|
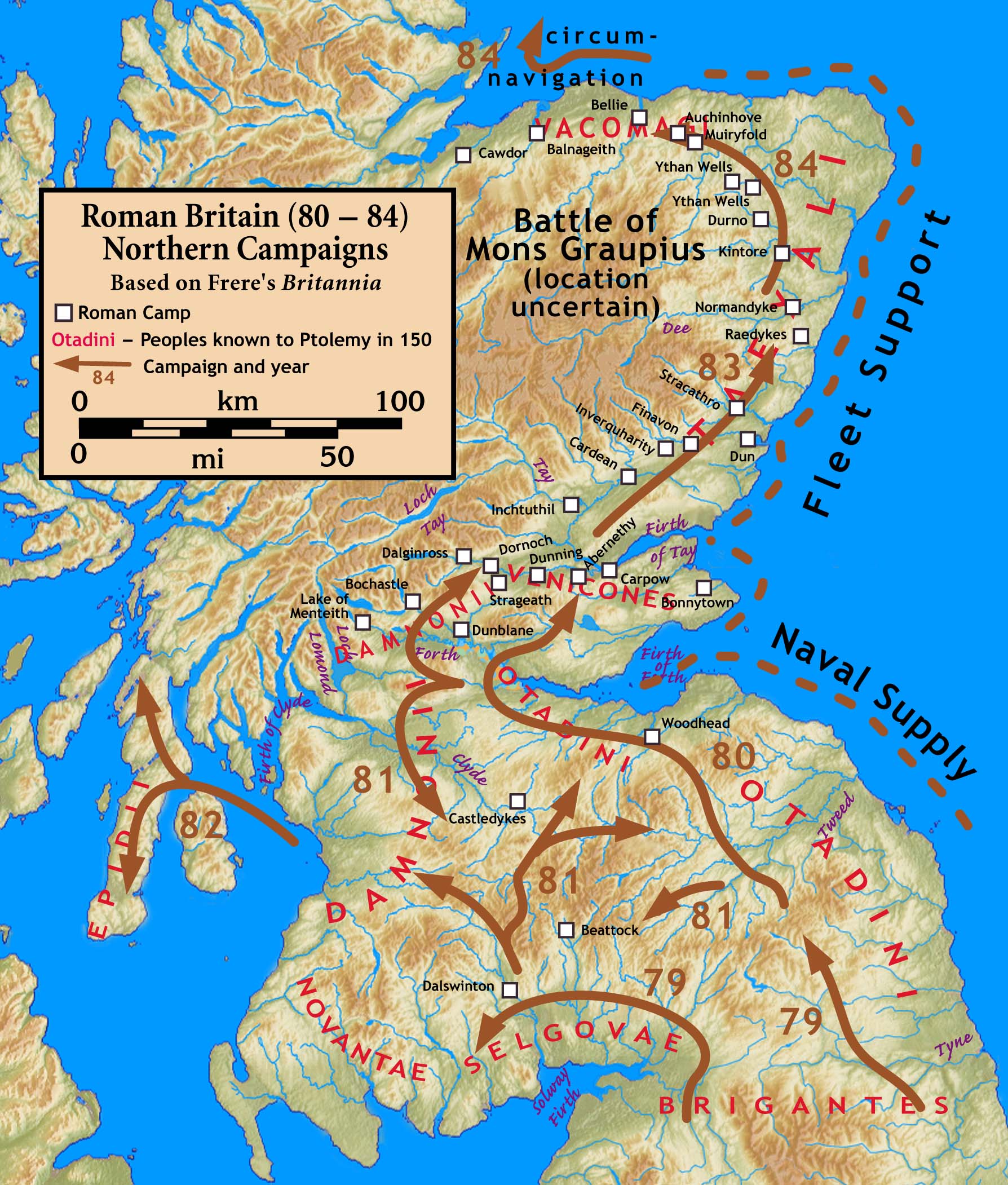
Raedykes
Raedykes is the site of a Roman marching camp located just over northwest of Stonehaven, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. National Grid Reference NO 842902. It is designated as a scheduled monument. A marching camp was a temporary camp used mainly for overnight stops on a long route between more permanent forts, or as a temporary base while on campaign in hostile territory. The site Raedykes probably dates from the late 1st century AD ( Agricolan), though it has been argued that it could be Antonine (2nd century) or Severan (early 3rd century). The camp rampart (vallum) encloses the summit and eastern slopes of Garrison Hill (), a prominent spur overlooking the valley of the Cowie Water, a small river draining into the North Sea on the outskirts of Stonehaven. The camp covered an area of about , and a computer model suggests that this would have been sufficient to house three full legions, or around 16,000 troopsRoger J.A.Wilson "A Guide to the Roman Remains in Britain" 2002 Cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stracathro
Stracathro ( gd, Srath Catharach) is a small place in Angus, Scotland. It was the site of a Roman marching camp as their forces invaded to the north. Location Stracathro is located southeast of Edzell in north-east Angus. It lies to the north-east of Brechin on the A90. History A Roman marching camp has been discovered at Stracathro. This camp is one day's march from the next camp, at Raedykes to the north. The gate design of the Stracathro Roman Camp is a distinctive bell-shaped indentation of the rampart perimeter. Stracathro was the site of the Battle of Stracathro in 1130. This was the culmination of an invasion into southern Scotland led by Angus, ruler of the partially independent "kingdom" of Moray. He wanted to expand his territory and obtain recognition as a ruler independent of the Scottish kings. Angus was met by the royal army, led by the Constable of Scotland in the absence of King David, who had pressing business in England. The result was a decisive victory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normandykes
Normandykes (Grid Reference: NO 830994) is the site of a Roman marching camp to the southwest of Peterculter, City of Aberdeen, Scotland. The near-rectangular site, measuring approximately , covers about of the summit and eastern slopes of a hill overlooking the River Dee and the B9077 road further south. Aerial photographs for Normandykes have been archived between 1947 and 1976. The camp is about , or less than half a day's march, north of the Raedykes camp. It is possible that the actual route taken would have entailed one day's march, over a route likely chosen to avoid the Red Moss, a virtually uncrossable bog near the present day village of Netherley. Normandykes was first excavated in the year 1935 by Richmond and MacIntyre; construction is thought to date to the Antonine or Severan periods. The site is designated a scheduled ancient monument. See also * Raedykes * Balbridie * Crynoch Burn * Deers Den * Glenmailen * Leuchar Burn * Maryculter House * Ythan Wells * Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenmailen
Ythan Wells, also known as Glenmailen, is the site of a Roman military camp, near the farm of Glenmellan, east of the village of Ythanwells in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The site is a designated scheduled monument. Traces of two marching camps have been found at the site. The larger camp, covering some was discovered in 1785 by Col. Alex Shand. A smaller camp, extending to and partially overlapping the area of the first, was discovered by J. K. St Joseph in 1968. This smaller camp predates the larger and has been dated to the campaigns of Agricola. The site is situated at the headwaters of the River Ythan, where a series of natural springs supplies potable water, that was convenient for the large marching camp installed here by the Romans in the first few centuries AD. The Roman legions established a chain of very large forts at Ardoch, Strageath, Inchtuthil, Battledykes, Stracathro and Raedykes, taking the Elsick Mounth on the way to Normandykes, then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battledykes
Battledykes is a Roman camp slightly to the north of Forfar, Scotland. According to Hector Boece, Pictish chiefs met at a castle by Forfar Loch to plan how to repel the Roman armies, who invaded several times between the 1st and 4th centuries AD. Eventually, the better equipped Romans prevailed, later to be displaced again by the Picts. The Romans established a Roman Camp at Battledykes, approximately three miles north of Forfar; this camp was assessed to have held 50,000 to 60,000 men. From Battledykes northward the Romans established a succession of camps including Stracathro, Raedykes and Normandykes.C Michael Hogan, ''The history of Muchalls Castle Muchalls Castle stands overlooking the North Sea in the countryside of Kincardine and Mearns, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The lower course is a well-preserved Romanesque, double-groined 13th-century tower house structure, built by the Frasers of ...'', Lumina Technologies Press, Aberdeen, Scotland (2005) Line notes External ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kempstone Hill
Kempstone Hill is a landform in Aberdeenshire, Scotland within the Mounth Range of the Grampian Mountains. The peak elevation of this mountain is 132 metres above mean sea level. This hill has been posited by Gabriel Jacques Surenne, Archibald Watt and C.Michael Hogan as the location for the noted Battle of Mons Graupius between the Romans and the indigenous Caledonians. The major Roman Camp of Raedykes is situated about three kilometres to the west. From Kempstone Hill there are fine views to the North Sea facing east and slightly to the north of Muchalls Castle. There is a UK trigpoint installation on Kempstone Hill. Geology and hydrology Kempstone Hill is situated approximately 2.3 kilometers to the north of Stonehaven; surface runoff and drainage from the northern and eastern slopes of Kempstone Hill flow north to the Burn of Muchalls. Surface runoff from the south and west flanks flow to the Burn of Monboys, a very slightly alkaline stream These low pH levels (compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberdeenshire
Aberdeenshire ( sco, Aiberdeenshire; gd, Siorrachd Obar Dheathain) is one of the 32 Subdivisions of Scotland#council areas of Scotland, council areas of Scotland. It takes its name from the County of Aberdeen which has substantially different boundaries. The Aberdeenshire Council area includes all of the area of the Counties of Scotland, historic counties of Aberdeenshire and Kincardineshire (except the area making up the City of Aberdeen), as well as part of Banffshire. The county boundaries are officially used for a few purposes, namely land registration and Lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy. Aberdeenshire Council is headquartered at Woodhill House, in Aberdeen, making it the only Scottish council whose headquarters are located outside its jurisdiction. Aberdeen itself forms a different council area (Aberdeen City). Aberdeenshire borders onto Angus, Scotland, Angus and Perth and Kinross to the south, Highland (council area), Highland and Moray to the west and Aber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muchalls Castle
Muchalls Castle stands overlooking the North Sea in the countryside of Kincardine and Mearns, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The lower course is a well-preserved Romanesque, double-groined 13th-century tower house structure, built by the Frasers of Muchalls. Upon this structure, the 17th-century castle was begun by Alexander Burnett of Leys and completed by his son, Sir Thomas Burnett, 1st Baronet, in 1627. The Burnetts of Leys built the remaining four-storey present-day castle. One of the most interesting castles of North-East Scotland, according to noted architectural historian Nigel Tranter, it is designed in the classic L style with a further extension wing at the west end. Muchalls Castle entered national history in 1638 when a seminal Covenanter gathering took place here precedent to the English Civil War. The plasterwork ceilings of the principal drawing rooms are generally regarded as among the three finest examples of plasterwork ceilings in Scotland. These adornments date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetteresso Castle
Fetteresso Castle is a 14th-century tower house, rebuilt in 1761 as a Scottish Gothic style Palladian manor, with clear evidence of prehistoric use of the site. It is situated immediately west of the town of Stonehaven in Kincardineshire, slightly to the west of the A90 dual carriageway. Other notable historic fortified houses or castles in this region are Dunnottar Castle, Muchalls Castle, Fiddes Castle, Cowie Castle and Monboddo House. Prehistory From cropmarks in the "policies" (improved areas) around Fetteresso Castle, there is evidence of a ring ditch sited at the north end of a cursus. A cursus is a prehistoric set of parallel linear structures of unknown purpose that were, somewhat fancifully, considered by antiquarians as used for some type of athletic competition, possibly related to hunting or archery; this is unsubstantiated. In 1822 a cairn was discovered near Fetteresso Castle with some human remains inside. The size and shape of the chamber made of unhewn whins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnaeus Julius Agricola
Gnaeus Julius Agricola (; 13 June 40 – 23 August 93) was a Roman general and politician responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain. Born to a political family of senatorial rank, Agricola began his military career as a military tribune under Governor Gaius Suetonius Paulinus. In his subsequent career, he served in a variety of political positions in Rome. In 64, he was appointed quaestor in Asia (Roman province), Asia province. Two years later, he was appointed Plebeian Tribune, and in 68, he was made praetor. During the Year of the Four Emperors in 69, he supported Vespasian, general of the Roman Syria, Syrian army, in his bid for the throne. When Vespasian became Roman emperor, emperor, Agricola was made a Patrician (ancient Rome), patrician and appointed governor of Gallia Aquitania. In 77, he was made Roman consul, consul and Governor of Roman Britain, governor of Britannia. As governor, he completed the conquest of what is today Wales and northern England, and le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strageath
Strageath is a Roman camp near the River Earn in eastern Scotland. Strageath was one of a chain of camps that the Romans used in their march northward. Other notable camps in this chain are Ardoch, Battledykes, Stracathro, Raedykes and Normandykes. In the Middle Ages the parish church of ''Strogeath'' lay within the area of the fort. The dedication was to St. Patrick ST, St, or St. may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Stanza, in poetry * Suicidal Tendencies, an American heavy metal/hardcore punk band * Star Trek, a science-fiction media franchise * Summa Theologica, a compendium of Catholic philosophy an .... The site is marked by a graveyard, and some scant remains of the church building. Footnotes Roman fortified camps in Scotland Scheduled monuments in Scotland Roman auxiliary forts in Scotland {{AncientRome-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Mons Graupius
The Battle of Mons Graupius was, according to Tacitus, a Roman military victory in what is now Scotland, taking place in AD 83 or, less probably, 84. The exact location of the battle is a matter of debate. Historians have long questioned some details of Tacitus's account of the fight, suggesting that he exaggerated Roman success. Background Tacitus states that Gnaeus Julius Agricola, who was the Roman governor and Tacitus's father-in-law, had sent his fleet ahead to panic the Caledonians, and, with light infantry reinforced with British auxiliaries, reached the site, which he found occupied by the enemy. Even though the Romans were outnumbered in their campaign against the tribes of Britain, they often had difficulties in getting their foes to face them in open battle. The Caledonii were the last unconquered British tribe (and were never fully subdued). After many years of avoiding the fight, the Caledonians were forced to join battle when the Romans marched on the main gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardoch Fort
Ardoch Roman Fort is an archaeological site just outside the village of Braco, Perth and Kinross, Braco in Perthshire, Scotland, about south of Crieff. At Ardoch are the remains of a castra, Roman fort and several marching camps which included a signal tower. Part of the Roman Gask Ridge, it is said to be one of the most complete Roman camps in Britain, and is one of the best-preserved series of Roman military earthworks in the whole Empire. It is protected as a scheduled monument. Description The remains consist of grass-covered earthworks, and are considered among the best preserved Roman earthworks in Britain.David John Breeze, (2002), ''Roman Forts in Britain'', page 60. The site, which has a complex history, comprises two intersecting forts. The earliest fort is believed to be associated with the campaigns of Gnaeus Julius Agricola, Agricola (1st century). The later fort was apparently reconstructed within two outer ditches so that this later fort was protected by five dit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |