|
RBU (radio Station)
RBU is a time code radio station located in Moscow (). It transmits a continuous 10 kW time code on 66⅔ kHz. Supplement to Recommendation ITU-R TF.768 "Standard frequencies and time signals". This is commonly written as 66.66 or 66.666 kHz, but is actually 200/3 kHz. Until 2008, the transmitter site was near Kupavna and used as antenna three T-antennas spun between three 150 metres tall grounded masts. In 2008, it has been transferred to the Taldom transmitter at . RBU is controlled by All-Russian Scientific Research Institute for Physical-Engineering and Radiotechnical Metrology. It is operated by Russian Television and Radio Broadcasting Network. Time code Every 100 ms, synchronized to the UTC second, one bit is transmitted: 100 Hz modulation encodes a binary 0, while 312.5 Hz modulation encodes a binary 1. Each UTC second consists of 10 such bits. 6 of them are fixed, two encode minute boundaries, and two provide time code information: Eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taldom Transmitter
Taldom transmitter (russian: переда́тчик Та́лдом) is a large facility for longwave and shortwave broadcasting located near Taldom, Russia. It transmits on two longwave frequencies, on 153 kHz with 300 kW and on 261 Hertz, kHz with a power of 2500 Watt, kW, the latter is, according to the World Radio TV Handbook's listings, the most powerful broadcasting station in the world. There are two longwave transmissions aerial systems: a single 257 metres tall mast radiator for 153 kHz and a ring antenna system consisting of five masts arranged in a circle around a 275 metre high guyed radio masts and towers, mast for 261 kHz. The latter antenna delivers good skywave suppression. The shortwave antenna system consists of several masts arranged in a row which are interconnected by cables at various heights. See also * List of masts External links * {{Structurae, id=20014896, title=Taldom LW Transmitters * http://www.skyscraperpage.com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All-Russian Scientific Research Institute For Physical-Engineering And Radiotechnical Metrology
All-Russian Scientific Research Institute for Physical-Engineering and Radiotechnical Metrology (VNIIFTRI; russian: Всероссийский научно-исследовательский институт физико-технических и радиотехнических измерений (ВНИИФТРИ)) was founded in 1955. It is located in the settlement of Mendeleyevo of Solnechnogorsky District, Moscow Oblast, Russia (), and also it includes West-Siberian ( Novosibirsk – ), East-Siberian ( Irkutsk – ), Far-Eastern ( Khabarovsk – ) and Kamchatka (Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky – ) branches. The Institute was awarded the status of the State Scientific Center of the Russian Federation in 1994, the status was repeatedly confirmed in 1997-2013. VNIIFTRI is the State Scientific Metrology Institute, conducts fundamental and applied research in the field of metrology and ensuring the uniformity of measurements, the creation and improvement of state standards, the devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Television And Radio Broadcasting Network
Russian Television and Radio Broadcasting Network (RTRN) (russian: Российская телевизионная и радиовещательная сеть) is a unitary enterprise created on August 13, 2001, by decree of the president of the Russian Federation. The company is included in the list of Russian strategic enterprises. RTRN operates Russia’s digital terrestrial television (DTT) network — the largest operating broadcasting network in the world. It consists of 5040 transmission sites and 10,080 transmitters. Almost 75% out of the 5040 transmission sites were built from scratch. RTRN’s DTT services cover 98,4% of the Russian population. RTRN provides terrestrial transmission of 20 must-carry public television channels and three radio stations broadcasting over the territory of the Russian Federation. RTRN also serves other radio and television channels of both all-Russian and regional types distributing the programs of the latter. Multichannel terrestrial radio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
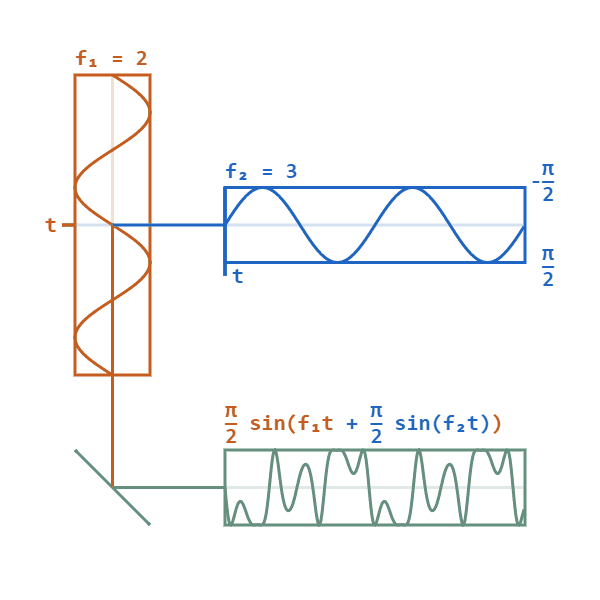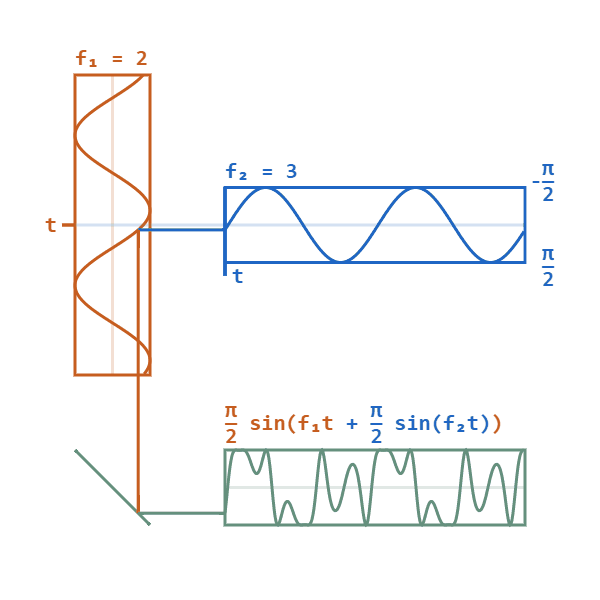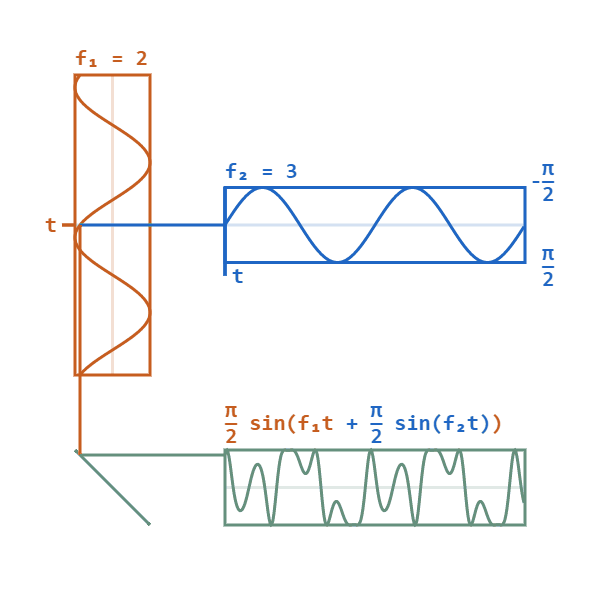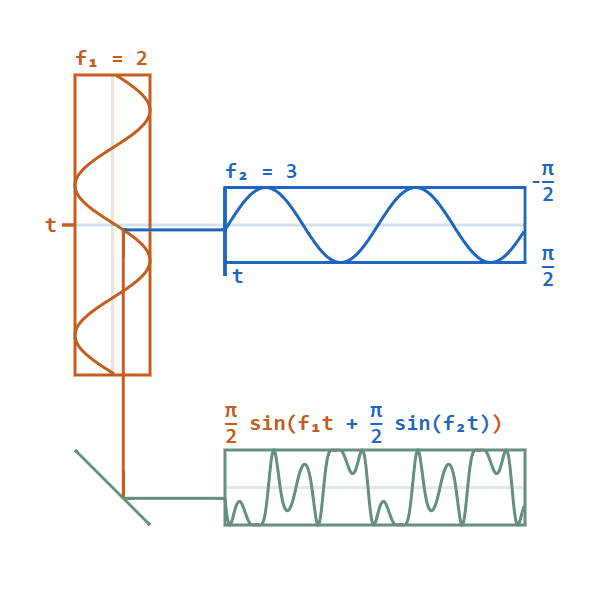
Phase Modulation
Phase modulation (PM) is a modulation pattern for conditioning communication signals for transmission. It encodes a message signal as variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave. Phase modulation is one of the two principal forms of angle modulation, together with frequency modulation. In phase modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the baseband signal modifies the phase of the carrier signal keeping its amplitude and frequency constant. The phase of a carrier signal is modulated to follow the changing signal level (amplitude) of the message signal. The peak amplitude and the frequency of the carrier signal are maintained constant, but as the amplitude of the message signal changes, the phase of the carrier changes correspondingly. Phase modulation is widely used for transmitting radio waves and is an integral part of many digital transmission coding schemes that underlie a wide range of technologies like Wi-Fi, GSM and satellite television. It is also used fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DCF77
DCF77 is a German longwave time signal and standard-frequency radio station. It started service as a standard-frequency station on 1 January 1959. In June 1973 date and time information was added. Its primary and backup transmitter are located at in Mainflingen, about 25 km south-east of Frankfurt am Main, Germany. The transmitter generates a nominal power of 50 kW, of which about 30 to 35 kW can be radiated via a T-antenna. DCF77 is controlled by the ''Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt'' (PTB), Germany's national physics laboratory and transmits in continuous operation (24 hours). It is operated by ''Media Broadcast GmbH'' (previously a subsidiary of ''Deutsche Telekom AG''), on behalf of the PTB. With Media Broadcast GmbH, a temporal transmission availability of at least 99.7% per year or under 26.28 hours of annual downtime has been agreed upon. Most service interruptions are short-term disconnections of under two minutes. Longer lasting transmission servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterfall Diagram
Waterfall plots are often used to show how two-dimensional phenomena change over time. A three-dimensional ''spectral waterfall plot'' is a plot in which multiple curves of data, typically spectra, are displayed simultaneously. Typically the curves are staggered both across the screen and vertically, with "nearer" curves masking the ones behind. The result is a series of "mountain" shapes that appear to be side by side. The waterfall plot is often used to show how two-dimensional information changes over time or some other variable such as rotational speed. Waterfall plots are also often used to depict ''spectrograms'' or ''cumulative spectral decay'' (CSD). Uses * The results of spectral density estimation, showing the spectrum of the signal at successive intervals of time. * The delayed response from a loudspeaker or listening room produced by impulse response testing or MLSSA. * Spectra at different engine speeds when testing engines. See also * Loudspeaker acoustics * L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sideband
In radio communications, a sideband is a band of frequencies higher than or lower than the carrier frequency, that are the result of the modulation process. The sidebands carry the information transmitted by the radio signal. The sidebands comprise all the spectral components of the modulated signal except the carrier. The signal components above the carrier frequency constitute the upper sideband (USB), and those below the carrier frequency constitute the lower sideband (LSB). All forms of modulation produce sidebands. Sideband creation We can illustrate the creation of sidebands with one trigonometric identity: :\cos(A)\cdot \cos(B) \equiv \tfrac\cos(A+B) + \tfrac\cos(A-B) Adding \cos(A) to both sides: :\cos(A)\cdot +\cos(B)= \tfrac\cos(A+B) + \cos(A) + \tfrac\cos(A-B) Substituting (for instance) A \triangleq 1000\cdot t and B \triangleq 100\cdot t, where t represents time: :\underbrace_\cdot \underbrace_ = \underbrace_ + \underbrace_ + \unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unary Code
{{Disambiguation ...
Unary may refer to: *Unary numeral system, the simplest numeral system to represent natural numbers *Unary function, a function that takes one argument; in computer science, a unary operator is a subset of unary function *Unary operation, a kind of mathematical operator that has only one operand *Unary relation, a mathematical relation that has one argument *Unary coding, an entropy encoding that represents a number ''n'' with n − 1 ones followed by a zero See also * Primary (other) * Binary (other) Binary may refer to: Science and technology Mathematics * Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1) * Binary function, a function that takes two arguments * Binary operation, a mathematical operation that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow Time
Moscow Time (MSK, russian: моско́вское вре́мя) is the time zone for the city of Moscow, Russia, and most of western Russia, including Saint Petersburg. It is the second-westernmost of the eleven time zones of Russia. It has been set to UTC+03:00 without DST since 26 October 2014; before that date it had been set to UTC+04:00 year-round on 27 March 2011. Moscow Time is used to schedule trains, ships, etc. throughout Russia, but airplane travel is scheduled using local time. Times in Russia are often announced throughout the country on radio stations as Moscow Time, which is also registered in telegrams, etc. Descriptions of time zones in Russia are often based on Moscow Time rather than UTC. For example, Yakutsk ( UTC+09:00) is said to be MSK+6 in Russia. History Until the October Revolution, the official time in Moscow corresponded to GMT+02:30:17 (according to the longitude of the Astronomical Observatory of Moscow State University). In 1919 the Council ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time or UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is within about one second of mean solar time (such as UT1) at 0° longitude (at the IERS Reference Meridian as the currently used prime meridian) and is not adjusted for daylight saving time. It is effectively a successor to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). The coordination of time and frequency transmissions around the world began on 1 January 1960. UTC was first officially adopted as CCIR Recommendation 374, ''Standard-Frequency and Time-Signal Emissions'', in 1963, but the official abbreviation of UTC and the official English name of Coordinated Universal Time (along with the French equivalent) were not adopted until 1967. The system has been adjusted several times, including a brief period during which the time-coordination radio signals broadcast both UTC and "Stepped Atomic Time (SAT)" before a new UTC was adopted in 1970 and implemented in 1972. This change also a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UTC+3
UTC+03:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +03:00. In areas using this time offset, the time is three hours later than the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Following the ISO 8601 standard, a time with this offset would be written as, for example, 2019-02-08T23:36:06+03:00. As standard time (year-round) :''Principal cities: Moscow, Saint Petersburg, Doha, Riyadh, Baghdad, Nairobi, Dire Dawa, Addis Ababa, Manama, Sana'a, Aden, Minsk, Kuwait City, Asmara, Antananarivo, Kampala, Amman, Damascus'' Africa East Africa *Comoros *Djibouti *Eritrea *Ethiopia *France **French Southern and Antarctic Lands ***Scattered Islands in the Indian Ocean ****Bassas da India, Europa Island and Juan de Nova Island **Mayotte *Kenya *Madagascar *Somalia *Somaliland ''(disputed territory)'' *South Africa **Prince Edward Islands *Tanzania *Uganda Antarctica *Some bases in Antarctica. See also Time in Antarctica **Japan *** Showa Station Asia Arabia Standard Time Arabia Standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modified Julian Day
The Julian day is the continuous count of days since the beginning of the Julian period, and is used primarily by astronomers, and in software for easily calculating elapsed days between two events (e.g. food production date and sell by date). The Julian period is a chronological interval of 7980 years; year 1 of the Julian Period was . The Julian calendar year is year of the current Julian Period. The next Julian Period begins in the year . Historians used the period to identify Julian calendar years within which an event occurred when no such year was given in the historical record, or when the year given by previous historians was incorrect. The Julian day number (JDN) is the integer assigned to a whole solar day in the Julian day count starting from noon Universal Time, with Julian day number 0 assigned to the day starting at noon on Monday, January 1, 4713 BC, proleptic Julian calendar (November 24, 4714 BC, in the proleptic Gregorian calendar), a date at whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |