|
Rustad Knoll
Rustad Knoll () is a rounded, snow-topped elevation (365 m) which surmounts the south shore of the island of Bouvetøya immediately east of Cato Point. First charted in 1898 by a German expedition under Carl Chun Carl Chun (1 October 1852 – 11 April 1914) was a German marine biologist. Chun was born in Höchst, today a part of Frankfurt, and studied zoology at the University of Leipzig, where from 1878 to 1883 he was privat-docent of zoology and an a .... The knoll was recharted in December 1927 by the Norvegia expedition under Captain Harald Horntvedt. They named it for Ditlef Rustad who was in charge of the biological research of the expedition. References Hills of Antarctica Landforms of Bouvet Island {{BouvetIsland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouvet Map
Bouvet can have the following meanings: Places * Bouvet Island, an uninhabited Norwegian island in the South Atlantic People * Joachim Bouvet (1656–1730), French Jesuit who worked in China, leading member of the Figurist movement * Jean-Baptiste Charles Bouvet de Lozier (1705–1786), French explorer, discovered Bouvet Island *René Joseph Bouvet de Précourt (1715 — 1782), French Navy officer, captain of ''Ajax'' in Suffren's squadron during the War of American Independence * Pierre-Servan-René Bouvet (1750 — 1795), French Navy officer, officer in Suffren's squadron during the War of American Independence * François Joseph Bouvet de Précourt (1753–1832), French admiral *Pierre François Étienne Bouvet de Maisonneuve (1775–1860), French Navy officer *Gustave Bouvet On Bastille Day 1922, anarchist Gustave Bouvet attempted to assassinate French President Alexandre Millerand. Background Gustave Bouvet (1898–1984) was raised in Angers and moved to Paris as a tee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
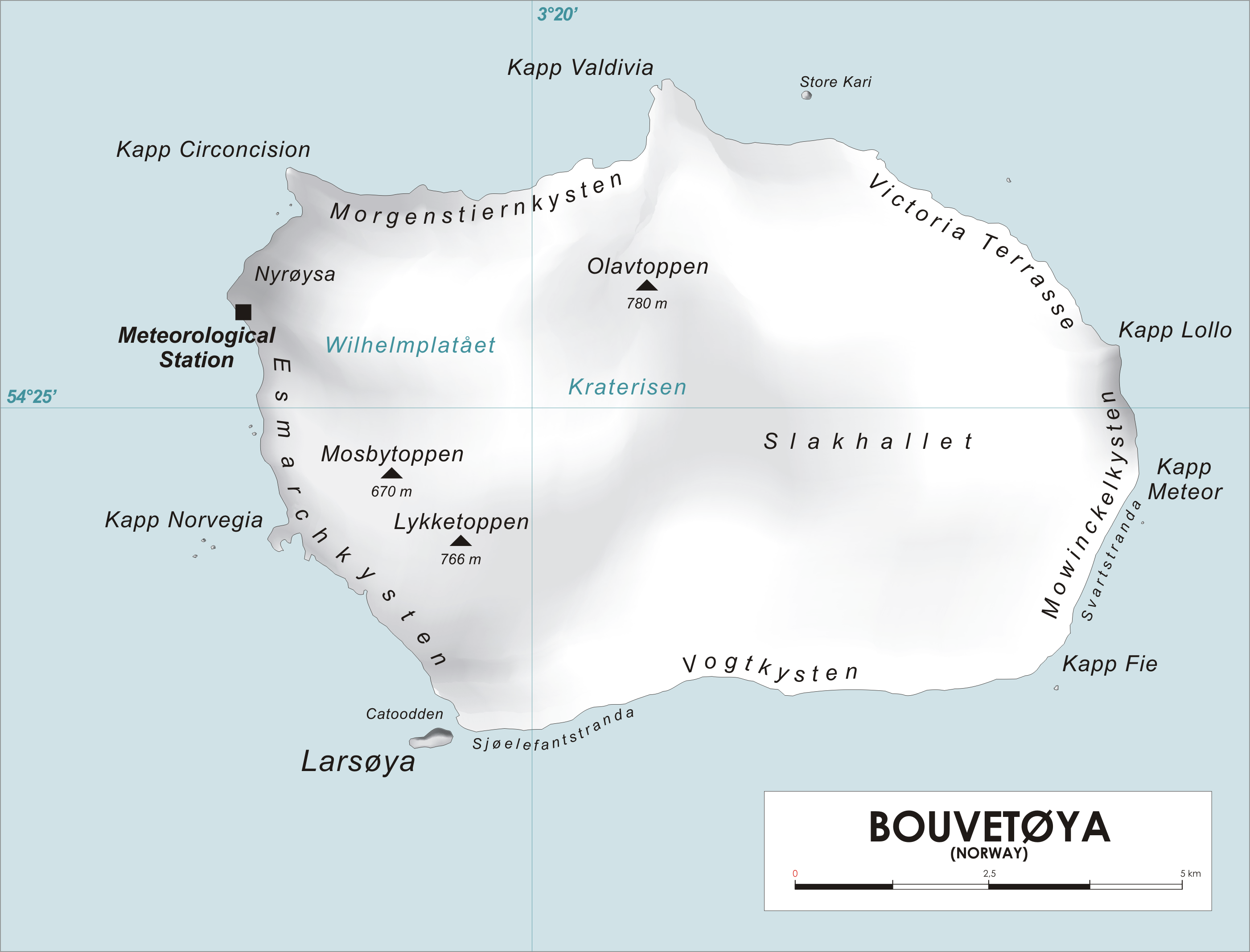
Bouvet Island
Bouvet Island ( ; or ''Bouvetøyen'') is an island claimed by Norway, and declared an uninhabited protected nature reserve. It is a subantarctic volcanic island, situated in the South Atlantic Ocean at the southern end of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, making it the world's most remote island. It is not part of the southern region covered by the Antarctic Treaty System. The island lies north of the Princess Astrid Coast of Queen Maud Land, Antarctica, east of the South Sandwich Islands, south of Gough Island, and south-southwest of the coast of South Africa. It has an area of , 93 percent of which is covered by a glacier. The centre of the island is the ice-filled crater of an inactive volcano. Some skerries and one smaller island, Larsøya, lie along its coast. Nyrøysa, created by a rock slide in the late 1950s, is the only easy place to land and is the location of a weather station. The island was first spotted on 1 January 1739 by the Frenchman Jean-Bapt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cato Point
Cato Point ()is a headland forming the southwest extremity of Bouvet Island. It was first charted in 1898 by a German expedition under Carl Chun. The Norwegian expedition under Captain Harald Horntvedt Harald or Haraldr is the Old Norse form of the given name Harold. It may refer to: Medieval Kings of Denmark * Harald Bluetooth (935–985/986) Kings of Norway * Harald Fairhair (c. 850–c. 933) * Harald Greycloak (died 970) * Harald Hardrada ... made a landing here from the ''Norvegia'' in December 1927; they applied the name. References * Headlands of Bouvet Island {{BouvetIsland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Chun
Carl Chun (1 October 1852 – 11 April 1914) was a German marine biologist. Chun was born in Höchst, today a part of Frankfurt, and studied zoology at the University of Leipzig, where from 1878 to 1883 he was privat-docent of zoology and an assistant to Rudolf Leuckart. After professorial posts in Königsberg (1883–1891) and Breslau (1891–1898), he returned to Leipzig as a professor of zoology.UNI Leipzig Professorenkatalog (biographical sketch) In 1888, Chun described seasonal vertical migration (SVM) which has a periodicity of ca. 1 year. Chun examined depth-stratified net samples from the |
Harald Horntvedt
Harald or Haraldr is the Old Norse form of the given name Harold. It may refer to: Medieval Kings of Denmark * Harald Bluetooth (935–985/986) Kings of Norway * Harald Fairhair (c. 850–c. 933) * Harald Greycloak (died 970) * Harald Hardrada (1015–1066) * Harald Gille (reigned 1130–1136) Grand Dukes of Kiev * Mstislav the Great (1076–1132), known as Harald in Norse sagas King of Mann and the Isles * Haraldr Óláfsson (died 1248) Earls of Orkney * Harald Haakonsson (died 1131) * Harald Maddadsson (–1206) * Harald Eiriksson Others * Hagrold (fl. 944–954), also known as Harald, Scandinavian chieftain in Normandy * Harald Grenske (10th century), petty king in Vestfold in Norway * Harald Klak (–), king in Jutland * Harald Wartooth, legendary king of Sweden, Denmark and Norway * Harald the Younger, 9th-century Viking leader Modern name Royalty * Harald V of Norway (born 1937), present King of Norway * Prince Harald of Denmark (1876–1949) Arts and enter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ditlef Rustad
Ditlef is a given name. Notable people with the name include: * Ditlef Hvistendahl Christiansen (1865–1944), Norwegian Supreme Court Justice * Ditlef Eckhoff (born 1942), Norwegian jazz musician See also * Detlef {{given name Norwegian masculine given names Masculine given names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hills Of Antarctica
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit. Terminology The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not as tall, or as steep as a mountain. Geographers historically regarded mountains as hills greater than above sea level, which formed the basis of the plot of the 1995 film ''The Englishman who Went up a Hill but Came down a Mountain''. In contrast, hillwalkers have tended to regard mountains as peaks above sea level. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' also suggests a limit of and Whittow states "Some authorities regard eminences above as mountains, those below being referred to as hills." Today, a mountain is usually defined in the UK and Ireland as any summit at least high, while the official UK government's definition of a mountain is a summit of or higher. Some definitions include a topographical prominence requirement, typically or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |