|
Radymno
Radymno ( uk, Ради́мно ''Radymno'', yi, רעדעם ''Redem'') is a town in south-eastern Poland with 5,543 inhabitants (02.06.2009). It has been part of the Podkarpackie Voivodeship since its creation in 1999. Radymno was previously in the Przemyśl Voivodeship from 1975–1998. History First traces of human settlement in what today is Radymno date back to the Neolithic times, as in 1958, archaeologists found remains of a 2nd-century settlement. In early Middle Ages, the area was part of Polish state, but in 981, it was seized by Kievan Rus'. The area was then regained and lost by Poland two more times. In the mid-13th century it fell under Mongol suzerainty, and afterwards it was eventually recaptured by Polish King Casimir III the Great in mid-14th century. In 1366, a nobleman Bernard of Szynwałd received permission from Casimir III to establish a settlement in the fields. In 1384, Radymno was presented to the Bishops of Przemyśl, and in 1431 King Władysław I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jarosław County
__NOTOC__ Jarosław County ( pl, powiat jarosławski) is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland, on the border with Ukraine. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Jarosław, which lies east of the regional capital Rzeszów. The only other towns in the county are Radymno, lying south-east of Jarosław, and Pruchnik (a town since 2011). The county covers an area of . As of 2019 its total population was 120,462, out of which the population of Jarosław was 37,585, that of Radymno was 5,279, that of Próchnik was 3,764, and the rural population was 73,834. Neighbouring counties Jarosław County is bordered by Przemyśl County to the south, Przeworsk County to the west and Lubaczów County to the east. It also borders Ukraine to the east. Administrative division The county is subdivided into 11 g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podkarpackie Voivodeship
Subcarpathian Voivodeship or Subcarpathia Province (in pl, Województwo podkarpackie ) is a voivodeship, or province, in the southeastern corner of Poland. Its administrative capital and largest city is Rzeszów. Along with the Marshall, it is governed by the Subcarpathian Regional Assembly. Historically, most of the province's territory was part of the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria and the Ruthenian Voivodeship. In the interwar period, it was part of the Lwów Voivodeship. The voivodeship was created on 1 January 1999 out of the former Rzeszów, Przemyśl, Krosno and (partially) Tarnów and Tarnobrzeg Voivodeships, pursuant to the Polish local-government reforms adopted in 1998. The name derives from the region's location near the Carpathian Mountains, and the voivodeship comprises areas of two historic regions of Eastern Europe — Lesser Poland (western and northwestern counties) and Red Ruthenia. During the interwar period (1918-1939) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcarpathian Voivodeship
Subcarpathian Voivodeship or Subcarpathia Province (in pl, Województwo podkarpackie ) is a voivodeship, or province, in the southeastern corner of Poland. Its administrative capital and largest city is Rzeszów. Along with the Marshall, it is governed by the Subcarpathian Regional Assembly. Historically, most of the province's territory was part of the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria and the Ruthenian Voivodeship. In the interwar period, it was part of the Lwów Voivodeship. The voivodeship was created on 1 January 1999 out of the former Rzeszów, Przemyśl, Krosno and (partially) Tarnów and Tarnobrzeg Voivodeships, pursuant to the Polish local-government reforms adopted in 1998. The name derives from the region's location near the Carpathian Mountains, and the voivodeship comprises areas of two historic regions of Eastern Europe — Lesser Poland (western and northwestern counties) and Red Ruthenia. During the interwar period (1918-1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San (river)
The San ( pl, San; uk, Сян ''Sian''; german: Saan) is a river in southeastern Poland and western Ukraine, a tributary of the river Vistula, with a length of (it is the 6th-longest Polish river) and a basin area of 16,877 km2 (14,426 km2 of it in Poland). Etymology in proto-Indo-European languages means 'speed' or 'rapid stream'. In Celtic languages, means 'river'. Course The San arises in the Carpathian Mountains near the village of Sianky, at an elevation of , exactly on the Polish-Ukrainian border () and on the continental watershed, and forms the border between Poland and Ukraine for approximately its first . Poland's largest artificial lake, Lake Solina, was created by a dam on the San River near Lesko. Tributaries History of the region Historical records first mention the river in 1097 as ''Sanъ'', ''reku Sanъ'', ''k Sanovi''; then as ''nad Sanomъ'' (1152) and ''Sanu'' (1287). On the old maps of the Ruthenian Voivodeship, Poland 1339–177 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivodeships Of Poland
A voivodeship (; pl, województwo ; plural: ) is the highest-level administrative division of Poland, corresponding to a province in many other countries. The term has been in use since the 14th century and is commonly translated into English as "province". The Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998, which went into effect on 1 January 1999, created sixteen new voivodeships. These replaced the 49 former voivodeships that had existed from 1 July 1975, and bear a greater resemblance (in territory, but not in name) to the voivodeships that existed between 1950 and 1975. Today's voivodeships are mostly named after historical and geographical regions, while those prior to 1998 generally took their names from the cities on which they were centered. The new units range in area from under (Opole Voivodeship) to over (Masovian Voivodeship), and in population from nearly one million (Opole Voivodeship) to over five million (Masovian Voivodeship). Administrative authority at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Władysław II Jagiełło
Jogaila (; 1 June 1434), later Władysław II Jagiełło ()He is known under a number of names: lt, Jogaila Algirdaitis; pl, Władysław II Jagiełło; be, Jahajła (Ягайла). See also: Names and titles of Władysław II Jagiełło. was Grand Duke of Lithuania (1377–1434) and then King of Poland (1386–1434), first alongside his wife Jadwiga until 1399, and then sole ruler of Poland. Born a pagan, he converted to Catholicism in 1386 and was baptized as Władysław in Kraków, married the young Queen Jadwiga, and was crowned King of Poland as Władysław II Jagiełło. In 1387, he converted Lithuania to Catholicism. His own reign in Poland started in 1399, upon the death of Queen Jadwiga, lasted a further thirty-five years, and laid the foundation for the centuries-long Polish–Lithuanian union. He was a member of the Jagiellonian dynasty in Poland that bears his name and was previously also known as the Gediminid dynasty in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The dynast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vlachs
"Vlach" ( or ), also "Wallachian" (and many other variants), is a historical term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate mainly Romanians but also Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, Istro-Romanians and other Eastern Romance-speaking subgroups of Central and Eastern Europe. As a contemporary term, in the English language, the Vlachs are the Balkan Romance-speaking peoples who live south of the Danube in what are now southern Albania, Bulgaria, northern Greece, North Macedonia, and eastern Serbia as native ethnic groups, such as the Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians and the Timok Romanians. The term also became a synonym in the Balkans for the social category of shepherds, and was also used for non-Romance-speaking peoples, in recent times in the western Balkans derogatively. The term is also used to refer to the ethnographic group of Moravian Vlachs who speak a Slavic language but originate from Romanians. "Vlachs" were initially identified and des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
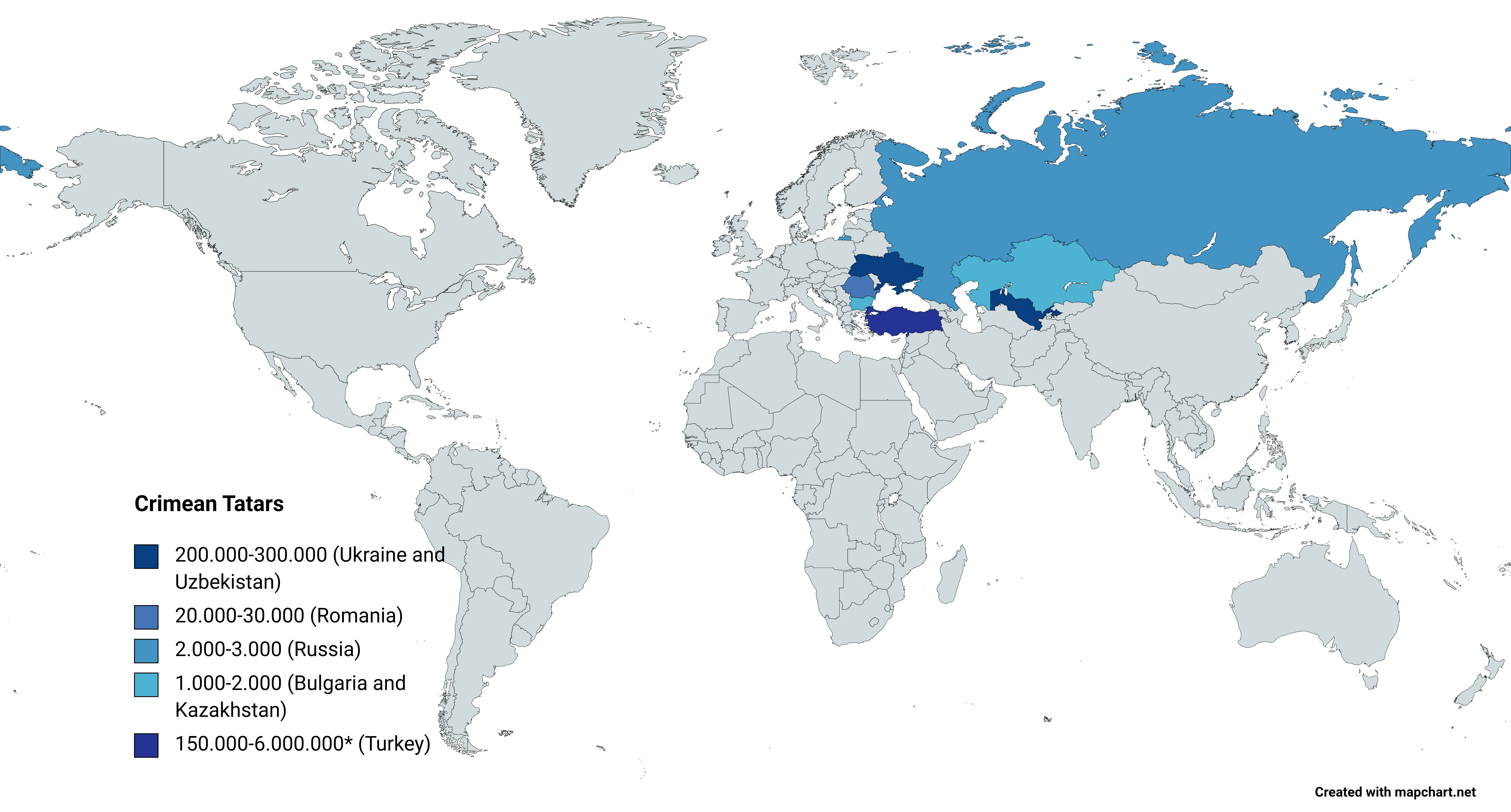
Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg , flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars , image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg , caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace , poptime = , popplace = , region1 = , pop1 = 3,500,000 6,000,000 , ref1 = , region2 = * , pop2 = 248,193 , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 239,000 , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 24,137 , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 2,449 , ref5 = , region7 = , pop7 = 1,803 , ref7 = , region8 = , pop8 = 1,532 , ref8 = , region9 = *() , pop9 = 7,000(500–1,000) , ref9 = , region10 = Total , pop10 = 4.024.114 (or 6.524.11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deluge (history)
The Deluge ( pl, potop szwedzki, lt, švedų tvanas) was a series of mid-17th-century military campaigns in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In a wider sense it applies to the period between the Khmelnytsky Uprising of 1648 and the Truce of Andrusovo in 1667, thus comprising the Polish theatres of the Russo-Polish War (1654–1667), Russo-Polish and Second Northern Wars. In a stricter sense, the term refers to the Swedish Empire, Swedish invasion and occupation of the Commonwealth as a theatre of the Second Northern War (1655–1660) only; in Poland and Lithuania this period is called the Swedish Deluge ( pl, potop szwedzki, sv, Svenska syndafloden), or less commonly the Russo–Swedish Deluge ( pl, Potop szwedzko-rosyjski) due to the simultaneous Russo-Polish War (1654–1667), Russo-Polish War. The term "deluge" (''potop'' in Polish) was popularized by Henryk Sienkiewicz in his novel ''The Deluge (novel), The Deluge'' (1886). During the wars the Commonwealth lost approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanisław Jan Jabłonowski
Prince Stanisław Jan Jabłonowski (1634–1702) was a Polish nobleman, magnate, Grand Guardian of the Crown since 1660, the Grand Camp Leader of the Crown since 1661, voivode of the Ruthenian Voivodship since 1664, Field Crown Hetman since 1676, Great Crown Hetman since 1683 and castellan of Kraków since 1692. Jabłonowski was a candidate for the Polish Throne following the death of King John III Sobieski. A talented and skillful political and military leader, Jabłonowski participated in the War with Sweden during The Deluge, then with the Cossacks and Muscovy. He took part in the Chocim campaign of 1673 and participated in the Vienna expedition of 1683. He led the right wing of Polish cavalry forces at the Battle of Vienna. He also stopped the Tatars at Lwów in 1695. In 1692 Jabłonowski built the stronghold and the neighbouring town of Okopy Świętej Trójcy. During the Royal election of 1697, he supported Augustus II, later in opposition to the King. In 1698, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hetmans Of The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
Hetmans of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth were the highest-ranking military officers, second only to the King, in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The first Polish title of Grand Crown Hetman was created in 1505. The title of hetman was given to the leader of the Polish Army and until 1581 it was awarded only for a specific campaign or war. Later it became a permanent title, as did all the titles in the Kingdom of Poland and Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It could not be revoked unless treachery had been proven (from 1585). Hetmans were not paid for their services by the Royal Treasury. Field and Great Hetmans From the end of 16th century there were two hetmans in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and two hetmans in the Crown: a Field Hetman and a Great Hetman (sometimes translated as Grand Hetman). As a result, there were in total four hetman titles: Great Crown Hetman, Field Crown Hetman, Great Lithuanian Hetman and Field Lithuanian Hetman. During joint milit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szynwałd, Lesser Poland Voivodeship
Szynwałd is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Skrzyszów, within Tarnów County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, in southern Poland. It lies approximately south-east of Tarnów and east of the regional capital Kraków Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 .... The village has a population of 3,000. References Villages in Tarnów County {{Tarnów-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

_in_1655.png)
