|
Railroad Wheel
A train wheel or rail wheel is a type of wheel specially designed for use on railway tracks. The wheel acts as a rolling component, typically press fitted onto an axle and mounted directly on a railway carriage or locomotive, or indirectly on a bogie (in the UK), also called a ''truck'' (in North America). The powered wheels under the locomotive are called driving wheels. Wheels are initially cast or forged and then heat-treated to have a specific hardness. New wheels are machined using a lathe to a standardized shape, called a profile, before being installed onto an axle. All wheel profiles are regularly checked to ensure proper interaction between the wheel and the rail. Incorrectly profiled wheels and worn wheels can increase rolling resistance, reduce energy efficiency and may even cause a derailment. The International Union of Railways has defined a standard wheel diameter of , although smaller sizes are used in some rapid transit railway systems and on ro-ro carriage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rollingstock Axle
The term rolling stock in the rail transport industry refers to railway vehicles, including both powered and unpowered vehicles: for example, locomotives, Railroad car#Freight cars, freight and Railroad car#Passenger cars, passenger cars (or coaches), and Railroad car#Non-revenue cars, non-revenue cars. Passenger vehicles can be un-powered, or self-propelled, Railcar, single or Multiple unit, multiple units. A connected series of railway vehicles is a train (this term applied to a locomotive is a common misnomer). In North America, Australia and other countries, the term consist ( ) is used to refer to the rolling stock in a train. In the United States, the term ''rolling stock'' has been expanded from the older broadly defined "trains" to include wheeled vehicles used by businesses on roadways. The word ''stock'' in the term is used in a sense of inventory. Rolling stock is considered to be a liquid asset, or close to it, since the value of the vehicle can be readily estimate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Railways
The International Union of Railways (UIC, french: Union internationale des wikt:chemin de fer, chemins de fer) is an international rail transport industry body. History The railways of Europe originated as many separate concerns, and there were many border changes after World War I and the Treaty of Versailles. Colonial railways were the responsibility of the mother country. Into this environment the UIC was created on 17 October 1922, with the aim of standardising industry practices. Ticket revenue sharing was originally undertaken with the UIC Franc currency equivalent. UIC classification and UIC Country Codes allowed precise determination of rolling stock capabilities and ownership, with wagons assigned unique UIC wagon numbers. The 1990s GSM-R radio telecommunication system is an international interoperability specification covering voice and signalling systems for railway communications whose specification is maintained by the International Union of Railways project Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in England, or, more broadly, to the collective dialects of English throughout the British Isles taken as a single umbrella variety, for instance additionally incorporating Scottish English, Welsh English, and Ulster English, Northern Irish English. Tom McArthur (linguist), Tom McArthur in the ''Oxford Guide to World English'' acknowledges that British English shares "all the ambiguities and tensions [with] the word 'British people, British' and as a result can be used and interpreted in two ways, more broadly or more narrowly, within a range of blurring and ambiguity". Variations exist in formal (both written and spoken) English in the United Kingdom. For example, the adjective ''wee'' is almost exclusively used in parts of Scotland, North E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tire
A tire (American English) or tyre (British English) is a ring-shaped component that surrounds a Rim (wheel), wheel's rim to transfer a vehicle's load from the axle through the wheel to the ground and to provide Traction (engineering), traction on the surface over which the wheel travels. Most tires, such as those for automobiles and bicycles, are pneumatically inflated structures, which also provide a flexible cushion that absorbs shock as the tire rolls over rough features on the surface. Tires provide a footprint, called a contact patch, that is designed to match the weight of the vehicle with the bearing strength of the surface that it rolls over by providing a bearing pressure that will not deform the surface excessively. The materials of modern pneumatic tires are synthetic rubber, natural rubber, fabric, and wire, along with carbon black and other chemical compounds. They consist of a tire tread, tread and a body. The tread provides Traction (engineering), traction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolling Stock
The term rolling stock in the rail transport industry refers to railway vehicles, including both powered and unpowered vehicles: for example, locomotives, freight and passenger cars (or coaches), and non-revenue cars. Passenger vehicles can be un-powered, or self-propelled, single or multiple units. A connected series of railway vehicles is a train (this term applied to a locomotive is a common misnomer). In North America, Australia and other countries, the term consist ( ) is used to refer to the rolling stock in a train. In the United States, the term ''rolling stock'' has been expanded from the older broadly defined "trains" to include wheeled vehicles used by businesses on roadways. The word ''stock'' in the term is used in a sense of inventory. Rolling stock is considered to be a liquid asset, or close to it, since the value of the vehicle can be readily estimated and then shipped to the buyer without much cost or delay. The term contrasts with fixed stock (infrastru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Road–rail Vehicle
A road–rail vehicle or a rail–road vehicle is a dual-mode vehicle which can operate both on rail tracks and roads. They are also known as two-way vehicles (german: Zweiwegefahrzeug), hi-rail (from ''highway'' and ''railway'', or variations such as high-rail, HiRail, Hy-rail), and rail and road vehicles. They are often converted road vehicles, keeping their normal wheels with rubber tires, but fitted with additional flanged steel wheels for running on rails. Propulsion is typically through the conventional tires, the flanged wheels being free-rolling, used to keep the vehicle on the rails; the rail wheels are raised and lowered as needed. There are also purpose-built road–rail vehicles. In case of jeep trains, road wheels are directly replaced with railway wheels. Vehicles with tires need special areas like level crossings to change modes. A vehicle on caterpillar tracks rather than road wheels, which allows mode change anywhere without the need to use a level crossing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Cruiser Hyrail Conversion
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of the planet Earth that is not submerged by the ocean or other bodies of water. It makes up 29% of Earth's surface and includes the continents and various islands. Earth's land surface is almost entirely covered by regolith, a layer of rock, soil, and minerals that forms the outer part of the crust. Land plays important roles in Earth's climate system and is involved in the carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and water cycle. One-third of land is covered in trees, 15% is used for crops, and 10% is covered in permanent snow and glaciers. Land terrain varies greatly and consists of mountains, deserts, plains, plateaus, glaciers, and other landforms. In physical geology, the land is divided into two major categories: mountain ranges and relatively flat interiors called cratons. Both are formed over millions of years through plate tectonics. A major part of Earth's water cycle, streams shape the lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
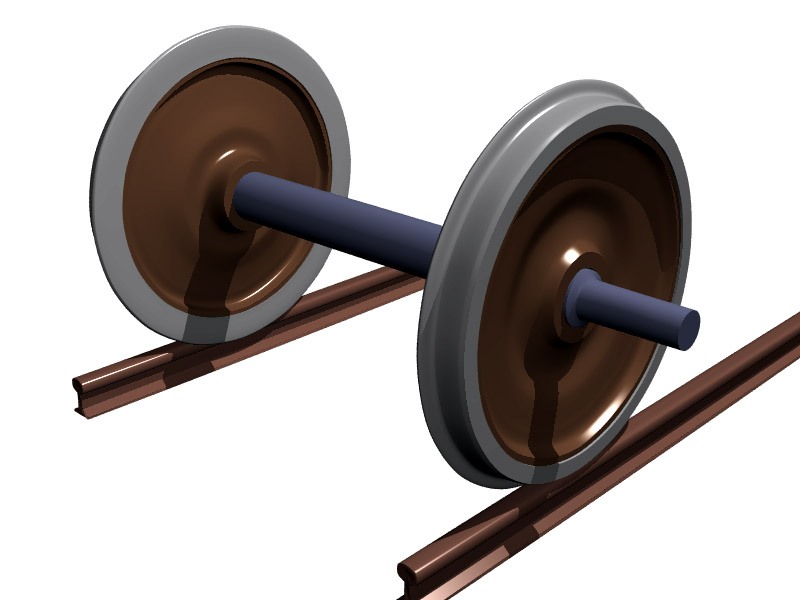
Wheelset (rail Transport)
A wheelset is a pair of railroad vehicle wheels mounted rigidly on an axle such that both wheels rotate in unison. Wheelsets are often mounted in a bogie ("truck" in North America) – a pivoted frame assembly holding at least two wheelsets – at each end of the vehicle. Most modern freight cars and passenger cars have bogies each with two wheelsets, but three wheelsets (or more) are used in bogies of freight cars that carry heavy loads, and three-wheelset bogies are under some passenger cars. Four-wheeled goods wagons that were once near-universal in Europe and Great Britain and their colonies have only two wheelsets; in recent decades such vehicles have become less common as trainloads have become heavier. Conical wheel-tread Most train wheels have a conical taper of about 1 in 20 to enable the wheelset to follow curves with less chance of the wheel flanges coming in contact with the rail sides, and to reduce curve resistance. The rails generall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunting Oscillation
Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system "hunts" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering. Railway wheelsets A classical hunting oscillation is a swaying motion of a railway vehicle (often called ''truck hunting'' or ''bogie hunting'') caused by the coning action on which the directional stability of an adhesion railway depends. It arises from the interaction of adhesion forces and inertial forces. At low speed, adhesion dominates but, as the speed increases, the adhesion forces and inertial forces become comparable in magnitude and the oscillation begins at a critical speed. Above this speed, the motion can be violent, damaging track and wheels and potentially causing derailment. The problem does not occur on systems with a differential because the action dep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flanged Wheel
A flange is a protruded ridge, lip or rim, either external or internal, that serves to increase strength (as the flange of an iron beam such as an I-beam or a T-beam); for easy attachment/transfer of contact force with another object (as the flange on the end of a pipe, steam cylinder, etc., or on the lens mount of a camera); or for stabilizing and guiding the movements of a machine or its parts (as the inside flange of a rail car or tram wheel, which keep the wheels from running off the rails). Flanges are often attached using bolts in the pattern of a bolt circle. The term "flange" is also used for a kind of tool used to form flanges. Plumbing or piping A flange can also be a plate or ring to form a rim at the end of a pipe when fastened to the pipe (for example, a closet flange). A blind flange is a plate for covering or closing the end of a pipe. A flange joint is a connection of pipes, where the connecting pieces have flanges by which the parts are bolted together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_maintenance_vehicle.jpg)


