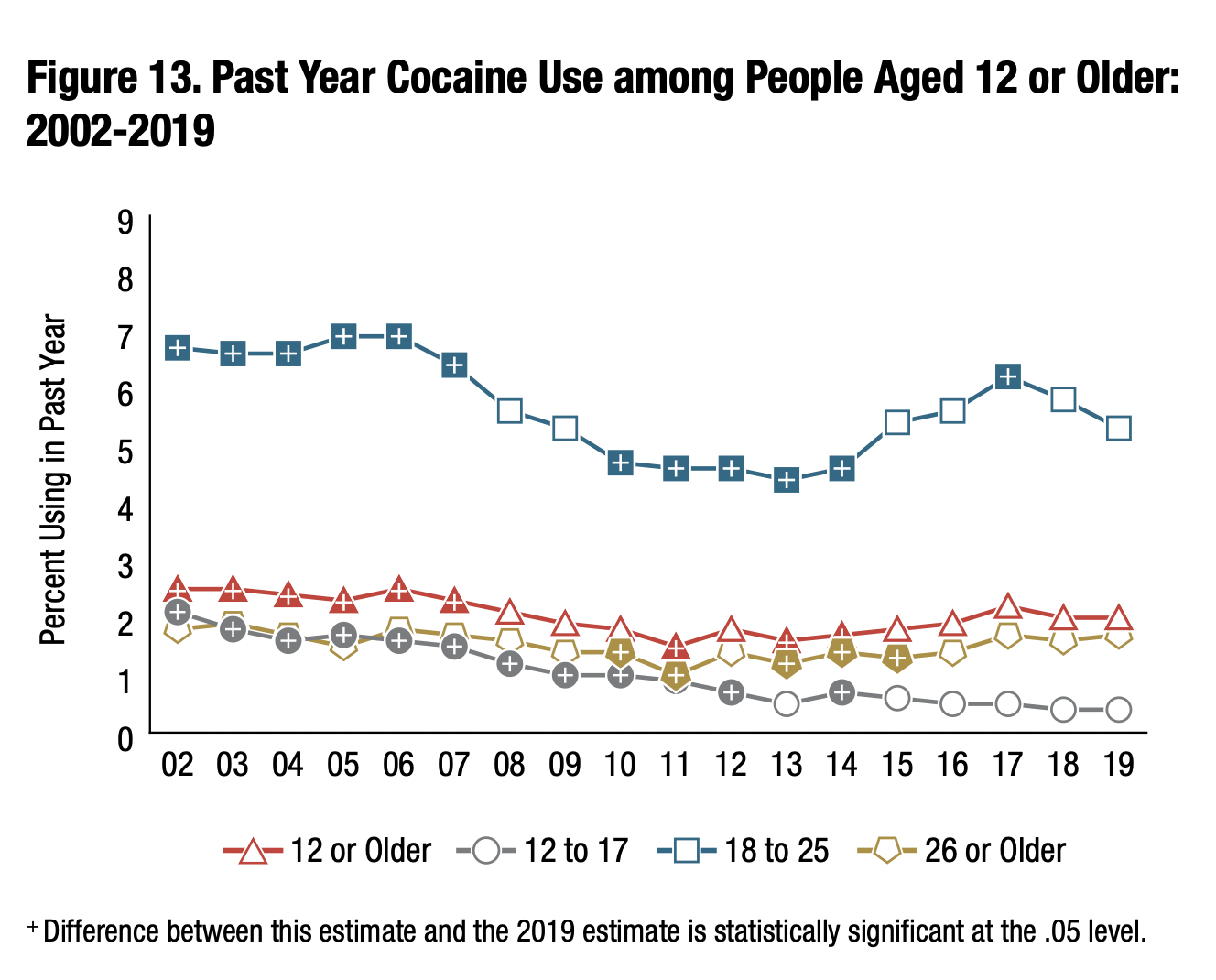
|
RTIOX-276
RTIOX-276 is an orexin antagonist. RTIOX-276 binds selectively to the orexin 1 receptor (KE = 8.5nM) and lacks significant affinity for the orexin 2 receptor (KE = > 10,000nM). RTIOX-276 may have therapeutic utility for the treatment of cocaine addiction. In conditioned place preference studies, RTIOX-276 attenuated the development of place preference in mice exposed to cocaine Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechuan languages, Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly recreational drug use, used recreationally for its euphoria, euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from t .... References Amides Benzylisoquinolines Orexin antagonists 3-Pyridyl compounds {{Sedative-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orexin Antagonist
An orexin receptor antagonist, or orexin antagonist, is a drug that inhibits the effect of orexin by acting as a receptor antagonist of one or both of the orexin receptors, Hypocretin (orexin) receptor 1, OX1 and Hypocretin (orexin) receptor 2, OX2. Medical applications include treatment of sleep disorders such as insomnia. Examples Marketed * Daridorexant (nemorexant; Quviviq) – dual OX1 and OX2 antagonist – approved for insomnia in January 2022, formerly under development for sleep apnea – half-life 8 hours * Lemborexant (Dayvigo) – dual OX1 and OX2 antagonist – approved for insomnia in December 2019 and released June 1 2020, under development for circadian rhythm sleep disorders, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and sleep apnea – half-life 17–55 hours * Suvorexant (Belsomra) – dual OX1 and OX2 antagonist – approved for insomnia in August 2014, under development for delirium – half-life 12 hours Under development * Seltorexant (MIN-202, JNJ-42847922, JNJ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orexin 1 Receptor
Orexin receptor type 1 (Ox1R or OX1), also known as hypocretin receptor type 1 (HcrtR1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCRTR1 gene. Function The orexin 1 receptor (OX1), is a G-protein coupled receptor that is heavily expressed in projections from the lateral hypothalamus and is involved in the regulation of feeding behaviour. OX1 selectively binds the orexin-A neuropeptide. It shares 64% identity with Hypocretin (orexin) receptor 2, OX2. Ligands Agonists * Orexin-A Antagonists * RTIOX-276 - Selective OX1 antagonist * ACT-335827 - Selective OX1 antagonist * Almorexant - Dual OX1 and Hypocretin (orexin) receptor 2, OX2 receptor antagonist, antagonist * Lemborexant - Dual OX1 and Hypocretin (orexin) receptor 2, OX2 receptor antagonist, antagonist * Nemorexant - Dual OX1 and OX2 antagonist * SB-334,867 - Selective OX1 antagonist * SB-408,124 - Selective OX1 antagonist * SB-649,868 - Dual OX1 and Hypocretin (orexin) receptor 2, OX2 receptor antagonist, antagon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orexin Antagonists
An orexin receptor antagonist, or orexin antagonist, is a drug that inhibits the effect of orexin by acting as a receptor antagonist of one or both of the orexin receptors, OX1 and OX2. Medical applications include treatment of sleep disorders such as insomnia. Examples Marketed * Daridorexant (nemorexant; Quviviq) – dual OX1 and OX2 antagonist – approved for insomnia in January 2022, formerly under development for sleep apnea – half-life 8 hours * Lemborexant (Dayvigo) – dual OX1 and OX2 antagonist – approved for insomnia in December 2019 and released June 1 2020, under development for circadian rhythm sleep disorders, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and sleep apnea – half-life 17–55 hours * Suvorexant (Belsomra) – dual OX1 and OX2 antagonist – approved for insomnia in August 2014, under development for delirium – half-life 12 hours Under development * Seltorexant (MIN-202, JNJ-42847922, JNJ-922) – selective OX2 antagonist – under development fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binding Selectivity
Binding selectivity is defined with respect to the binding of ligands to a substrate forming a complex. Binding selectivity describes how a ligand may bind more preferentially to one receptor than another. A selectivity coefficient is the equilibrium constant for the reaction of displacement by one ligand of another ligand in a complex with the substrate. Binding selectivity is of major importance in biochemistry and in chemical separation processes. Selectivity coefficient The concept of selectivity is used to quantify the extent to which one chemical substance, A, binds each of two other chemical substances, B and C. The simplest case is where the complexes formed have 1:1 stoichiometry. Then, the two interactions may be characterized by equilibrium constants ''K''AB and ''K''AC.The constant used here are ''association'' constants. ''Dissociation'' constants are used in some contexts. A dissociation constant is the reciprocal of an association constant. : + B AB; \mathit K_ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affinity (pharmacology)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism (conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure. Binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. The association or docking is actually reversible through dissociation. Measurably irreversible covalent bonding between a ligand and target molecule is atypical in biological systems. In contrast to the definition of liga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orexin 2 Receptor
Orexin receptor type 2 (Ox2R or OX2), also known as hypocretin receptor type 2 (HcrtR2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCRTR2 gene. Structure The structure of the receptor has been solved to 2.5 Å resolution as a fusion protein bound to suvorexant using lipid-mediated crystallization. Function OX2 is a G-protein coupled receptor expressed exclusively in the brain. It has 64% identity with OX1. OX2 binds both orexin A and orexin B neuropeptides. OX2 is involved in the central feedback mechanism that regulates feeding behaviour. Mice with enhanced OX2 signaling are resistant to high-fat diet-induced obesity. This receptor is activated by Hipocretin, which is a wake-promoting hypothalamic neuropeptide that acts as a critical regulator of sleep in animals as Zebrafish or Mammals. This protein has mutations in Astyanax mexicanus that reduces the sleep needs of the cavefish. Ligands Agonists * Danavorexton (TAK-925) – selective OX2 receptor agonist * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocaine Addiction
Cocaine dependence is a neurological disorder that is characterized by withdrawal symptoms upon cessation from cocaine use. It also often coincides with cocaine addiction which is a biopsychosocial disorder characterized by persistent use of cocaine and/or crack despite substantial harm and adverse consequences. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed., abbreviated DSM-5), classifies problematic cocaine use as a " Stimulant use disorder". The International Classification of Diseases (11th rev., abbreviated ICD-11), includes "Cocaine dependence" as a classification (diagnosis) under "Disorders due to use of cocaine". The use of cocaine creates euphoria and high amounts of energy. If taken in large doses, it is possible to cause mood swings, paranoia, insomnia, psychosis, high blood pressure, a fast heart rate, panic attacks, seizures that are extremely difficult to control, cognitive impairments and drastic changes in personality. Cocaine overdose may re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conditioned Place Preference
Conditioned place preference (CPP) is a form of Pavlovian conditioning used to measure the motivational effects of objects or experiences. This motivation comes from the pleasurable aspect of the experience, so that the brain can be reminded of the context that surrounded the "encounter". By measuring the amount of time an animal spends in an area that has been associated with a stimulus, researchers can infer the animal's liking for the stimulus. This paradigm can also be used to measure conditioned place aversion with an identical procedure involving aversive stimuli instead. Both procedures usually involve mice or rats as subjects. This procedure can be used to measure extinction and reinstatement of the conditioned stimulus. Certain drugs are used in this paradigm to measure their reinforcing properties. Two different methods are used to choose the compartments to be conditioned, and these are biased vs. unbiased. The biased method allows the animal to explore the apparatus, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechuan languages, Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly recreational drug use, used recreationally for its euphoria, euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South America, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense''. After extraction from coca leaves and further processing into cocaine hydrochloride (powdered cocaine), the drug is often Insufflation (medicine), snorted, applied topical administration, topically to the mouth, or dissolved and injection (medicine), injected into a vein. It can also then be turned into free base form (crack cocaine), in which it can be heated until sublimated and then the vapours can be smoking, inhaled. Cocaine stimulates the mesolimbic pathway, reward pathway in the brain. Mental effects may include an euphoria, intense feeling of happiness, sexual arousal, psychosis, loss of contact with reality, or psychomo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amides
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, such as in the amino acids asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a derivative of a carboxylic acid () with the hydroxyl group () replaced by an amine group (); or, equivalently, an acyl (alkanoyl) group () joined to an amine group. Common examples of amides are acetamide (), benzamide (), and dimethylformamide (). Amides are qualified as primary, secondary, and tertiary according to whether the amine subgroup has the form , , or , where R and R' are groups other than hydrogen. The core of amides is called the amide group (specifically, carboxamide group). Amides are pervasive in nature and technology. Proteins and important plastics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |