|
RSPO3
R-spondin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RSPO3'' gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the thrombospondin type 1 repeat gene superfamily. In addition, the protein contains a furin-like cysteine-rich region. Furin-like repeat domains have been found in a variety of eukaryotic proteins involved in the mechanism of signal transduction by receptor tyrosine kinases. During embryonic development An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ..., ''RSPO3'' is expressed in the tail bud and the posterior presomitic mesoderm of the embryo. In tissue engineering, R-spondin 3 has been used to differentiate pluripotent stem cells into paraxial mesoderm progenitors References Further reading * * * {{gene-6-stub Glycoproteins Extracellular m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryonic Development
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of the body. Neurulation forms the nervous syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tail Bud
In humans and other mammals, the caudal cell mass (also tail bud or caudal eminence in humans) is the aggregate of undifferentiated cells at the caudal end on the spine. The caudal end of the spinal cord first begins to form after primary neurulation has taken place, indicating that it develops after the cranial portion of the spinal cord has developed. Following neurulation, the caudal tail begins to form a neurocele as it develops a hollow core. After this, secondary neurulation occurs in which the medullary cord begins to form and is filled with many cavities that ultimately form the lumen. The cavities formed from the initial and secondary neurulation combine to form one uninterrupted cavity. There is still speculation on the formation of the caudal cell mass in humans with arguments being made for it arising from many cavities or the continuing growth of the neurocele from the initial neurulation. The caudal cell mass will ultimately differentiate and form into many sacral str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somite
The somites (outdated term: primitive segments) are a set of bilaterally paired blocks of paraxial mesoderm that form in the embryonic stage of somitogenesis, along the head-to-tail axis in segmented animals. In vertebrates, somites subdivide into the dermatomes, myotomes, sclerotomes and syndetomes that give rise to the vertebrae of the vertebral column, rib cage, part of the occipital bone, skeletal muscle, cartilage, tendons, and skin (of the back). The word ''somite'' is sometimes also used in place of the word '' metamere''. In this definition, the somite is a homologously-paired structure in an animal body plan, such as is visible in annelids and arthropods. Development The mesoderm forms at the same time as the other two germ layers, the ectoderm and endoderm. The mesoderm at either side of the neural tube is called paraxial mesoderm. It is distinct from the mesoderm underneath the neural tube which is called the chordamesoderm that becomes the notochord. The pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
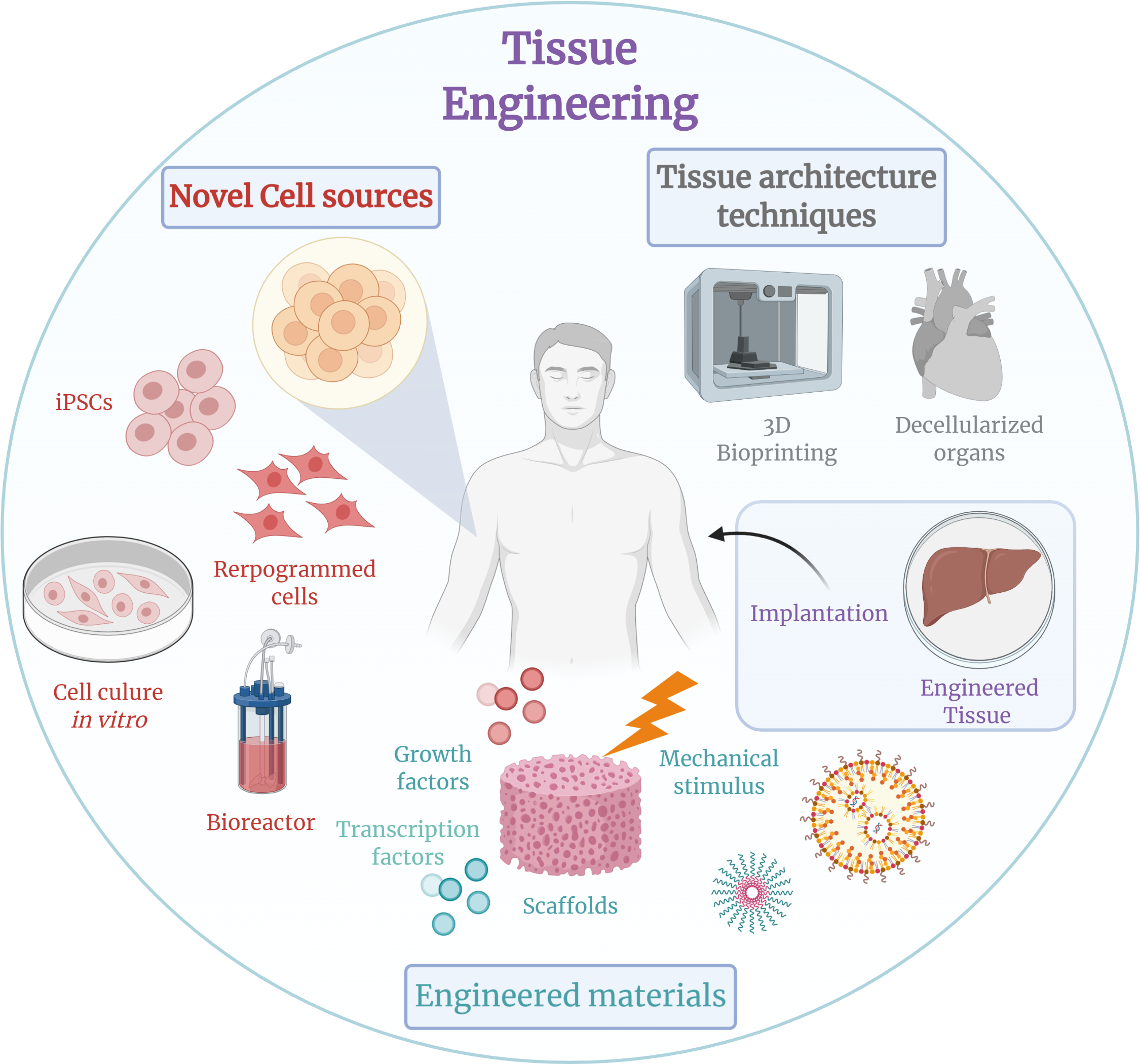
Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering is a biomedical engineering discipline that uses a combination of Cell (biology), cells, engineering, Materials science, materials methods, and suitable biochemistry, biochemical and physicochemical factors to restore, maintain, improve, or replace different types of biology, biological tissues. Tissue engineering often involves the use of cells placed on tissue scaffolds in the formation of new viable tissue for a medical purpose but is not limited to applications involving cells and tissue scaffolds. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field of its own. While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e. bone, Autologous chondrocyte implantation, cartilage, blood vessels, Urinary bladder, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directed Differentiation
Directed differentiation is a bioengineering methodology at the interface of stem cell biology, developmental biology and tissue engineering. It is essentially harnessing the potential of stem cells by constraining their differentiation in vitro toward a specific cell type or tissue of interest. Stem cells are by definition pluripotent, able to differentiate into several cell types such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, hepatocytes, etc. Efficient ''directed differentiation'' requires a detailed understanding of the lineage and cell fate decision, often provided by developmental biology. Conceptual frame During differentiation, pluripotent cells make a number of developmental decisions to generate first the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm) of the embryo and intermediate progenitors, followed by subsequent decisions or check points, giving rise to all the body's mature tissues. The differentiation process can be modeled as sequence of binary decisions based on probabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Induced pluripotent stem cells (also known as iPS cells or iPSCs) are a type of pluripotent stem cell that can be generated directly from a somatic cell. The iPSC technology was pioneered by Shinya Yamanaka's lab in Kyoto, Japan, who showed in 2006 that the introduction of four specific genes (named Myc, Oct3/4, Sox2 and Klf4), collectively known as Yamanaka factors, encoding transcription factors could convert somatic cells into pluripotent stem cells. He was awarded the 2012 Nobel Prize along with Sir John Gurdon "for the discovery that mature cells can be reprogrammed to become pluripotent." Pluripotent stem cells hold promise in the field of regenerative medicine. Because they can propagate indefinitely, as well as give rise to every other cell type in the body (such as neurons, heart, pancreatic, and liver cells), they represent a single source of cells that could be used to replace those lost to damage or disease. The most well-known type of pluripotent stem cell is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraxial Mesoderm
Paraxial mesoderm, also known as presomitic or somitic mesoderm is the area of mesoderm in the neurulating embryo that flanks and forms simultaneously with the neural tube. The cells of this region give rise to somites, blocks of tissue running along both sides of the neural tube, which form muscle and the tissues of the back, including connective tissue and the dermis. Formation and somitogenesis The paraxial and other regions of the mesoderm are thought to be specified by bone morphogenetic proteins, or BMPs, along an axis spanning from the center to the sides of the body. Members of the FGF family also play an important role, as does the WNT pathway. In particular, Noggin, a downstream target of the Wnt pathway, antagonizes BMP signaling, forming boundaries where antagonists meet and limiting this signaling to a particular region of the mesoderm. Together, these pathways provide the initial specification of the paraxial mesoderm and maintain this identity. This specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycoproteins
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. Secreted extracellular proteins are often glycosylated. In proteins that have segments extending extracellularly, the extracellular segments are also often glycosylated. Glycoproteins are also often important integral membrane proteins, where they play a role in cell–cell interactions. It is important to distinguish endoplasmic reticulum-based glycosylation of the secretory system from reversible cytosolic-nuclear glycosylation. Glycoproteins of the cytosol and nucleus can be modified through the reversible addition of a single GlcNAc residue that is considered reciprocal to phosphorylation and the functions of these are likely to be an additional regulatory mechanism that controls phosphorylation-based signalling. In contrast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
