|
RAF Llandwrog
Royal Air Force Llandwrog or, more simply, RAF Llandwrog is a former Royal Air Force station located at Llandwrog, southwest of Caernarfon, Gwynedd, Wales. The site opened in January 1941 as a RAF Bomber Command airfield for training gunners, radio operators and navigators and closed after the end of the Second World War in 1945. It reopened in 1969 and remains in civil operation today as Caernarfon Airport. History No. 9 Air Gunnery School was the first tenant of the base when it opened at the end of January 1941. It was equipped with Armstrong Whitworth Whitley bombers and Avro Anson training aircraft. Two days after flying commenced, the airfield was attacked by a single Junkers Ju 88 bomber that strafed the airfield, damaging one Whitley. Airspeed Oxford trainers from No. 11 Service Flying Training School were deployed to Llandwrog in mid-1941 to complete its students' night flying requirements. The following year, three of its Whitleys were deployed to RAF Driffield to parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llandwrog
Llandwrog (; Welsh language: meaning 'The church of Saint Twrog') is a village and community in Gwynedd, north-west Wales, most notable for the presence of the headquarters of Welsh record label Sain and the site of Caernarfon Airport. It has a population of 2,466, increasing to 2,539 at the 2011 Census. The community includes the villages of Groeslon, Carmel, Gwynedd, Y Fron, Dinas Dinlle, and Cilgwyn. As suggested by the village name, the parish church is dedicated St Twrog. ChurchinWales.org. Accessdate 18 November 2022. It was the base of the first ever Sea and Mountain Rescue team, and includes the estate of . |
Bombing Of Cologne In World War II
The German city of Cologne was bombed in 262 separate air raidsStadtlandschaften versus Hochstadt at www.koelnarchitektur.de "Internet portal for the architecture of Cologne". (In German). by the during , all by the (RAF). A total of 34,711 long tons of bombs were dropped on the city by the RAF. 20,000 people died during the war in Cologne due to aerial bombardments. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scuttled
Scuttling is the deliberate sinking of a ship. Scuttling may be performed to dispose of an abandoned, old, or captured vessel; to prevent the vessel from becoming a navigation hazard; as an act of self-destruction to prevent the ship from being captured by an enemy force (or, in the case of a vessel engaged in illegal activities, by the authorities); as a blockship to restrict navigation through a channel or within a harbor; to provide an artificial reef for divers and marine life; or to alter the flow of rivers. Notable historical examples Skuldelev ships (around 1070) The Skuldelev ships, five Viking ships, were sunk to prevent attacks from the sea on the Danish city of Roskilde. The scuttling blocked a major waterway, redirecting ships to a smaller one that required considerable local knowledge. Cog near Kampen (early 15th century) In 2012, a cog preserved from the keel up to the decks in the silt was discovered alongside two smaller vessels in the river IJssel in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairnryan
Cairnryan ( sco, The Cairn; gd, Machair an Sgithich) is a village in the historical county of , , Scotland. It lies on the eastern shore of , north of and south west of |
Operation Sandcastle
Operation Sandcastle was a United Kingdom non-combat military operation conducted between 1955–1956. Its purpose was to dispose of chemical weapons by dumping them in the sea. Background The British possessed almost 71,000 air-dropped bombs of 250 kilograms in weight, each of which was filled with tabun. These had been seized from German ammunition dumps during the final months of World War II. A total of 250,000 tons of German chemical weapons had been discovered, the majority of which were destroyed because they comprised warfare agents which the allies already possessed in great abundance e.g. mustard gas at sites such as RAF Bowes Moor. However, the stocks of tabun and sarin were considered more valuable because the allies did not possess nerve agent technology at that time. As a result, captured stocks of German nerve agents were divided between Britain and the United States after discussion, with the Americans taking the sarin. The British transferred their 14,000 tons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabun (nerve Agent)
Tabun or GA is an extremely toxic synthetic organophosphorus compound. It is a clear, colorless, and tasteless liquid with a faint fruity odor.Facts About Tabun National Terror Alert Response System It is classified as a because it fatally interferes with normal functioning of the mammalian nervous system. Its production is strictly controlled and stockpiling outlawed by the Chemical Weapons Convention of 1993. Tabun is the first of the ''G-series'' nerve agents along with GB ( [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
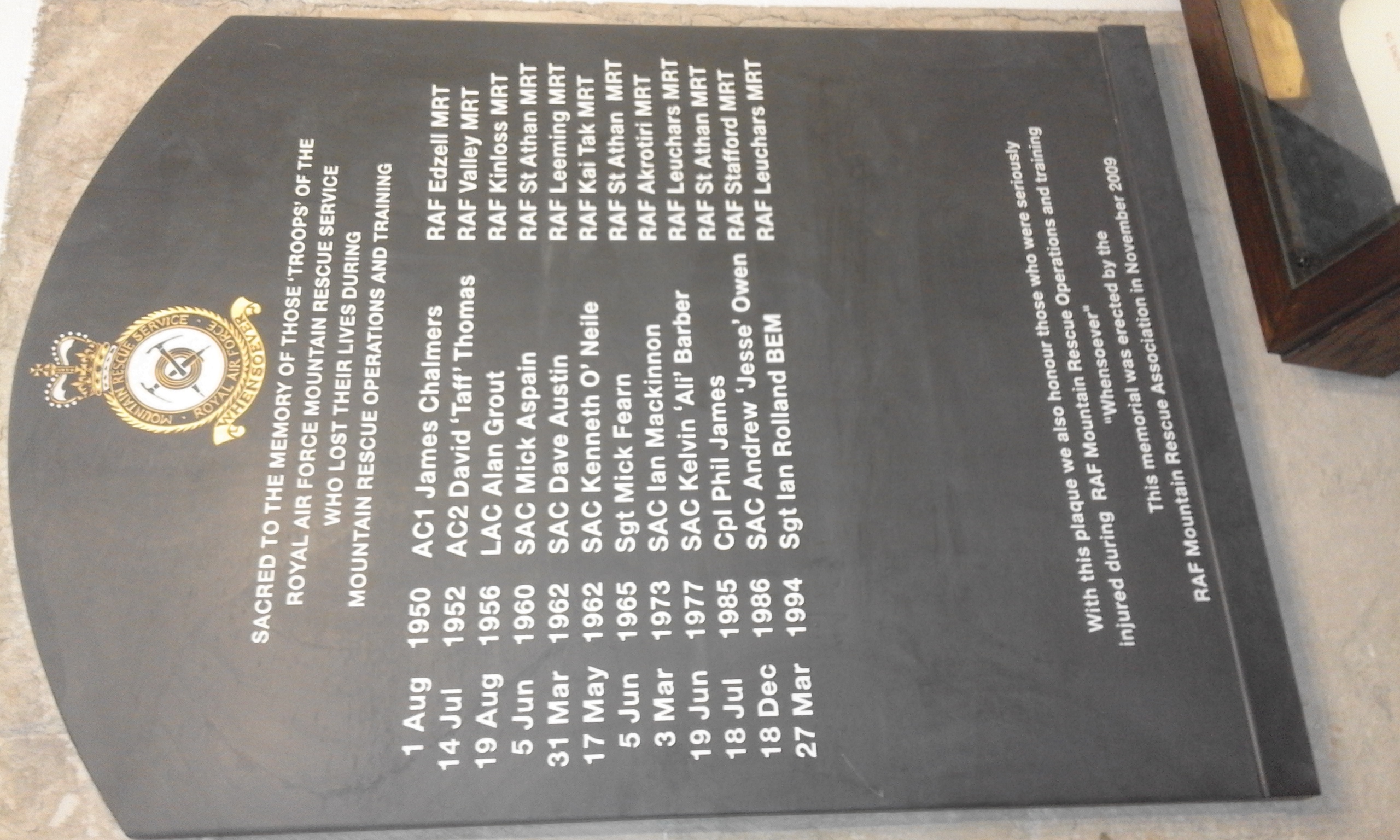
Royal Air Force Mountain Rescue Service
The Royal Air Force Mountain Rescue Service (RAFMRS) provides the UK military's only all-weather search and rescue asset for the United Kingdom. Royal Air Force mountain rescue teams (MRTs) were first organised during World War II to rescue aircrew from the large number of aircraft crashes then occurring due to navigational errors in conjunction with bad weather and resulting poor visibility when flying in the vicinity of high ground. The practice at the time was to organise ad-hoc rescue parties from station medical sections and other ground personnel. Experience demonstrated that this could be dangerous. While the mountains of the United Kingdom are not very tall, they contain much formerly glaciated terrain with steep cliffs, talus slopes, high peaks and cirque basins, and generally experience a sub-Arctic climate at relatively low altitudes. Snow and high winds, sometimes in excess of , are possible any month of the year. Rescue operations in these conditions require personne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Lieutenant
Flight lieutenant is a junior commissioned rank in air forces that use the Royal Air Force (RAF) system of ranks, especially in Commonwealth countries. It has a NATO rank code of OF-2. Flight lieutenant is abbreviated as Flt Lt in the Indian Air Force (IAF) and RAF, and as FLTLT in the Pakistan Air Force (PAF), Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) and Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF) and has sometimes also been abbreviated as F/L in many services; it has never been correctly abbreviated as "lieutenant". A flight lieutenant ranks above flying officer and below a squadron leader and is sometimes used as an English language translation of a similar rank in non-English-speaking countries. The rank originated in the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) in 1914. It fell into abeyance when the RNAS merged with the Royal Flying Corps during the First World War but was revived in 1919 in the post-war RAF. An RAF flight lieutenant is the equivalent of a lieutenant in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airfields Of Britain Conservation Trust
The Airfields of Britain Conservation Trust (ABCT), founded 2006, is a non-profit organisation that works to preserve and protect airfields in Great Britain, as well as educating people about their history. The Trust is a registered charity. They place inscribed memorial stones on or near disused airfields, which have included a memorial at Fambridge, Essex in February 2009, at Windermere in Cumbria in 2011 and at Montrose Air Station Heritage Centre in May 2012. Other memorial locations include Harrowbeer, Hatfield, Lanark, Leavesden, Matlaske, Okehampton, Podington, Swannington, Westcott and Woburn Park Woburn Abbey (), occupying the east of the village of Woburn, Bedfordshire, England, is a country house, the family seat of the Duke of Bedford. Although it is still a family home to the current duke, it is open on specified days to visitors, .... References External links * Charities based in Glasgow Conservation in the United Kingdom Aviation history of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hangar
A hangar is a building or structure designed to hold aircraft or spacecraft. Hangars are built of metal, wood, or concrete. The word ''hangar'' comes from Middle French ''hanghart'' ("enclosure near a house"), of Germanic origin, from Frankish *''haimgard'' ("home-enclosure", "fence around a group of houses"), from *''haim'' ("home, village, hamlet") and ''gard'' ("yard"). The term, ''gard'', comes from the Old Norse ''garðr'' ("enclosure, garden"). Hangars are used for protection from the weather, direct sunlight and for maintenance, repair, manufacture, assembly and storage of aircraft. History The Wright brothers stored and repaired their aircraft in a wooden hangar constructed in 1902 at Kill Devil Hills in North Carolina for their glider. After completing design and construction of the ''Wright Flyer'' in Ohio, the brothers returned to Kill Devil Hills only to find their hangar damaged. They repaired the structure and constructed a new workshop while they waited for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxiway
A taxiway is a path for aircraft at an airport connecting runways with aprons, hangars, terminals and other facilities. They mostly have a hard surface such as asphalt or concrete, although smaller general aviation airports sometimes use gravel or grass. Most airports do not have a specific speed limit for taxiing (though some do). There is a general rule on safe speed based on obstacles. Operators and aircraft manufacturers might have limits. Typical taxi speeds are 20–30 knots (37–56 km/h; 23–35 mph). High-speed exit Busy airports typically construct high-speed or rapid-exit taxiways to allow aircraft to leave the runway at higher speeds. This allows the aircraft to vacate the runway quicker, permitting another to land or take off in a shorter interval of time. This is accomplished by reducing the angle the exiting taxiway intercepts the runway at to 30 degrees, instead of 90 degrees, thus increasing the speed at which the aircraft can exit the runway onto the taxiway. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runway
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt concrete, asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface (sod, grass, soil, dirt, gravel, ice, sand or road salt, salt). Runways, as well as taxiways and Airport apron, ramps, are sometimes referred to as "tarmac", though very few runways are built using Tarmacadam, tarmac. Takeoff and landing areas defined on the surface of water for seaplanes are generally referred to as waterways. Runway lengths are now International Civil Aviation Organization#Use of the International System of Units, commonly given in meters worldwide, except in North America where feet are commonly used. History In 1916, in a World War I war effort context, the first concrete-paved runway was built in Clermont-Ferrand in France, allowing local company Michelin to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |