|
Rüdiger Valk
Rüdiger Valk (born 5 August 1945) is a German mathematician. From 1976 to 2010 he was Professor for Theoretical Computer Science (Informatics) at the ''Institut für Informatik'' (later ''Fachbereich Informatik'') of the University of Hamburg, Germany.http://www.informatik.uni-hamburg.de/TGI/mitarbeiter/profs/valk_eng.html (accessed 30 July 2013) Valk studied mathematics at the University of Bonn (Germany). Supervised by Wilfried Brauer, he continued studying for a postgraduate degree at Bonn and received his PhD in Mathematics in 1974. In 1976 he became Professor for Theoretical Computer Science (Informatics). From 1985 until 2010 he was head of the research group on theoretical foundations of computer science (Theoretische Grundlagen der Informatik, TGI) at the University of Hamburg. Research career His early research is characterised by work on topological automata and systems,''Discrete and Continuous Realizations of General Time Systems.'' In: ''Journal of Cybernetics.'' 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change. History One of the earliest known mathematicians were Thales of Miletus (c. 624–c.546 BC); he has been hailed as the first true mathematician and the first known individual to whom a mathematical discovery has been attributed. He is credited with the first use of deductive reasoning applied to geometry, by deriving four corollaries to Thales' Theorem. The number of known mathematicians grew when Pythagoras of Samos (c. 582–c. 507 BC) established the Pythagorean School, whose doctrine it was that mathematics ruled the universe and whose motto was "All is number". It was the Pythagoreans who coined the term "mathematics", and with whom the study of mathematics for its own sake begins. The first woman mathematician recorded by history was Hypati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Hamburg
The University of Hamburg (german: link=no, Universität Hamburg, also referred to as UHH) is a public research university in Hamburg, Germany. It was founded on 28 March 1919 by combining the previous General Lecture System ('' Allgemeines Vorlesungswesen''), the Hamburg Colonial Institute ('' Hamburgisches Kolonialinstitut''), and the Academic College ('' Akademisches Gymnasium''). The main campus is located in the central district of Rotherbaum, with affiliated institutes and research centres distributed around the city-state. The university has been ranked in the top 200 universities worldwide by the ''Times Higher Education Ranking'', the Shanghai Ranking and the CWTS Leiden Ranking, placing it among the top 1% of global universities. Seven Nobel Prize winners and one Wolf Prize winner are affiliated with UHH. On a national scale, '' U.S. News & World Report'' ranks UHH 7th and ''QS World University Rankings'' 14th out of a total of 426 German institutions of higher educa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Bonn
The Rhenish Friedrich Wilhelm University of Bonn (german: Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn) is a public research university located in Bonn, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It was founded in its present form as the ( en, Rhine University) on 18 October 1818 by Frederick William III, as the linear successor of the ( en, Academy of the Prince-elector of Cologne) which was founded in 1777. The University of Bonn offers many undergraduate and graduate programs in a range of subjects and has 544 professors. The University of Bonn is a member of the U15 (German universities), German U15 association of major research-intensive universities in Germany and has the title of "University of Excellence" under the German Universities Excellence Initiative; it is consistently ranked amongst the best German universities in the world rankings and is one of the most research intensive universities in Germany. Bonn has 6 Clusters of Excellence, the most of any German university; t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilfried Brauer
Wilfried Brauer (8 August 1937 – 25 February 2014) was a German computer scientist and professor emeritus at Technical University of Munich. Life and work Brauer studied Mathematics, Physics, and Philosophy at the Free University of Berlin. He received a PhD in Mathematics 1966 from the University of Bonn for a dissertation on the theory of profinite groups. Wilfried Brauer and his wife Ute were two of the 19 founding members of the German Informatics Society. From 1998 to 2001, he was chairman of the German Informatics Society. From 1994 to 1999, he was vice president of the International Federation of Information Processing. He received several awards and honours: * Felix Hausdorff-Gedächtnispreis (1966) * IFIP Silver Core (1986) * honorary doctor of the University of Hamburg (1996) * Werner Heisenberg Medal (2000) * IFIP Isaac L. Auerbach Award (2002) * honorary doctor of the Freie Universität Berlin (2004) * One of ten inaugural fellows of the European Association fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postgraduate Degree
Postgraduate or graduate education refers to academic or professional degrees, certificates, diplomas, or other qualifications pursued by post-secondary students who have earned an undergraduate ( bachelor's) degree. The organization and structure of postgraduate education varies in different countries, as well as in different institutions within countries. While the term "graduate school" or "grad school" is typically used in North America, "postgraduate" is often used in countries such as ( Australia, Bangladesh, India, Ireland, New Zealand, Pakistan, South Africa, and the UK). Graduate degrees can include master's degrees, doctoral degrees, and other qualifications such as graduate certificates and professional degrees. A distinction is typically made between graduate schools (where courses of study vary in the degree to which they provide training for a particular profession) and professional schools, which can include medical school, law school, business school, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lecture Notes In Computer Science
''Lecture Notes in Computer Science'' is a series of computer science books published by Springer Science+Business Media since 1973. Overview The series contains proceedings, post-proceedings, monographs, and Festschrifts. In addition, tutorials, state-of-the-art surveys, and "hot topics" are increasingly being included. The series is indexed by DBLP. See also *''Monographiae Biologicae'', another monograph series published by Springer Science+Business Media *''Lecture Notes in Physics'' *''Lecture Notes in Mathematics'' *''Electronic Workshops in Computing ''Electronic Workshops in Computing'' (eWiC) is a publication series by the British Computer Society. The series provides free online access for conferences and workshops in the area of computing. For example, the EVA London Conference proceeding ...'', published by the British Computer Society References External links * Publications established in 1973 Computer science books Series of non-fiction books Springer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
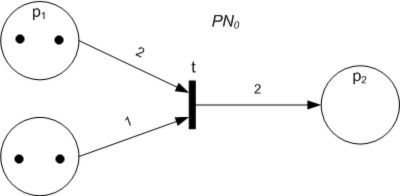
Petri Net
A Petri net, also known as a place/transition (PT) net, is one of several mathematical modeling languages for the description of distributed systems. It is a class of discrete event dynamic system. A Petri net is a directed bipartite graph that has two types of elements, places and transitions. Place elements are depicted as white circles and transition elements are depicted as rectangles. A place can contain any number of tokens, depicted as black circles. A transition is enabled if all places connected to it as inputs contain at least one token. Some sources state that Petri nets were invented in August 1939 by Carl Adam Petri—at the age of 13—for the purpose of describing chemical processes. Like industry standards such as UML activity diagrams, Business Process Model and Notation, and event-driven process chains, Petri nets offer a graphical notation for stepwise processes that include choice, iteration, and concurrent execution. Unlike these standards, Petri nets hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nets Within Nets
Nets within Nets is a modelling method belonging to the family of Petri nets. This method is distinguished from other sorts of Petri nets by the possibility to provide their tokens with a proper structure, which is based on Petri net modelling again. Hence, a net can contain further net items, being able to move around and fire themselves. Motivation Nets within nets are well suited for the modelling of distributed systems under the particular aspects of * hierarchy, * mobility * encapsulation. In a lot of publications in relation to object-oriented design is given, in order to combine the ability of Petri nets in modelling distributed computing with the modelling of objects, being able to be created and to interact. History Starting from the need of practical applications, by the mid of nineties, different formalisms have been created, which fit the description of „nets within nets“. Lomazova and Schnoebelen are listing some of these approaches, namely by Sibertin- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Adam Petri
Carl Adam Petri (12 July 1926 in Leipzig – 2 July 2010 in Siegburg) was a German mathematician and computer scientist. Life and work Petri created his major scientific contribution, the concept of the Petri net, in 1939 at the age of 13, for the purpose of describing chemical processes. In 1941, his father told him about Konrad Zuse's work on computing machines and Carl Adam started building his own analog computer. After earning his Abitur at Thomasschule in 1944, he was drafted into the Wehrmacht. He was taken into British captivity until 1949, when he departed England. Petri started studying mathematics at the Technische Hochschule Hannover (today, the Leibniz University Hannover) in 1950. He documented Petri nets in 1962 as part of his dissertation, (Communication with automata). From 1959 until 1962 he worked at the University of Bonn and received his PhD degree in 1962 from the Technische Universität Darmstadt. From 1963 to 1968 he established and directed the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1945 Births
1945 marked the end of World War II and the fall of Nazi Germany and the Empire of Japan. It is also the only year in which Nuclear weapon, nuclear weapons Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, have been used in combat. Events Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix. January * January 1 – WWII: ** Nazi Germany, Germany begins Operation Bodenplatte, an attempt by the ''Luftwaffe'' to cripple Allies of World War II, Allied air forces in the Low Countries. ** Chenogne massacre: German prisoners are allegedly killed by American forces near the village of Chenogne, Belgium. * January 6 – WWII: A German offensive recaptures Esztergom, Kingdom of Hungary (1920–1946), Hungary from the Russians. * January 12 – WWII: The Soviet Union begins the Vistula–Oder Offensive in Eastern Europe, against the German Army (Wehrmacht), German Army. * January 13 – WWII: The Soviet Union begins the East Prussian Offensive, to eliminate German forces in East Pruss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Computer Scientists
German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) **Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman times) * German language **any of the Germanic languages * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (other) * Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)