|
Rục Language
Rục is a Vietic language spoken by the Ruc people of Tuyên Hóa district, Quảng Bình province, Vietnam. ''Rục'' literally means 'underground spring', and is a critically endangered language spoken by a small ethnic group that practiced a hunter-gatherer lifestyle until the late 20th century. History Ruc speakers were hunter-gatherers until the late 1970s, when they were relocated into sedentary villages by the Vietnamese government. The 1985 Soviet-Vietnamese Linguistic Expedition found that there were no more than 200 Ruc people. Half of the Ruc died from a cholera epidemic in the late 1980s. Today, the Ruc live together with the Sach in villages close to the Laotian border. Ruc settlements include Yên Hợp and Phú Minh. Phonology Unlike Vietnamese, Rục allows for presyllables with a minor vowel, such as ''cakuː4'' 'bear' (cf. Vietnamese ''gấu''). Rục is notable for preserving many prefixes that have been lost in Vietnamese, including prefixes (such as *k.- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifteenth-most populous country. One of two communist states in Southeast Asia, Vietnam shares land borders with China to the north, and Laos and Cambodia to the west. It shares Maritime boundary, maritime borders with Thailand through the Gulf of Thailand, and the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia through the South China Sea. Its capital is Hanoi and its largest city is Ho Chi Minh City. Vietnam was inhabited by the Paleolithic age, with states established in the first millennium BC on the Red River Delta in modern-day northern Vietnam. Before the Han dynasty's invasion, Vietnam was marked by a vibrant mix of religion, culture, and social norms. The Han dynasty annexed Northern and Central Vietnam, which were subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
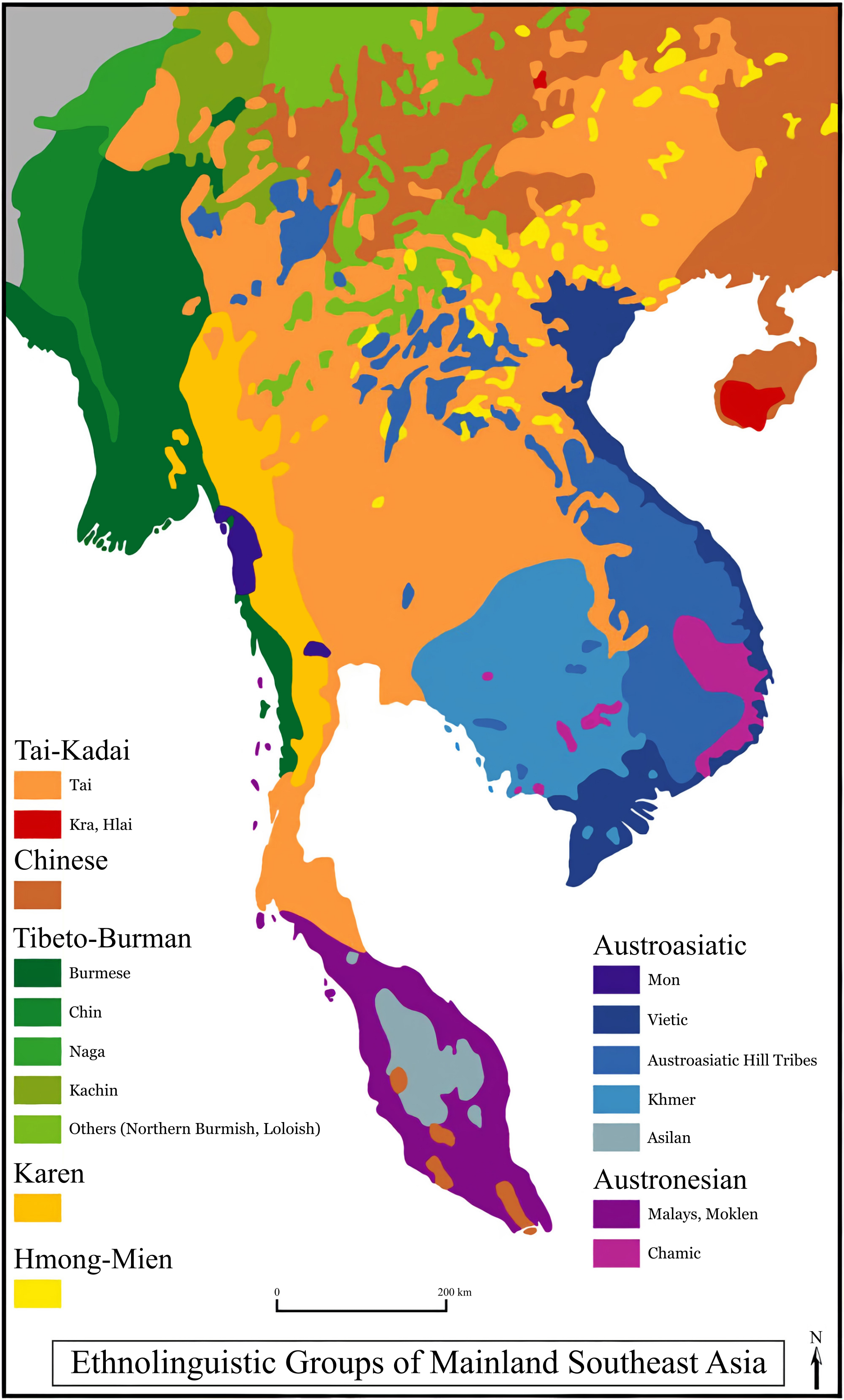
Mainland Southeast Asian Languages
The Mainland Southeast Asia linguistic area is a sprachbund including languages of the Sino-Tibetan, Hmong–Mien (or Miao–Yao), Kra–Dai, Austronesian and Austroasiatic families spoken in an area stretching from Thailand to China. Neighbouring languages across these families, though presumed unrelated, often have similar typological features, which are believed to have spread by diffusion. James Matisoff referred to this area as the "Sinosphere", contrasted with the "Indosphere", but viewed it as a zone of mutual influence in the ancient period. Language distribution The Austroasiatic languages include Vietnamese and Khmer, as well as many other languages spoken in scattered pockets as far afield as Malaya and eastern India. Most linguists believe that Austroasiatic languages once ranged continuously across southeast Asia and that their scattered distribution today is the result of the subsequent migration of speakers of other language groups from southern China. Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |