|
Rainbow Codes
The Rainbow Codes were a series of code names used to disguise the nature of various British military research projects. They were mainly used by the Ministry of Supply from the end of the Second World War until 1958, when the ministry was broken up and its functions distributed among the forces. The codes were replaced by an alphanumeric code system. History During WWII, British intelligence was able to glean details of new German technologies simply by considering their code names. For instance, when they heard of a new system known as '' Wotan'', Reginald Victor Jones asked around and found that Wotan was a one-eyed god. Based on this, he guessed it was a radio navigation system using a single radio beam. This proved correct, and the Royal Air Force was able to quickly render it useless through jamming. Wishing to avoid making this sort of mistake, Ministry of Supply (MoS) initiated a system that would be entirely random and deliberately unrelated to the program in any w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Code Name
A code name, call sign or cryptonym is a code word or name used, sometimes clandestinely, to refer to another name, word, project, or person. Code names are often used for military purposes, or in espionage. They may also be used in industrial counter-espionage to protect secret projects and the like from business rivals, or to give names to projects whose marketing name has not yet been determined. Another reason for the use of names and phrases in the military is that they transmit with a lower level of cumulative errors over a walkie-talkie or radio link than actual names. Military origins During World War I, names common to the Allies referring to nations, cities, geographical features, military units, military operations, diplomatic meetings, places, and individual persons were agreed upon, adapting pre-war naming procedures in use by the governments concerned. In the British case names were administered and controlled by the Inter Services Security Board (ISSB) staffed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
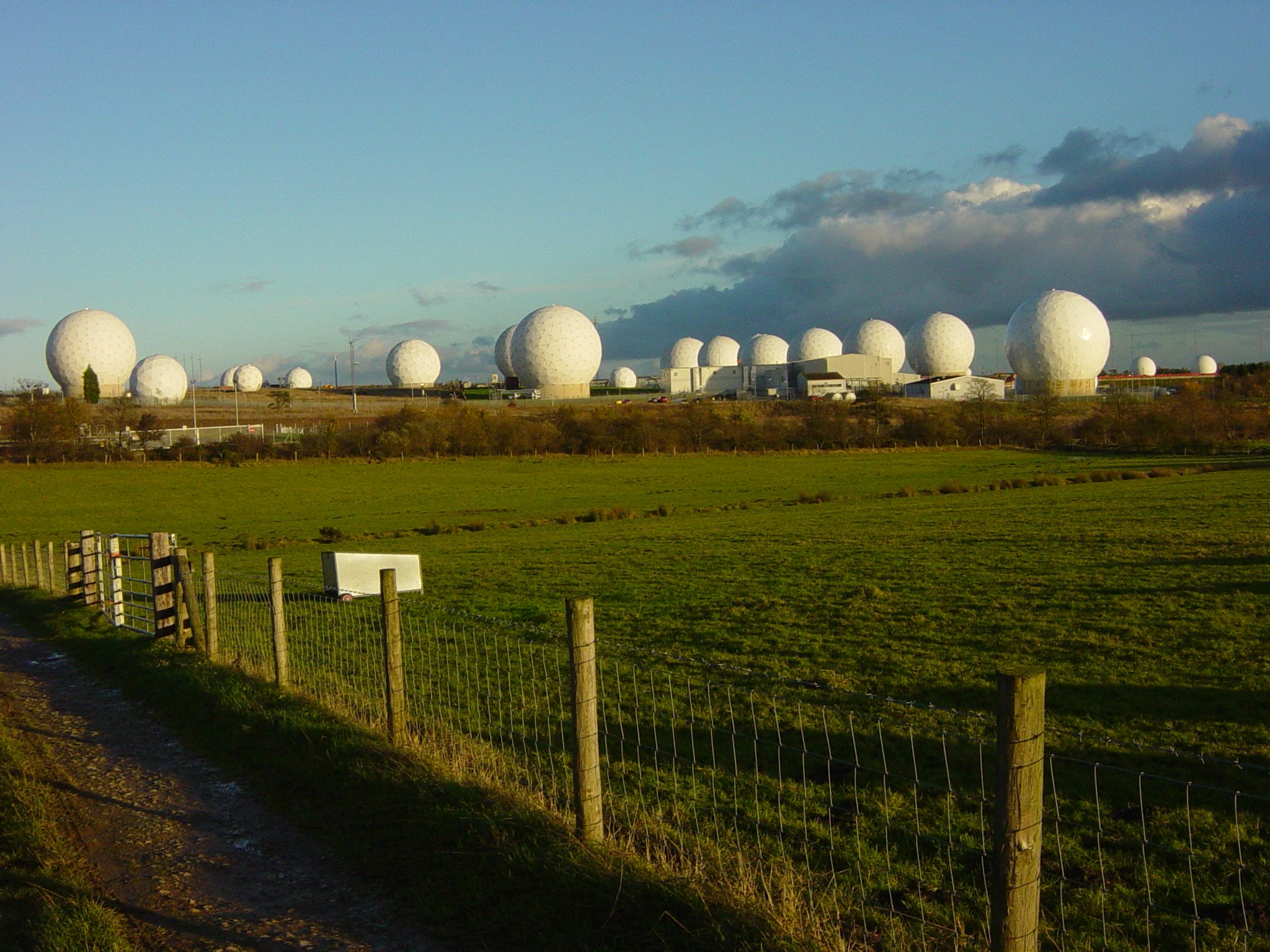
Blue Riband (radar)
The AMES Type 85, also known by its rainbow code Blue Yeoman, was an extremely powerful early warning (EW) and fighter direction (GCI) radar used by the Royal Air Force (RAF) as part of the Linesman/Mediator radar network. First proposed in early 1958, it was eleven years before they became operational in late 1968, by which time they were already considered obsolete. The Type 85 remained the RAF's primary air defense radar until it was replaced by Marconi Martello sets in the late-1980s as part of the new IUKADGE network. In the 1950s the RAF deployed the ROTOR reporting network, and later improved this system with the AMES Type 80 radar. While these were being built, the carcinotron radar jammer was tested against it and found to completely blank out its display. At first, it was feared the carcinotron would render all long-range radars useless, but over time a number of new concepts emerged to deal with this threat. Among them was the Blue Riband radar, which used a dozen 8&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Maria (IFF)
Black Maria was the rainbow code name for an identification friend or foe (IFF) interrogator carried by interceptor aircraft in the Royal Air Force and US Navy. When initially developed, beginning in 1951, it was based on the World War II-era IFF Mark III IFF system because the newer IFF Mark X IFF Mark X was the NATO standard military identification friend or foe transponder system from the early 1950s until it was slowly replaced by the IFF Mark XII in the 1970s. It was also adopted by ICAO, with some modifications, as the civilian ai ... units were not available from US at the time. Marconi received interim Mark X equipment in mid-1953 and quickly added support, but it was not until mid-1955 that the first production units became available. During development in the UK, it was also referred to as the Fighter Identity System, or FIS. In the US it was known as TN-103/APX. References Citations Bibliography * * * {{cite encyclopedia , url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Knight (rocket)
Black Knight was a British research sounding rocket, originally developed to test and verify the design of a re-entry vehicle for the Blue Streak missile. It was the United Kingdom's first indigenous space launcher. Design work on what would become the Black Knight launch vehicle commenced in 1955, being performed by the Royal Aircraft Establishment (RAE) and British manufacturer Saunders-Roe. Saunders-Roe was the principal manufacturer for the Black Knight at its facility on the Isle of Wight. On 7 September 1958, the first Black Knight was launched at Woomera in Australia. Between 1958 and 1965, a total of 22 launch vehicles were fired, none of which suffered any major failures. After 22 launches, the Black Knight programme was closed. The success of the Black Knight as a cheap and successful test vehicle led to many studies being performed into further derivatives of the vehicle, including its adaption to serve as an intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) and as a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Knight
The black knight is a literary stock character who masks his identity and that of his liege by not displaying heraldry. Black knights are usually portrayed as villainous figures who use this anonymity for misdeeds. They are often contrasted with the knight-errant (white knight). The character appeared in Arthurian literature and has been adapted and adopted by various authors, in cinema and popular culture. The character is sometimes associated with death or darkness. Organizations The Order Of The Black Knights : An anarchic arch liberal international organization which aims towards abolishing any form of "State" as their view is that The State itself removes freedom from people by imposing rules the People don't want to, and keeps "the Citizens of The World" stagnated in the past and/or the present, instead of looking towards the future, which is Human Nature, progress. It fights in favour of removing The State as well as any Army or Military force affiliated to specific Nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Streak
Blue Streak or Bluestreak may refer to: Entertainment * ''Blue Streak'' (album), a 1995 album by American blues guitarist Luther Allison * Blue Streak (comics), a secret identity used by three separate Marvel Comics supervillains * Bluestreak (comics), a fictional superhero character in the Marvel Comics series ''A-Next'' * ''Blue Streak'' (film), a 1999 comedy film starring Martin Lawrence ** ''Blue Streak'' (soundtrack), the soundtrack album for the 1999 comedy film ''Blue Streak'' * Blue Streak (Cedar Point), a roller coaster at Cedar Point in Sandusky, Ohio, United States * Blue Streak (Conneaut Lake), a former roller coaster at Conneaut Lake Park in Conneaut Lake, Pennsylvania, United States * Bluestreak (Transformers), several fictional robot superhero characters in the Transformers robot superhero franchise. * BlueStreak (video game), the codename for the upcoming video game ''LawBreakers'' by Boss Key Productions Transportation and military * Blue Streak (missile), a B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Arrow
Black Arrow, officially capitalised BLACK ARROW, was a British satellite carrier rocket. Developed during the 1960s, it was used for four launches between 1969 and 1971, all launched from the Woomera Prohibited Area in Australia. Its final flight was the first and only successful orbital launch to be conducted by the United Kingdom, and placed the Prospero satellite into low Earth orbit. Black Arrow originated from studies by the Royal Aircraft Establishment for carrier rockets based on the Black Knight rocket, with the project being authorised in 1964. It was initially developed by Saunders-Roe, and later Westland Aircraft as the result of a merger. Black Arrow was a three-stage rocket, fuelled by RP-1 paraffin (kerosene) and high test peroxide, a concentrated form of hydrogen peroxide (85% hydrogen peroxide + 15% water). It was retired after only four launches in favour of using American Scout rockets, which the Ministry of Defence calculated to be cheaper than maintaining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferranti Blue Fox
__NOTOC__ The Ferranti Blue Fox was a British multi-role airborne radar designed and built for the Royal Navy by Ferranti, Ferranti Defence Systems in the late 1970s. It had a mixed record in service, and was replaced by the more capable Blue Vixen. Design and development Blue Fox was developed to a Royal Navy requirement for a radar to equip the British Aerospace Sea Harrier FRS.1. Its primary role would be to detect large targets like maritime reconnaissance aircraft or anti-shipping bombers flying over the sea. A secondary role was air-to-surface search and strike against shipping. The system was designed within strict limits of size, time and cost. Ferranti developed the system using components of their Seaspray (radar), Ferranti Seaspray radar, used on the Westland Lynx naval helicopter to detect ships. It emerged as a Frequency agility, frequency agile I band (NATO), I band radar that weighed less than 85 kilograms in total. Three two-seat Hawker Hunters were also fitted wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Vixen
__NOTOC__ Blue Vixen was a British airborne radar designed and built for the Royal Navy by Ferranti Defence Systems (later, GEC-Marconi), Edinburgh, Scotland. It was the primary radar of later models of the British Aerospace Sea Harrier, replacing the Ferranti Blue Fox used on earlier models of the Harrier. Design and development Blue Vixen was a lightweight (145 kg) multimode, coherent, pulse-Doppler I band airborne radar, developed from the previous Ferranti Blue Fox radar, and designed for use on the British Aerospace Sea Harrier FA2. It was a multimode radar for airborne interception and air-to-surface strike roles over water and land, with look-down/shoot-down and look-up modes. Designed from the start to have full AIM-120 AMRAAM compatibility, it was also compatible with Sea Eagle and AIM-9 Sidewinder missiles. Development aircraft used Two British Aerospace 125 aircraft were used for the flight trial's program. The first (XW930 serial number 25009) was a Series 1 airc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Support Measures
In military telecommunications, electronic support (ES) or electronic support measures (ESM) gather intelligence through passive "listening" to electromagnetic radiations of military interest. They are an aspect of electronic warfare involving actions taken under direct control of an operational commander to detect, intercept, identify, locate, record, and/or analyze sources of radiated electromagnetic energy for the purposes of immediate threat recognition (such as warning that fire control RADAR has locked on a combat vehicle, ship, or aircraft) or longer-term operational planning.Polmar, Norman "The U. S. Navy Electronic Warfare (Part 1)" ''United States Naval Institute Proceedings'' October 1979 p.137 Thus, electronic support provides a source of information required for decisions involving electronic protection (EP), electronic attack (EA), avoidance, targeting, and other tactical employment of forces. Electronic support data can be used to produce signals intelligence (SIG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BL755
BL755 is a cluster bomb developed by Hunting Aircraft that contains 147 parachute-retarded high explosive anti-tank (HEAT) submunitions. Its primary targets are armoured vehicles and tanks with secondary soft target (anti personnel) capabilities. It entered service with the Royal Air Force (RAF) in 1973. BL755 was developed as a new-generation anti-tank weapon that would allow extremely low-level attacks against Soviet armoured formations. The introduction of the ZSU-23-4 Shilka self-propelled anti-aircraft gun rendered the pop-up attack profile demanded by iron bombs and air-to-ground rockets almost suicidal. The cluster munition would be dropped in pairs while the aircraft overflew the formation at and 300 feet altitude, covering an area of . The weapon's first use in combat was during the Falklands War where it was used in the anti-infantry role. When dropped from ultra-low altitudes, the bomblets proved to have a very high failure rate because the parachutes often di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Aviation
The Ministry of Aviation was a department of the United Kingdom government established in 1959. Its responsibilities included the regulation of civil aviation and the supply of military aircraft, which it took on from the Ministry of Supply. In 1967, the Ministry of Aviation merged into the Ministry of Technology which took on the supply of military aircraft, while regulatory responsibilities were switched to the Board of Trade. Ministers of Aviation * 14 October 1959: Duncan SandysDavid Butler and Gareth Butler, ''Twentieth Century British Political Facts 1900-2000'', Macmillan 2000, p. 27.Butler and Butler, p. 58. * 27 July 1960: Peter Thorneycroft * 16 July 1962: Julian Amery * 18 October 1964: Roy JenkinsButler and Butler, p. 30. * 23 December 1965: Frederick Mulley * 7 January 1967 – 15 February 1967: John Stonehouse Parliamentary Secretaries * 22 October 1959: Geoffrey Rippon * 9 October 1961: Christopher Woodhouse * 16 July 1962: Basil de Ferranti * 3 December 1962 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |