|
Runes
Runes are the Letter (alphabet), letters in a set of related alphabets, known as runic rows, runic alphabets or futharks (also, see ''#Futharks, futhark'' vs ''#Runic alphabets, runic alphabet''), native to the Germanic peoples. Runes were primarily used to represent a sound value (a phoneme) but they were also used to represent the concepts after which they are named (ideographic runes). Runology is the academic study of the runic alphabets, runic inscriptions, runestones, and their history. Runology forms a specialised branch of Germanic philology. The earliest secure runic inscriptions date from at latest AD 150, with a possible earlier inscription dating to AD 50 and Tacitus's possible description of rune use from around AD 98. The Svingerud Runestone dates from between AD 1 and 250. Runes were generally replaced by the Latin alphabet as the cultures that had used runes underwent Christianisation, by approximately AD 700 in central Europe and 1100 in northern Europe. Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runestones
A runestone is typically a raised stone with a runic alphabet, runic inscription, but the term can also be applied to inscriptions on boulders and on bedrock. The tradition of erecting runestones as a memorial to dead men began in the 4th century and lasted into the 12th century, but the majority of the extant runestones date from the late Viking Age. While most of these are located in Scandinavia, particularly Sweden, there are also scattered runestones in locations that were visited by Norsemen. Runestones were usually brightly coloured when erected, though this is no longer evident as the colour has worn off. History The tradition of raising stones that had runic inscriptions first appeared in the 4th and 5th century, in Norway and Sweden, and these early runestones were usually placed next to graves, though their precise function as commemorative monuments has been questioned. The earliest Danish runestones appeared in the 8th and 9th centuries, and there are about 50 runest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runic Alphabets
Runes are the Letter (alphabet), letters in a set of related alphabets, known as runic rows, runic alphabets or futharks (also, see ''#Futharks, futhark'' vs ''#Runic alphabets, runic alphabet''), native to the Germanic peoples. Runes were primarily used to represent a sound value (a phoneme) but they were also used to represent the concepts after which they are named (ideographic runes). Runology is the academic study of the runic alphabets, runic inscriptions, runestones, and their history. Runology forms a specialised branch of Germanic philology. The earliest secure runic inscriptions date from at latest AD 150, with a possible earlier inscription dating to AD 50 and Tacitus's possible description of rune use from around AD 98. The Svingerud Runestone dates from between AD 1 and 250. Runes were generally replaced by the Latin alphabet as the cultures that had used runes underwent Christianisation, by approximately AD 700 in central Europe and 1100 in northern Europe. Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elder Futhark
The Elder Futhark (or Fuþark, ), also known as the Older Futhark, Old Futhark, or Germanic Futhark, is the oldest form of the runic alphabets. It was a writing system used by Germanic peoples for Northwest Germanic dialects in the Migration Period. Inscriptions are found on artifacts including jewelry, amulets, plateware, tools, and weapons, as well as runestones, from the 2nd to the 8th centuries. In Scandinavia, beginning in the late 8th century, the script was simplified to the Younger Futhark, while the Anglo-Saxons and Frisians instead extended it, giving rise to the Anglo-Saxon runes, Anglo-Saxon futhorc. Both the Anglo-Saxon futhorc and the Younger Futhark remained in use during the Early Middle Ages, Early and the High Middle Ages respectively, but knowledge of how to read the Elder Futhark was forgotten until 1865, when it was deciphered by Norwegian scholar Sophus Bugge. Description The Elder Futhark is named after the initial phoneme of the first six rune names: /f/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runic Inscriptions
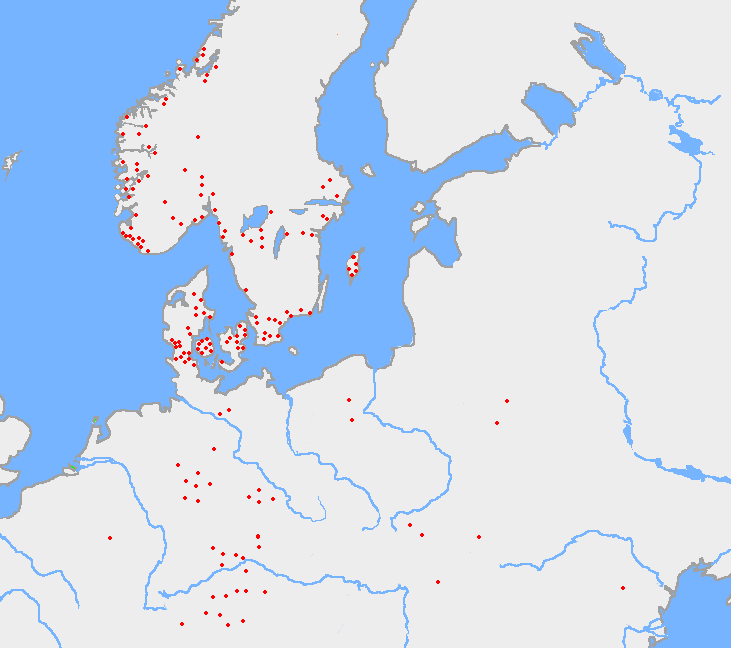
A runic inscription is an inscription made in one of the various runic alphabets. They generally contained practical information or memorials instead of magic or mythic stories. The body of runic inscriptions falls into the three categories of Elder Futhark (some 350 items, dating to between the 2nd and 8th centuries AD), Anglo-Frisian Futhorc (some 100 items, 5th to 11th centuries) and Younger Futhark (close to 6,000 items, 8th to 12th centuries). The total 350 known inscriptions in the Elder Futhark script fall into two main geographical categories, North Germanic (Scandinavian, c. 267 items) and Continental or South Germanic ( "German" and Gothic, c. 81 items). These inscriptions are on many types of loose objects, but the North Germanic tradition shows a preference for bracteates, while the South Germanic one has a preference for fibulae. The precise figures are debatable because some inscriptions are very short and/or illegible so that it is uncertain whether they quali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon Runes
Anglo-Saxon runes or Anglo-Frisian runes are runes that were used by the Anglo-Saxons and Medieval Frisians (collectively called Anglo-Frisians) as an alphabet in their native writing system, recording both Old English and Old Frisian (, ᚱᚢᚾᚪ, "rune"). Today, the characters are known collectively as the futhorc (ᚠᚢᚦᚩᚱᚳ, ''fuþorc'') from the sound values of the first six runes. The futhorc was a development from the older Germanic peoples, co-Germanic 24-character runic alphabet, known today as Elder Futhark, expanding to 28 characters in its older form and up to 34 characters in its younger form. In contemporary Scandinavia, the Elder Futhark developed into a shorter 16-character alphabet, today simply called Younger Futhark. Use of the Anglo-Frisian runes is likely to have started in the 5th century onward and they continued to see use into the High Middle Ages. They were later accompanied and eventually overtaken by the Old English Latin alphabet introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of the Roman Empire, but also all Germanic speaking peoples from this era, irrespective of where they lived, most notably the Goths. Another term, ancient Germans, is considered problematic by many scholars since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. Although the first Roman descriptions of ''Germani'' involved tribes west of the Rhine, their homeland of ''Germania'' was portrayed as stretching east of the Rhine, to southern Scandinavia and the Vistula in the east, and to the upper Danube in the south. Other Germanic speakers, such as the Bastarnae and Goths, lived further east in what is now Moldova and Ukraine. The term ''Germani ''is generally only used to refer to historical peoples from the 1st to 4th centuries CE. Different ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svingerud Runestone
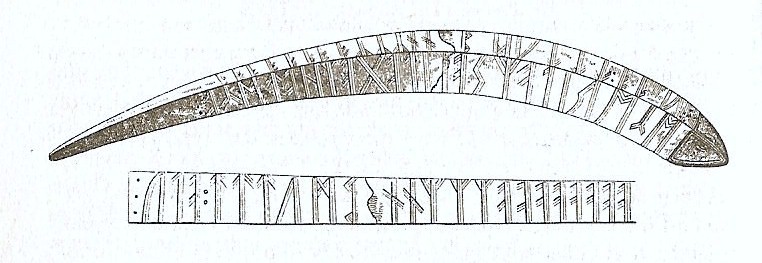
The Svingerud Runestone (or Hole Runestone) is a sandstone object featuring Elder Futhark inscriptions found in a grave in Hole (west of Oslo), Norway. Radiocarbon dating indicates that the grave and the runestone date to between 1 and 250 CE, during the Roman Iron Age, making it the oldest datable runestone known in the world, and potentially the oldest known runic inscription.Olsen 2023. The discovery is additionally notable for the content of its inscriptions. Discovery and context Archaeologists from the Museum of Cultural History, University of Oslo, discovered the stone in the autumn of 2021 while investigating a gravefield near Tyrifjorden. The runes, recording words of an early form of the Proto-Norse language (a northern development of Proto-Germanic), were carved, possibly with the tip of a needle or a knife, in a block of reddish-brown Ringerike sandstone measuring 31x32 cm (12.2 in by 12.6 in).Gulliksen 2023 Runologist Kristel Zilmer, Professor of Written Culture a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rök Runestone
The Rök runestone (; Rundata, Ög 136) is one of the most famous runestones, featuring the longest known runic alphabet, runic inscription in stone. It can now be seen beside the church in Rök, Ödeshög Municipality, Östergötland, Sweden. It is considered the first known piece of written Swedish literature and thus it marks the beginning of the history of Swedish literature.Gustafson, Alrik, Svenska litteraturens historia, 2 volums (Stockholm, 1963). First published as A History of Swedish Literature (American-Scandinavian Foundation, 1961). Chapter 1. About the stone The , tall stone was discovered built into the wall of a church in the 19th century and removed from the church wall a few decades later. The church was built in the 12th century, and it was common to use rune stones as building material for churches. The stone was probably carved in the early 9th century, judging from the main runic alphabet used ("short-twig" runes) and the form of the language. It is cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideographic Rune
Ideographic runes (, , 'term/notion runes') are runes used as ideographs instead of regular letters, that is, instead of representing their phoneme or syllable, they represent their name as a word or term. Such instances are sometimes referred to by way of the modern German loanword (singular ), but the descriptive term "ideographic runes" is also used. Ideographic runes appears to have mainly been used for saving space, but they were also mainly used without inflection. Some potential inscriptions might have used such cryptically. The criteria for the use of ideographic runes and the frequency of their use by ancient rune-writers remains controversial.See discussion in for example : 123–124 and : 17. The topic of has produced much discussion among runologists. Runologist Klaus Düwel has proposed two criteria for the identification of ideographic runes: A graphic argument and a semantic argument. Roman Iron Age (c. 1–350 AD) One of the earliest potential ideographic rune f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
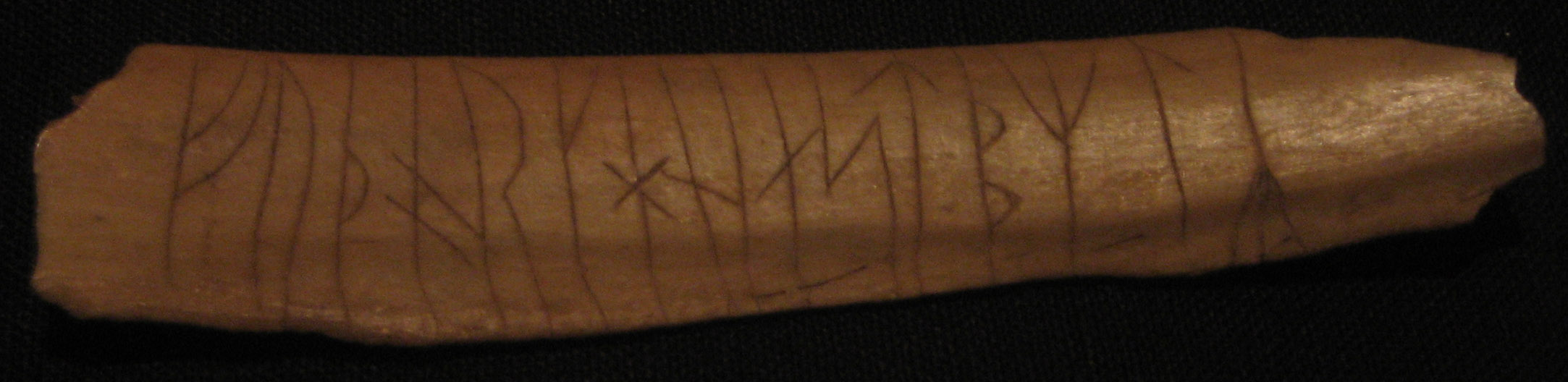
Runic Calendar
A Runic calendar (also Rune staff or Runic almanac) is a perpetual calendar, variants of which were used in Northern Europe until the 19th century. A typical runic calendar consisted of several horizontal lines of symbols, one above the other. Special days like solstices, equinoxes, and celebrations (including Christian holidays and feasts) were marked with additional lines of symbols. Runic calendars were written on parchment Parchment is a writing material made from specially prepared Tanning (leather), untanned skins of animals—primarily sheep, calves and goats. It has been used as a writing medium in West Asia and Europe for more than two millennia. By AD 400 ... or carved onto staves of wood, bone, or horn. The oldest one known, and the only one from the Middle Ages, is a staff from Nyköping, Sweden, believed to date from the 13th century. Most of the several thousand which survive are wooden calendars dating from the 16th and the 17th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letter (alphabet), letters written to represent particular sounds in a spoken language. Specifically, letters largely correspond to phonemes as the smallest sound segments that can distinguish one word from another in a given language. Not all writing systems represent language in this way: a syllabary assigns symbols to spoken syllables, while logographies assign symbols to words, morphemes, or other semantic units. The first letters were invented in Ancient Egypt to serve as an aid in writing Egyptian hieroglyphs; these are referred to as Egyptian uniliteral signs by lexicographers. This system was used until the 5th century AD, and fundamentally differed by adding pronunciation hints to existing hieroglyphs that had previously carried no pronunciation information. Later on, these phonemic symbols also became used to transcribe foreign words. The first fully phonemic script was the Proto-Sinaitic script, also descending from Egyptian hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania, and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, English language, English, is also the world's most List of languages by total number of speakers, widely spoken language with an estimated 2 billion speakers. All Germanic languages are derived from Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic, spoken in Iron Age Scandinavia, History of Germany#Iron Age, Iron Age Northern Germany and along the North Sea and Baltic coasts. The West Germanic languages include the three most widely spoken Germanic languages: English language, English with around 360–400 million native speakers; German language, German, with over 100 million native speakers; and Dutch language, Dutch, with 24 million native speakers. Other West Germanic languages include Afrikaans, an offshoot of Dutch origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |