|
Raghobadada
Raghunathrao Bhat (a.k.a. Ragho Ballal or Ragho Bharari) (18 August 1734 – 11 December 1783) was the 11th Peshwa of the Maratha Empire for a brief period from 1773 to 1774. He was known among the Hindus for his extremely successful North-western campaign of 1757-58 and for his works to liberate the Hindu holy places of Kashi and Ayodhya. Early life Raghunathrao Bhat, also known as "Raghoba", "Raghoba Dada" and "Ragho Bharari," was the younger brother of Nanasaheb Peshwa. His father was Peshwa Bajirao I & mother was Kashibai. Raghunathrao was born in Mahuli near Satara on 8 December 1734. Much of his childhood was spent in Satara. A small time after his birth, his step-mother, Mastani gave birth to his brother, Krishna Rao, also named Shamsher Bahadur I Maratha conquests In his early years he fought with great success in the north. His expedition during 1753–1755 was concluded by an advantageous treaty with the Jats. Raghunathrao imprisoned Mughal Emperor Ahmad Shah Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shivaji of the Bhonsle, Bhonsle Dynasty as the ''Chhatrapati'' (Marathi language, Marathi: "The title "Chhatrapati" was created by Shivaji upon his coronation"). Although Shivaji came from the Maratha_(caste), Maratha caste, the Maratha empire also included warriors, administrators and other notables from Maratha and several other castes from Maharashtra. They are largely credited for ending the Mughal Empire, Mughal control over the Indian subcontinent and establishing the Maratha Empire. The religious attitude of Aurangzeb, Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb estranged non-Muslims, and his inability to finish the resulting Maratha uprising after a Mughal–Maratha Wars, 27-year war at a great cost to his men and treasure, eventually ensued Maratha a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhat
Bhat (also spelled as Bhatt or Butt) is a surname in the Indian subcontinent. Bhat and Bhatt are shortened rendition of Bhatta. Etymology The word "Bhat" ( sa, भट, ) means "teacher" in Sanskrit. While the original shortened rendition of "Bhatta" was "Bhat" or "Bhatt," many of the migrants to the Punjab region started spelling their surname as "But" or "Butt" which is the spelling of the clan used in the Pahari language. Geographic distribution Goa The surname is in use among some Konkani Christians who trace their ancestry to the Goud Saraswat Brahmins of Goa.''Sarasvati's Children: A History of the Mangalorean Christians'', Alan Machado Prabhu, I.J.A. Publications, 1999, p. 137 Gujarat Hindu Bhatts who speak the Gujarati language reside in the Indian state belongs to Nagar Brahmins. Karnataka This is a common surname among the Tuluva Brahmins, Goud Saraswat Brahmins , Havyaka Brahmins and Hoysala Brahmins of Karnataka. Kashmir Bhat, also spelled as Bhatt or Butt, is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
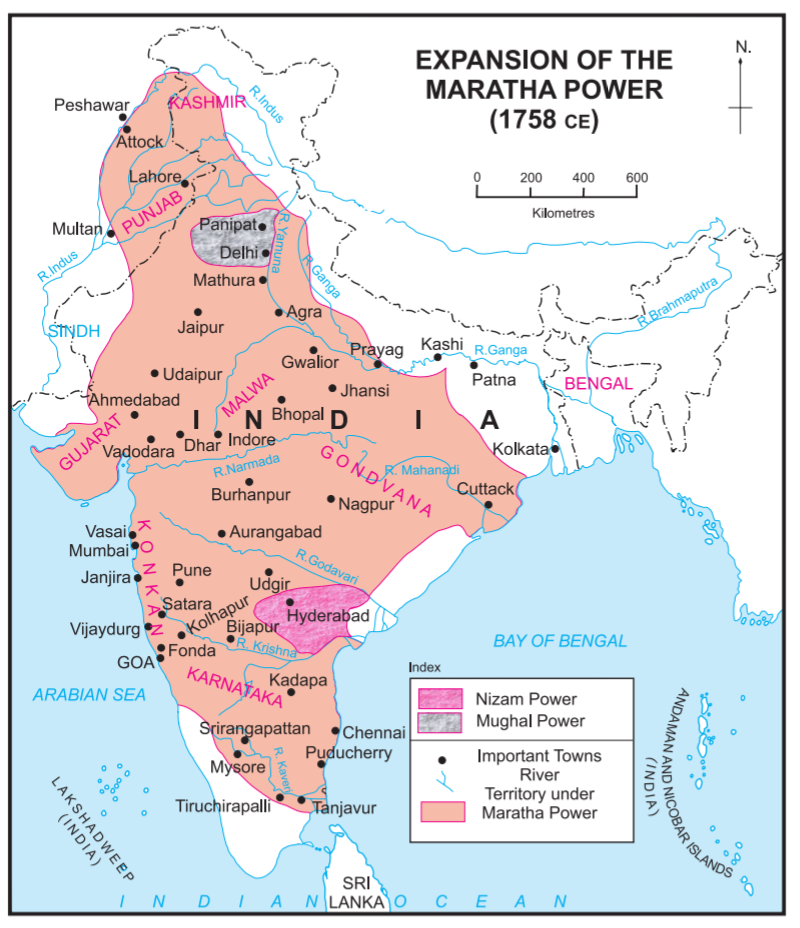
Maratha Conquest Of North-west India
The Maratha conquest of Northwest India occurred between 1757 and 1759, when the Maratha Empire captured the northwestern parts of the Indian subcontinent (in present-day Pakistan) from the Durrani Empire. It had long-lasting effects upon the future geopolitics of the Indian subcontinent. Background After the death of Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb in 1707, the Maratha War of Independence ended in Maratha victory. This was followed by the phase of rapid expansion of the Maratha Empire into North India for the next 50 years under Peshwa Baji Rao I and his brother Chimanji Appa. They conquered Gujarat, the whole of Central India and Orissa, subdued Rajputana and raided into Bengal and Tiruchirapalli in Tamil Nadu, and imposed chauth upon these areas. Their ambition pushed them further northwards than Delhi into Haryana, which collided with the ambitions of Ahmad Shah Abdali, the founder of Durrani Empire. In 1757, Ahmad Shah Abdali raided Delhi and captured Punjab and Kashmir with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adina Beg
