|
Radbod (prefect)
Radbod ( 833–54) was the East Frankish prefect of the Eastern March (''marcha orientalis''), the Bavarian frontier towards the Slavs, appointed in 833. He had been appointed the office after Louis the German's conquest in 828, and subsequent Christianization of the Moravians (828–33). In 833, according to the ''Conversio Bagoariorum et Carantanorum'', a Slavic prince, Pribina, had been "driven across the Danube by Mojmir, duke of the Moravians", and fled to Radbod in East Francia around 833. Radbod introduced him to King Louis the German, who ordered that Pribina should be "instructed in the faith and baptized", and that he serve with his followers in Radbod's army. Before long, however, Radbod and Pribina fell out, and the latter, fearing for his life, fled with his son Koceľ to the First Bulgarian Empire, and then to Lower Pannonia ruled by a Slavic duke, Ratimir. Since Lower Pannonia was part of Radbod's prefecture, Ratimir's harboring of Pribina was tantamount to rebelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carloman Of Bavaria
Carloman (german: Karlmann, la, Karlomannus; c. 830 – 22 March 880) was a Frankish king of the Carolingian dynasty. He was the eldest son of Louis the German, king of East Francia, and Hemma, daughter of a Bavarian count. His father appointed him governor of Carantania in 856, and commander of southeastern frontier marches in 864. Upon his father's death in 876 he became King of Bavaria. He was appointed by King Louis II of Italy as his successor, but the Kingdom of Italy was taken by his uncle Charles the Bald in 875. Carloman only conquered it in 877. In 879 he was incapacitated, perhaps by a stroke, and abdicated his domains in favour of his younger brothers: Bavaria to Louis the Younger and Italy to Charles the Fat. Early life Carloman's birth date is unknown, but was probably around 828 or 830. His naming can be connected to his father's push to rule Alemannia around the time of his father's assembly of Worms in 829. The first member of the Carolingian dynasty named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March Of Carniola
The March (or Margraviate) of Carniola ( sl, Kranjska krajina; german: Mark Krain) was a southeastern Imperial State, state of the Holy Roman Empire in the High Middle Ages, the predecessor of the Duchy of Carniola. It corresponded roughly to the central Carniolan region of present-day Slovenia. At the time of its creation, the March (territorial entity), march served as a frontier defense against the Kingdoms of Kingdom of Hungary (1000–1301), Hungary and Kingdom of Croatia (925–1102), Croatia. History Before the coming of the Romans (c. 200 BC), the Taurisci dwelt in the north of Carniola, the Pannonians in the south-east, the Iapodes or Carni, a Celtic tribe, in the south-west. Carniola formed part of the Roman province of Pannonia; the northern part was joined to Noricum, the south-western and south-eastern parts and the city of Aemona to Venice and Istria. In the time of Augustus all the region from Aemona to Kolpa river belonged to the province of Pannonia Savia, Savia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Peoples
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic language, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, mainly inhabiting Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe, and the Balkans to the west; and Siberia to the east. A large Slavic minority is also scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, while a substantial Slavic diaspora is found throughout the Americas, as a result of immigration. Present-day Slavs are classified into East Slavs (chiefly Belarusians, Russians, Rusyns, and Ukrainians), West Slavs (chiefly Czechs, Kashubians, Poles, Slovaks and Sorbs) and South Slavs (chiefly Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes). The vast majority of Slavs are traditionally Christians. However, modern Slavic nations and ethnic groups are considerably dive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe. Etymology Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not completely understood and difficult to trace back earlier than the 4th century AD, but it is possibly derived from the Proto-Turkic word ''*bulģha'' ("to mix", "shake", "stir") and its derivative ''*bulgak'' ("revolt", "disorder"). Alternative etymologies include derivation from a compound of Proto-Turkic (Oghuric) ''*bel'' ("five") and ''*gur'' ("arrow" in the sense of "tribe"), a proposed division within the Utigurs or Onogurs ("ten tribes"). Citizenship According to the Art.25 (1) of Constitution of Bulgaria, a Bulgarian citizen shall be anyone born to at least one parent holding a Bulgarian citizenship, or born on the territory of the Republic of Bulgaria, should they not be entitled to any other citizenship by virtue of origin. Bulgarian citizenship sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
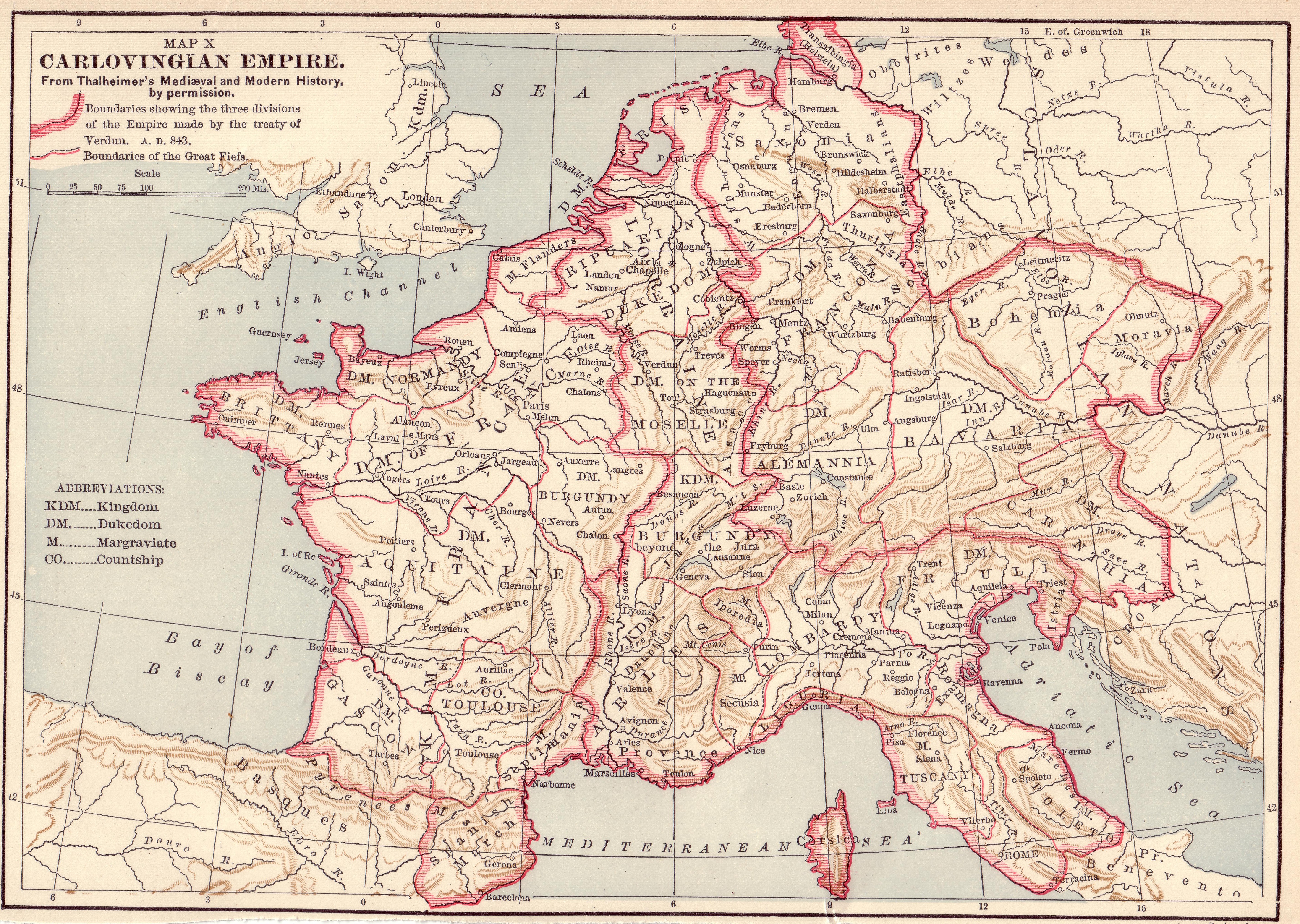
West Francia
In medieval history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from about 840 until 987. West Francia emerged from the partition of the Carolingian Empire in 843 under the Treaty of Verdun following the death of Charlemagne's son, Louis the Pious. It is considered the first polity in French history. West Francia extended further north and south than modern metropolitan France, but it did not extend as far east. It did not include such future French holdings as Lorraine, the County and Kingdom of Burgundy (the duchy was already a part of West Francia), Alsace and Provence in the east and southeast for example. It also did not include the Brittany peninsula in the west. In addition, by the 10th century the authority of the West Frankish monarchs was greatly reduced. This was contrasted by the evergrowing power of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles The Bald
Charles the Bald (french: Charles le Chauve; 13 June 823 – 6 October 877), also known as Charles II, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), king of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a series of civil wars during the reign of his father, Louis the Pious, Charles succeeded, by the Treaty of Verdun (843), in acquiring the western third of the empire. He was a grandson of Charlemagne and the youngest son of Louis the Pious by his second wife, Judith. Struggle against his brothers He was born on 13 June 823 in Frankfurt, when his elder brothers were already adults and had been assigned their own ''regna'', or subkingdoms, by their father. The attempts made by Louis the Pious to assign Charles a subkingdom, first Alemannia and then the country between the Meuse and the Pyrenees (in 832, after the rising of Pepin I of Aquitaine) were unsuccessful. The numerous reconciliations with the rebellious Lothair and Pepin, as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annales Bertiniani
''Annales Bertiniani'' (''Annals of Saint Bertin'') are late Carolingian, Frankish annals that were found in the Abbey of Saint Bertin, Saint-Omer, France, after which they are named. Their account is taken to cover the period 830-82, thus continuing the Royal Frankish Annals (741–829), from which, however, it has circulated independently in only one manuscript. They are available in the ''Monumenta Germaniæ Historica'' and in a later French edition taking into account a newly discovered manuscript . The ''Annals of St. Bertin'' are one of the principal sources of ninth-century Francia, and are particularly well-informed on events in the West Frankish sphere of Charles the Bald. The ''Annales Fuldenses'' are usually read as an East Frankish counterpart to their narrative. Authorship and manuscripts It has been suggested that the annals were first written by scribes in the court of Louis the Pious. There is no doubt that they were later continued as an independent narrative, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Moravia
Great Moravia ( la, Regnum Marahensium; el, Μεγάλη Μοραβία, ''Meghálī Moravía''; cz, Velká Morava ; sk, Veľká Morava ; pl, Wielkie Morawy), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavs, West Slavic to emerge in the area of Central Europe, possibly including territories which are today part of the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Austria, Germany, Poland, Romania, Croatia, Serbia and Ukraine. The only formation preceding it in these territories was Samo's Empire, Samo's tribal union known from between 631 and 658 AD. Its core territory is the region now called Moravia in the eastern part of the Czech Republic alongside the Morava (river), Morava River, which gave its name to the kingdom. The kingdom saw the rise of the first ever Slavic literary culture in the Old Church Slavonic language as well as the expansion of Christianity, first via missionaries from East Francia, and later after the arrival of Saints Cyril and Metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rastislav Of Moravia
Rastislav or Rostislav, also known as St. Rastislav, (Latin: ''Rastiz'', Greek: Ῥασισθλάβος / ''Rhasisthlábos'') was the second known ruler of Moravia (846–870).Spiesz ''et al.'' 2006, p. 20. Although he started his reign as vassal to Louis the German, king of East Francia, he consolidated his rule to the extent that after 855 he was able to repel a series of Frankish attacks. Upon his initiative, brothers Cyril and Methodius, sent by the Byzantine Emperor Michael III in 863, translated the most important Christian liturgical books into Slavonic. Rastislav was dethroned by his nephew Svatopluk I of Moravia, who handed him over to the Franks. He was canonized by the Eastern Orthodox Church in 1994. Early life According to the ''Annals of Fulda'', Rastislav was a nephew of Mojmir I, the first known ruler of Moravia. His career before 846 is unknown,The Slovakian historian Stanislav J. Kirschbaum refers to Rastislav as prince of Nitra in the period before 846 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratimir, Duke Of Lower Pannonia
Ratimir ( la, Ratimarus) was a duke or prince ('' knez'') of the Slavs in Lower Pannonia between ca. 829 to 838. It is believed that Ratimir descends from a royal dynasty that provided rulers for Moravia and Croatia. In 827, the Bulgars under Great Khan Omurtag invaded and conquered Lower Pannonia and parts of Frankish territories to the north. In 829 the Bulgars imposed a local prince, Ratimir, as the new ruler of the territory. His province is believed to have been the territory of the former Roman Pannonia Savia, which is located in modern-day Croatia. Earlier, Sigismund Calles (1750) called him "Slavic duke of the Drava". In 838, nine years later, following the Bulgarian conquest of Macedonia, the Danubian count Radbod, prefect of the East March, deposed Ratimir and restored Frankish rule. Ratimir fled the land, and the Franks instated dukes Pribina and Kocelj to rule Pannonian area in the name of the Franks. Unlike his predecessors, Ratimir experienced a rift in rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern March (Frankish)
The March of Pannonia or Eastern March ( la, marcha orientalis) was a frontier march of the Carolingian Empire, named after the former Roman province of ''Pannonia'' and carved out of the preceding and larger Avar march. It was referred to in some documents as ''terminum regni Baioariorum in Oriente'' or "the end of the kingdom of the Bavarians in the east", and from this is sometimes called the Bavarian Eastern March of the wider Bavarian eastern marches, a term used for any such territory, though today most commonly used to refer to the later Margraviate of Austria, established in 976 as a sort of late successor state. It was erected in the mid-ninth century in the lands of the former Avar Khaganate against the threat of Great Moravia and lasted only as long as the strength of that state. The East Frankish rulers appointed margraves (prefects) to govern the March. History Charlemagne, temporarily allied with Khan Krum of Bulgaria, from 791 onwards had launched several mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonian Slavs
Early Slavs settled in the eastern and southern parts of the former Roman province of Pannonia. The term ''Lower Pannonia'' ( la, Pannonia inferior, hu, Alsó-pannoniai grófság, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Donja Panonija, Доња Панонија, sl, Spodnja Panonija) was used to designate those areas of the Pannonian plain that lie to the east and south of the river Rába, with the division into ''Upper'' and ''Lower'' inherited from the Roman terminology. From the middle of the 6th to the end of the 8th century, the region was under the domination of the Avars, while the Slavic inhabitants lived under Avar rule. By the beginning of the 9th century, that state was destroyed and replaced by the supreme rule of the Frankish Empire, which lasted until the Magyar conquest (c. 900). During the Frankish period, the region of Lower Pannonia was governed by local Slavic rulers, who were under the suzerainty of Frankish kings. Within the Frankish administrative system, the March of Pannonia w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |