|
Rudder (software)
Rudder is an open source audit and configuration management utility to help automate system configuration across large IT infrastructures. Rudder relies on a lightweight local agent installed on each managed machine. Rudder is produced by Normation, founded in 2010. Its server-side web interface is written in Scala and its local agent is written in C, and are published as free software under the GNU General Public License 3.0. Features * Host inventory * Feature-complete Web interface * Standardized, reusable policies * Custom Policy ''editor'' * Central reporting and historic information for policy applied to hosts * Grouping based on search queries run against inventory * Automatic updating of such groups (dynamic groups) * Dynamic generation of per-host policies (lessens risk of data leaks from shared policy) * Change Request / Validation * REST API * Git backend History Rudder was created by the founding team of Normation and first released as free software in Oct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CFEngine
CFEngine is an open-source configuration management system, written by Mark Burgess. Its primary function is to provide automated configuration and maintenance of large-scale computer systems, including the unified management of servers, desktops, consumer and industrial devices, embedded networked devices, mobile smartphones, and tablet computers. History CFEngine 1 The CFEngine project began in 1993 as a way for author Mark Burgess (then a post-doctoral fellow of the Royal Society at Oslo University, Norway) to get his work done by automating the management of a small group of workstations in the Department of Theoretical Physics. Like many post-docs and PhD students, Burgess ended up with the task of managing Unix workstations, scripting and fixing problems for users manually. Scripting took too much time, the flavours of Unix were significantly different, and scripts had to be maintained for multiple platforms, drowning in exception logic. After discussing the probl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Administration Software
In computing, the term remote desktop refers to a software- or operating system feature that allows a personal computer's desktop environment to be run remotely off of one system (usually a PC, but the concept applies equally to a server or a smartphone), while being displayed on a separate client device. Remote desktop applications have varying features. Some allow attaching to an existing user's session and "remote controlling", either displaying the remote control session or blanking the screen. Taking over a desktop remotely is a form of remote administration. Overview Remote access can also be explained as the remote control of a computer by using another device connected via the internet or another network. This is widely used by many computer manufacturers and large businesses help desks for technical troubleshooting of their customer's problems. Remote desktop software captures the mouse and keyboard inputs from the local computer (client) and sends them to the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix Package Management-related Software
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley (BSD), Microsoft (Xenix), Sun Microsystems (SunOS/ Solaris), HP/ HPE (HP-UX), and IBM (AIX). In the early 1990s, AT&T sold its rights in Unix to Novell, which then sold the UNIX trademark to The Open Group, an industry consortium founded in 1996. The Open Group allows the use of the mark for certified operating systems that comply with the Single UNIX Specification (SUS). Unix systems are characterized by a modular design that is sometimes called the "Unix philosophy". According to this philosophy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Package Management-related Software
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, and Ubuntu, the latter of which itself consists of many different distributions and modifications, including Lubuntu and Xubuntu. Commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland, and a desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE Plasma. Distributions intended for s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Using The GNU AGPL License
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work. At the lowest programming level, executable code consists of machine language instructions supported by an individual processor—typically a central processing unit (CPU) or a graphics processing unit (GPU). Machine language consists of groups of binary values signifying processor instructions that change the state of the computer from its preceding state. For example, an instruction may change the value stored in a particular storage location in the computer—an effect that is not directly observable to the user. An instruction may also invoke one of many input or output operations, for example displaying some text on a computer screen; causing state changes which should be visible to the user. The processor executes the instructions in the order they are provided, unless it is instruc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtualization Software For Linux
In computing, virtualization or virtualisation (sometimes abbreviated v12n, a numeronym) is the act of creating a virtual (rather than actual) version of something at the same abstraction level, including virtual computer hardware platforms, storage devices, and computer network resources. Virtualization began in the 1960s, as a method of logically dividing the system resources provided by mainframe computers between different applications. An early and successful example is IBM CP/CMS. The control program CP provided each user with a simulated stand-alone System/360 computer. Since then, the meaning of the term has broadened. Hardware virtualization ''Hardware virtualization'' or ''platform virtualization'' refers to the creation of a virtual machine that acts like a real computer with an operating system. Software executed on these virtual machines is separated from the underlying hardware resources. For example, a computer that is running Arch Linux may host a virtual mach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otter (software)
Otter is an infrastructure automation tool, designed by the software company Inedo. Built specifically to support Windows, Otter utilizes Infrastructure as Code to model infrastructure and configuration. Otter provisions and configure servers automatically, without logging in to a command prompt. Key areas Otter focuses on two key areas: * Configuration Automation - Otter allows users to model the configuration of servers, roles, and environments; monitor for drift, schedule changes, and ensure consistency across servers * Orchestration Automation - Otter can spin up cloud servers, build containers, deploy packages, patch servers, or any other multi-server/service automation Otter also has drift monitoring capabilities. It can continuously monitor for server configuration drift, can automatically remediate drift, and can send notification when drift occurs. Key features Otter has a visual, web-based user interface that is designed to "create complex configurations and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Open Source Configuration Management Software
This is a comparison of notable free and open-source configuration management software, suitable for tasks like server configuration, orchestration and infrastructure as code typically performed by a system administrator. Basic properties "Verify mode" refers to having an ability to determine whether a node is conformant with a guarantee of not modifying it, and typically involves the exclusive use of an internal language supporting read-only mode for all potentially system-modifying operations. " Mutual auth" refers to the client verifying the server and vice versa. "Agent" describes whether additional software daemons are required. Depending on the management software these agents are usually deployed on the target system or on one or many central "controller" servers. Although "Agent-less" = "No" is colored red and might seem to be a negative, in fact having an agent can be considered quite advantageous to many. Consider the impact if an agent-less tool loses connecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt (software)
Salt (sometimes referred to as SaltStack) is a Python-based, open-source software for event-driven IT automation, remote task execution, and configuration management. Supporting the "infrastructure as code" approach to data center system and network deployment and management, configuration automation, SecOps orchestration, vulnerability remediation, and hybrid cloud control. History Salt originated from the need for high-speed data collection and task execution for data center systems administrators managing massive infrastructure scale and resulting complexity. The author of Salt, Thomas S. Hatch, had previously created several utilities for IT teams to solve the problem of systems management at scale, but found these and other open source solutions to be lacking. Hatch decided to use the ZeroMQ messaging library to facilitate the high-speed requirements and built Salt using ZeroMQ for all networking layers. In late May 2011 initial progress was made toward the delivery o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
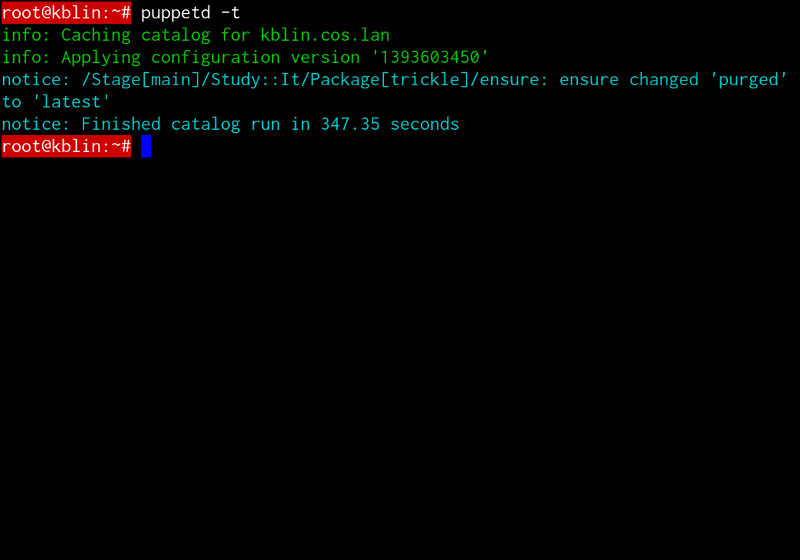
Puppet (software)
In computing, Puppet is a software configuration management tool which includes its own declarative language to describe system configuration. It is a model-driven solution that requires limited programming knowledge to use. Puppet is produced by Puppet Inc., founded by Luke Kanies in 2005. Its primary product, Puppet Enterprise, is a proprietary and closed-source version of its open-source Puppet software. They use Puppet's declarative language to manage stages of the IT infrastructure lifecycle, including the provisioning, patching, configuration, and management of operating system and application components in data centers and cloud infrastructures. Puppet uses an open-core model; its free-software version was released under version 2 of the GNU General Public License (GPL) until version 2.7.0, and later releases use the Apache License, while Puppet Enterprise uses a proprietary license. Puppet and Puppet Enterprise operate on multiple Unix-like systems (including L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)