Adina Mirza Beg Khan ( pa, ; 1710 - 15 September 1758) was a Punjabi General and administrator who served as the last governor of Punjab of the Mughal Empire, including the provinces of Lahore and Multan. He was the last Nawab of Punjab, de facto ruling Punjab as an independent ruler. Early life Named Dina at birth, Adina was born to Channu in 1710, into a Punjabi Muslim family of the Arain tribe, in the village of Sharaqpur (now in the Sheikhupura district of Punjab, Pakistan), 20 miles from Lahore. He was brought up as a worker in the homes of Mughal officials, for the most part in the Jalandhar Doab.Thomas William Beale, An Oriental Biographical Dictionary: Founded on Materials Collected by the Late Thomas William Beale, BiblioBazaar, 2010 Rise to power Adina began his career as a soldier in the Mughal army, however becoming disillusioned with his poor prospects he took up the more lucrative position of revenue collector in the village of Kang near Sultanpur. He soon cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirhind-Fategarh
Sirhind-Fategarh is a town and a municipal council in the Fatehgarh Sahib district in the Indian state of Punjab. Demographics In the 2011 census Sirhind-Fatehgarh had a population of 60852. Males constituted 54% of the population and females 46%. Sirhind-Fatehgarh had an average literacy rate of 90%, higher than the national average of 74%: male literacy is 84%, and female literacy was 80%. 12% of the population was under 6 years of age. Etymology According to popular notion, Sirhind, comes from 'Sar-i hind', meaning the Frontier of Hind, as Mughal saw it as the 'gateway to Hindustan'.Memories of a town known as Sirhind The Sunday Tribune, 15 April 2007. |
Jankoji Rao Scindia
Jankoji Rao Shinde was the third Maharaja of Gwalior State. He became Maharaja of Gwalior after death of his father, Jayappaji Rao Scindia. Biography He was younger son of Sardar Jayappaji Rao Shinde, and acceded to the position on the death of his father on 25 July 1755. As he was only 10 years of age at that time, a regency was established, led by his uncle Dattaji Rao Shinde, Jayappa Rao's brother, until 10 January 1760. Third Battle of Panipat He fought against the Afghans at the Third battle of Panipat on 14 January 1761. Jankoji with around 7,000 troops was positioned to the right of Shamsher Bahadur and was opposed to Najib Khan Rohilla. When the news spread around that Vishwas Rao has been shot dead, Jankoji and his uncle Tukoji on seeing the thinning crowd at the Maratha centre rushed to help Sadashiv Rao Bhau. Jankoji fought the Afghans who had penetrated into Maratha centre but was taken prisoner by Barkhurdar Khan secretly. Kashiraj met Jankoji secretly in a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dattaji Rao Scindia
Dattaji Rao Scindia, also known as Dattaji Rao Shinde, (1723 – 10 January 1760) was the second son of Ranoji Rao Shinde and Maina Bai, alias Nimba Bai. His elder brother was Jayappaji Rao Shinde and his younger brother was Jyotiba. Early life He was the elder half-brother of Mahadaji Shinde who later became the confederacy head of Gwalior, and regent for his nephew Jankoji Rao Shinde from 1755 until his death. Battle with Afghans and death Dattaji Shinde was a Maratha military general who was given the command of Punjab during the Afghan-Maratha Conflicts over the regions of North India in 1758–59. The Peshwa gave him command of Punjab contingents with an army of 18,000 men to stop the Afghan Invasion led by Ahmed Shah Durrani. Marathas won the forts of Attock and Peshawar in 1757–1758 and wanted to expand their rule up to Kandahar. After many centuries had Hindu rule come in Punjab and Indus River since 1020, when Mahmud of Ghazni had defeated the Hindu ruler Triloc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malharrao Holkar
Malhar Rao Holkar (16 March 1693 – 20 May 1766) was a noble subedar of the Maratha Empire, in present-day India. He was one of the early officers along with Ranoji Scindia to help spread the Maratha rule to northern states and was given the estate of Indore to rule by the Peshwas, during the reign of the Maratha emperor Shahu I. He was founder of the Holkar dynasty that ruled Malwa. Early life Malhar Rao Holkar was from the Dhangar(Sheepherder) community. He was born on 16 March 1693 in the village of Hol, near Jejuri, Pune District to Khanduji Holkar of Vir. His father died in 1696, when he was only three years of age. Malhar Rao grew up in Taloda (Nandurbar District, Maharashtra) in the castle of his maternal uncle, Sardar Bhojrajrao Bargal. His maternal uncle held a cavalry under Maratha noble Sardar Kadam Bande. Bargal asked Malhar Rao to join his cavalry and soon after that he was placed in-charge of cavalry detachment. He married Gautama Bai Bargal (d. 29 September 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran border, west, Turkmenistan to the Afghanistan–Turkmenistan border, northwest, Uzbekistan to the Afghanistan–Uzbekistan border, north, Tajikistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, northeast, and China to the Afghanistan–China border, northeast and east. Occupying of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains Afghan Turkestan, in the north and Sistan Basin, the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. , Demographics of Afghanistan, its population is 40.2 million (officially estimated to be 32.9 million), composed mostly of ethnic Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras, and Uzbeks. Kabul is the country's largest city and ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmad Shah Durrani
Ahmad Shāh Durrānī ( ps, احمد شاه دراني; prs, احمد شاه درانی), also known as Ahmad Shāh Abdālī (), was the founder of the Durrani Empire and is regarded as the founder of the modern Afghanistan. In July 1747, Ahmad Shah was appointed as King of the Afghans by a ''loya jirga'' in Kandahar, where he set up his capital. Primarily with the support of the Pashtun tribes, Ahmad Shah pushed east towards the Mughal and Maratha Empires of India, west towards the disintegrating Afsharid Empire of Iran, and north towards the Khanate of Bukhara of Turkestan. Within a few years, he extended his control from Khorasan in the west to North India in the east, and from the Amu Darya in the north to the Arabian Sea in the south. Soon after accession, Ahmad Shah adopted the epithet ''Shāh Durr-i-Durrān'', "King, Pearl of Pearls", and changed the name of his Abdali tribe to "Durrani" after himself. The Tomb of Ahmad Shah Durrani is located in the center of Kan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alamgir II
Aziz-ud-Din Muhammad (6 June 1699 – 29 November 1759), better known as Alamgir II, was the fifteenth Mughal Emperor of India, who reigned from 3 June 1754 to 29 November 1759. He was the son of Jahandar Shah. Born Aziz-ud-Din, the second son of Jahandar Shah, was raised to the throne by Imad-ul-Mulk after he deposed Ahmad Shah Bahadur in 1754. On ascending the throne, he took the title of Alamgir and tried to follow the approach of Aurangzeb (Alamgir I). At the time of his accession to throne he was an old man of 55 years. He had no experience of administration and warfare as he had spent most of his life in jail. He was a weak ruler, with all powers vested in the hand of his vizier, Imad-ul-Mulk. In 1756, Ahmad Shah Durrani invaded India once again and captured Delhi and plundered Mathura. Marathas became more powerful because of their collaboration with Imad-ul-Mulk, and dominated the whole of northern India. This was the peak of Maratha expansion, which caused great trou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmad Shah Bahadur
Ahmad Shah Bahadur , also known as Mirza Ahmad Shah or Mujahid-ud-Din Ahmad Shah Ghazi (23 December 1725 – 1775 AD), was the fourteenth Mughal Emperor, born to Emperor Muhammad Shah. He succeeded his father to the throne in 1748, at the age of 22. When Ahmed Shah Bahadur came to power, ( 1748–1754) the Mughal Empire was collapsing. Furthermore, his administrative weakness eventually led to the rise of the usurping Imad-ul-Mulk. As a Prince, he defeated Ahmed Shah Abdali in the Battle of Manupur in 1748, Ahmed Shah Bahadur inherited a much weakened Mughal state as emperor for six years, but left all affairs of state to rivalling factions. He was deposed by the Vizier Imad-ul-Mulk and later blinded along with his mother. He spent the remaining years of his life in prison and died in 1775 CE. Early life Prince Ahmad was born in 1725 to the Mughal Emperor Muhammad Shah and his consort Qudsia Begum. Decentralization during his father's reign, the Maratha Wars and the blow fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)