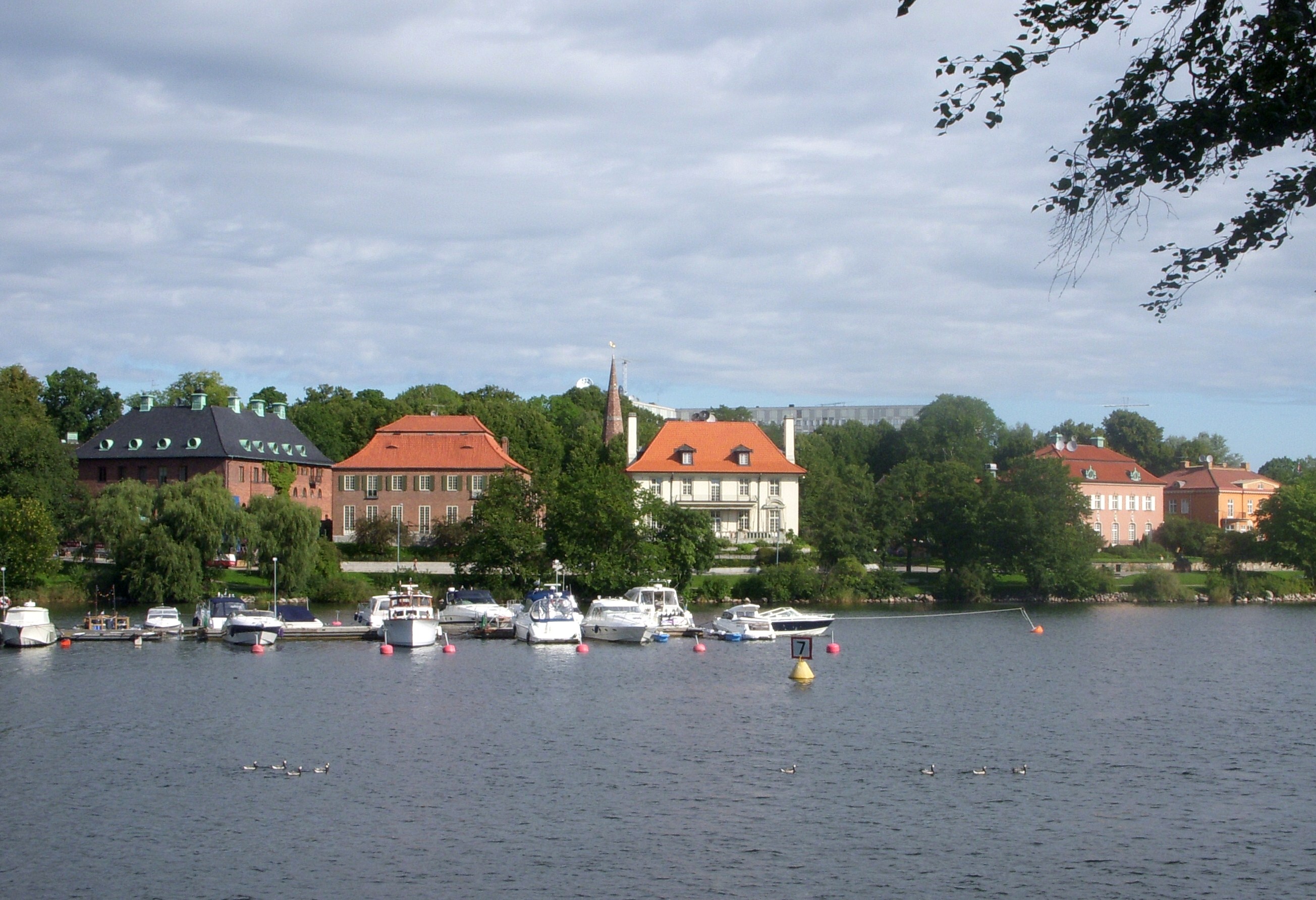|
Ralph Rapson
Ralph Rapson (September 13, 1914 – March 29, 2008) was Head of the School of Architecture at the University of Minnesota for 30 years. He was one of the world's oldest practicing architects at his death at age 93, and also one of the most prolific. He was the father of philanthropist Rip Rapson. Early life and education Rapson was born in Alma, Michigan with a deformed right arm that was amputated at birth; he learned to draw expertly with his left hand. He earned architecture degrees at the University of Michigan, and at the Cranbrook Academy of Art, where he studied under Eliel Saarinen. “Cranbrook was a very exciting, dynamic place where I met and worked with guys like Charlie Eames, Harry Bertoia, and Harry Weese,” Rapson said. As a young architect, Rapson worked for the Saarinen architectural office from 1940 to 1941. He moved to Chicago in 1941, where he worked with George Fred Keck and others. Teaching Rapson taught architecture at the New Bauhaus School (no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Fred Keck
George Frederick Keck (1895-1980) was an American modernist architect based in Chicago, Illinois. He was later assisted in his practice by his brother William Keck to form the firm of Keck & Keck. Biography Keck was born in Watertown, Wisconsin, the eldest of five boys. He studied engineering for a year at the University of Wisconsin and then studied architecture engineering at the University of Illinois. Starting in the 1920s, he worked as a draftsman for several Chicago firms, including D. H. Burnham & Company and Schmidt, Garden and Martin. He started his own practice in 1926, and was joined by his younger brother William five years later. George took an interest in the Deutscher Werkbund and the emerging International Style. Career Keck designed two key model structures for the Century of Progress exhibition in Chicago in 1933; dubbed the " House of Tomorrow".Roth, Leland M. ''American Architecture: A History'',Google Books, Westview Press, 2003, p. 361, (). These two stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
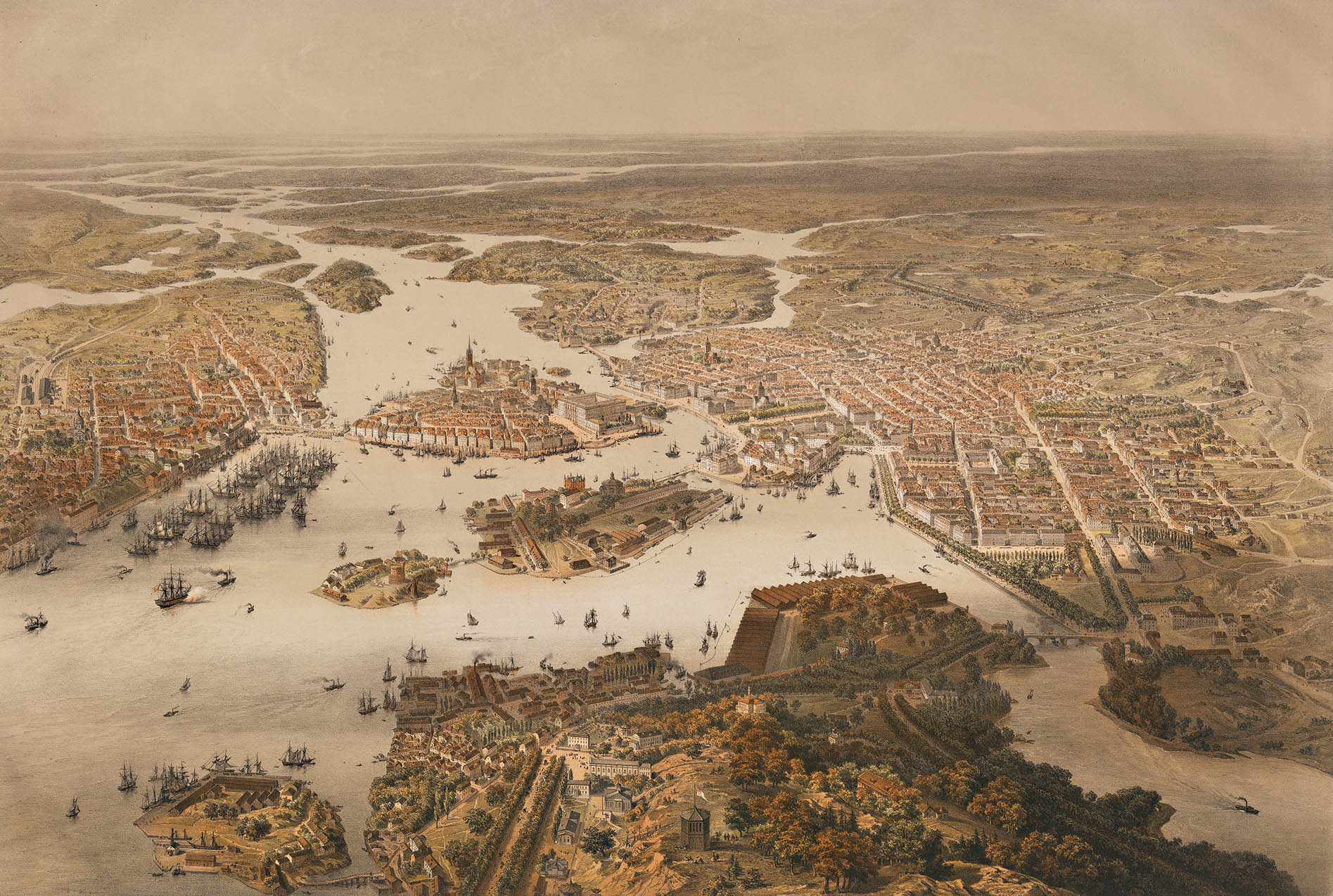
Stockholm, Sweden
Stockholm () is the capital and most populous city of Sweden as well as the largest urban area in the Nordic countries. Approximately 1 million people live in the municipality, with 1.6 million in the urban area, and 2.4 million in the metropolitan area. The city stretches across fourteen islands where Lake Mälaren flows into the Baltic Sea. Outside the city to the east, and along the coast, is the island chain of the Stockholm archipelago. The area has been settled since the Stone Age, in the 6th millennium BC, and was founded as a city in 1252 by Swedish statesman Birger Jarl. The city serves as the county seat of Stockholm County. Stockholm is the cultural, media, political, and economic centre of Sweden. The Stockholm region alone accounts for over a third of the country's GDP, and is among the top 10 regions in Europe by GDP per capita. Considered a global city, it is the largest in Scandinavia and the main centre for corporate headquarters in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplomatstaden
Diplomatstaden (Swedish for "Diplomat City") is a neighbourhood in the Östermalm district in central Stockholm, Sweden. As the name suggests, the neighbourhood is the home of many embassies and ambassadorial residencies. Diplomatstaden encompasses the area facing the Djurgårdsbrunnsviken bay which is located south of the easternmost part of Strandvägen. It is an exclusive residential area composed of a group of brick villas built mostly in the 1910s and 1920s.Johansson, ''Guide till Stockholms arkitektur'', p 184 History The municipal council had scrapped its plans for a Nobel institute in the neighbouring Nobel Park (''Nobelparken'') in 1906.Stugart, ''Diplomatstaden vore kul...'' Instead, city planning authority Per Olof Hallman designed a city plan for the area in 1911 and 1914. His plan strictly specified what materials should be used and detailed much of the exterior shapes of the buildings. Additionally, the irregularly shaped sites, over time increasingly critici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwell Home Design Invitational
{{disambiguation ...
Dwell may refer to: * ''Dwell'' (album), a 2020 album by Recondite * ''Dwell'' (magazine), a monthly American publication focused on modern architecture and design * Dwell (retailer), a leading UK furniture and accessories company * "Dwell" (song), a 2020 song by Odette * Dwell angle meter, an instrument used to tune ignition systems * "Dwell", a song by Recondite from the 2020 album ''Dwell'' * Dwell Community Church, a non-denominational cell church system in Columbus, Ohio See also * Dweller (other) * Dwell time (other) * Dwelling In law, a dwelling (also known as a residence or an abode) is a self-contained unit of accommodation used by one or more households as a home - such as a house, apartment, mobile home, houseboat, vehicle, or other "substantial" structure. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapson Greenbelt
Rapson may refer to: People *John Rapson (born 1953), American jazz trombonist * Edward James Rapson (1861–1937), numismat and historian * Ralph Rapson (1914–2008), American architect *Rip Rapson (born 1952), American attorney and philanthropist *Syd Rapson (born 1942), British politician; MP from Portsmouth North 1997–2005 *William Sage Rapson William Sage Rapson (14 August 1912 – 25 June 1999) was a New Zealand and South African chemist. His initial career was in organic chemistry but he moved into inorganic chemistry with particular emphasis on gold. His research interests ranged f ... (1912–1999), New Zealand and South African chemist Places * Rapson, Michigan, an unincorporated community in the United States {{disambig, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esther McCoy
Esther McCoy (November 18, 1904 in Horatio, Arkansas – December 30, 1989) was an American author and architectural historian who was instrumental in bringing the modern architecture of California to the attention of the world. Early life and education Born in Horatio, Arkansas, Esther McCoy was raised in Kansas. She attended the Central College for Women, a preparatory school in Lexington, Missouri, prior to a college career which took her from Baker University, to the University of Arkansas, then to Washington University, and finally the University of Michigan. She left the University of Michigan in 1925, and by 1926 was living in New York City and embarking on a writing career. California and later life In 1932 McCoy was diagnosed with pneumonia and headed West for Los Angeles to recover. She purchased in a bungalow in the Ocean Park section of Santa Monica in the late 1930s, where she lived for the remainder of her life, although she traveled widely. During Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cesar Pelli
Cesar, César or Cèsar may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * ''César'' (film), a 1936 film directed by Marcel Pagnol * ''César'' (play), a play by Marcel Pagnolt * César Award, a French film award Places * Cesar, Portugal * Cesar River, a river within the Magdalena Basin of Colombia * Cesar River, Chile * Cesar Department, Colombia Other uses * César (grape), an ancient red wine grape from northern Burgundy * French ship ''César'' (1768), ship of the line, destroyed 1782 * Recife Center for Advanced Studies and Systems (C.E.S.A.R), in Brazil * Cesar, a brand of dog food manufactured by Mars, Incorporated People with the given name * César (footballer, born May 1979), César Vinicio Cervo de Luca, Brazilian football centre-back * César (footballer, born July 1979), Clederson César de Souza, Brazilian football winger * César Alierta (born 1945), Spanish businessman * César Augusto Soares dos Reis Ribela (born 1995), Brazilian footballer * César ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bauhaus
The Staatliches Bauhaus (), commonly known as the Bauhaus (), was a German art school operational from 1919 to 1933 that combined crafts and the fine arts.Oxford Dictionary of Art and Artists (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 4th edn., 2009), , pp. 64–66 The school became famous for its approach to design, which attempted to unify individual artistic vision with the principles of mass production and emphasis on function. The Bauhaus was founded by architect Walter Gropius in Weimar. It was grounded in the idea of creating a Gesamtkunstwerk ("comprehensive artwork") in which all the arts would eventually be brought together. The Bauhaus style later became one of the most influential currents in modern design, modernist architecture, and architectural education. The Bauhaus movement had a profound influence upon subsequent developments in art, architecture, graphic design, interior design, industrial design, and typography. Staff at the Bauhaus included prominent ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modernist
Modernism is both a philosophy, philosophical and arts movement that arose from broad transformations in Western world, Western society during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The movement reflected a desire for the creation of new forms of art, philosophy, and social organization which reflected the newly emerging industrial society, industrial world, including features such as urbanization, architecture, new technologies, and war. Artists attempted to depart from traditional forms of art, which they considered outdated or obsolete. The poet Ezra Pound's 1934 injunction to "Make it New" was the touchstone of the movement's approach. Modernist innovations included abstract art, the stream-of-consciousness novel, montage (filmmaking), montage cinema, atonal and twelve-tone music, divisionist painting and modern architecture. Modernism explicitly rejected the ideology of Realism (arts), realism and made use of the works of the past by the employment of reprise, incorpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Grove 4
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |