|
Rubredoxin A
Ruberedoxin A (RubA) is a protein conserved across all studied oxygenic photoautotrophs. Structure As of March 2015 there was no crystal structure of RubA although a structure of the homologous protein from a cryptomonad was determined using NMR. Investigation of the gene however indicates that it differs from other known rubredoxins in being bound to the thylakoid membrane via a C-terminal transmembrane helix. Function An investigation of '' Guillardia theta'' noted that RubA had a similar distribution to Photosystem II (PSII) and immunological experiments indicated the presence of RubA in PSII complexes isolated from ''Spinacia oleracea''. In ''Synechocystis'' sp. PCC 6803 it has been demonstrated that the insertion of an antibiotic cassette into the ''rubA'' gene results in a marked decrease in the amount of PSII present, while the same mutation within ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' and in ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' results in a total absence of PSII. Conversely, another stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinacia Oleracea
Spinach (''Spinacia oleracea'') is a leafy green flowering plant native to central and western Asia. It is of the order Caryophyllales, family Amaranthaceae, subfamily Chenopodioideae. Its leaves are a common edible vegetable consumed either fresh, or after storage using preservation techniques by canning, freezing, or dehydration. It may be eaten cooked or raw, and the taste differs considerably; the high oxalate content may be reduced by steaming. It is an annual plant (rarely biennial), growing as tall as . Spinach may overwinter in temperate regions. The leaves are alternate, simple, ovate to triangular, and very variable in size: long and broad, with larger leaves at the base of the plant and small leaves higher on the flowering stem. The flowers are inconspicuous, yellow-green, in diameter, and mature into a small, hard, dry, lumpy fruit cluster across containing several seeds. In 2018, world production of spinach was 26.3 million tonnes, with China alone accounting f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosystem I
Photosystem I (PSI, or plastocyanin–ferredoxin oxidoreductase) is one of two photosystems in the photosynthetic light reactions of algae, plants, and cyanobacteria. Photosystem I is an integral membrane protein complex that uses light energy to catalyze the transfer of electrons across the thylakoid membrane from plastocyanin to ferredoxin. Ultimately, the electrons that are transferred by Photosystem I are used to produce the moderate-energy hydrogen carrier NADPH. The photon energy absorbed by Photosystem I also produces a proton-motive force that is used to generate ATP. PSI is composed of more than 110 cofactors, significantly more than Photosystem II. History This photosystem is known as PSI because it was discovered before Photosystem II, although future experiments showed that Photosystem II is actually the first enzyme of the photosynthetic electron transport chain. Aspects of PSI were discovered in the 1950s, but the significance of these discoverie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synechococcus
''Synechococcus'' (from the Greek ''synechos'', in succession, and the Greek ''kokkos'', granule) is a unicellular cyanobacterium that is very widespread in the marine environment. Its size varies from 0.8 to 1.5 µm. The photosynthetic coccoid cells are preferentially found in well–lit surface waters where it can be very abundant (generally 1,000 to 200,000 cells per ml). Many freshwater species of ''Synechococcus'' have also been described. The genome of ''S. elongatus'' strain PCC7002 has a size of 3,008,047 bp, whereas the oceanic strain WH8102 has a genome of size 2.4 Mbp. Introduction ''Synechococcus'' is one of the most important components of the prokaryotic autotrophic picoplankton in the temperate to tropical oceans. The genus was first described in 1979, and was originally defined to include "small unicellular cyanobacteria with ovoid to cylindrical cells that reproduce by binary traverse fission in a single plane and lack sheaths". This definition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabidopsis Thaliana
''Arabidopsis thaliana'', the thale cress, mouse-ear cress or arabidopsis, is a small flowering plant native to Eurasia and Africa. ''A. thaliana'' is considered a weed; it is found along the shoulders of roads and in disturbed land. A winter annual with a relatively short lifecycle, ''A. thaliana'' is a popular model organism in plant biology and genetics. For a complex multicellular eukaryote, ''A. thaliana'' has a relatively small genome around 135 mega base pairs. It was the first plant to have its genome sequenced, and is a popular tool for understanding the molecular biology of many plant traits, including flower development and light sensing. Description ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' is an annual (rarely biennial) plant, usually growing to 20–25 cm tall. The leaves form a rosette at the base of the plant, with a few leaves also on the flowering stem. The basal leaves are green to slightly purplish in color, 1.5–5 cm long, and 2–10 mm broad, with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
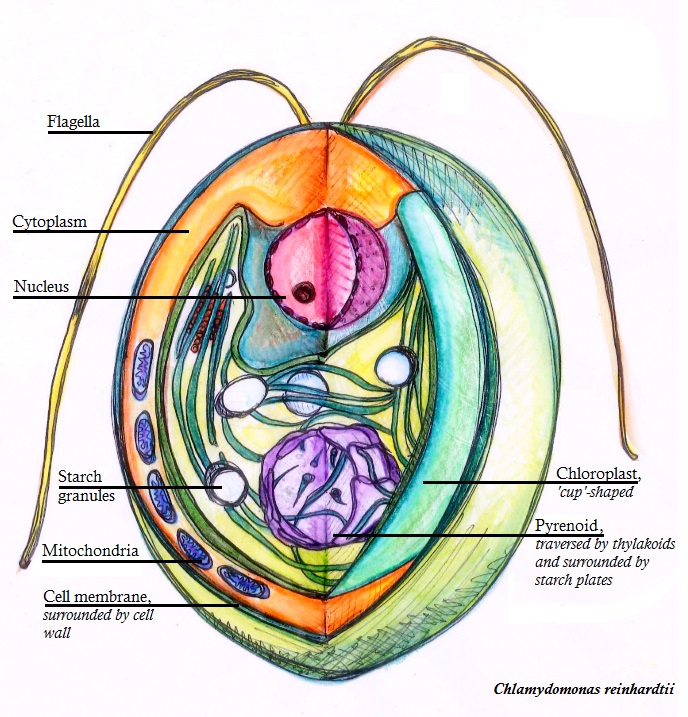
Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii
''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' is a single-cell green alga about 10 micrometres in diameter that swims with two flagella. It has a cell wall made of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins, a large cup-shaped chloroplast, a large pyrenoid, and an eyespot that senses light. '' Chlamydomonas'' species are widely distributed worldwide in soil and fresh water. ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' is an especially well studied biological model organism, partly due to its ease of culturing and the ability to manipulate its genetics. When illuminated, ''C. reinhardtii'' can grow photoautotrophically, but it can also grow in the dark if supplied with organic carbon. Commercially, ''C. reinhardtii'' is of interest for producing biopharmaceuticals and biofuel, as well being a valuable research tool in making hydrogen. History The ''C. reinhardtii'' wild-type laboratory strain c137 (mt+) originates from an isolate collected near Amherst, Massachusetts, in 1945 by Gilbert M. Smith. The species' n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Cassette
In biology, a gene cassette is a type of mobile genetic element that contains a gene and a recombination site. Each cassette usually contains a single gene and tends to be very small; on the order of 500–1000 base pairs. They may exist incorporated into an integron or freely as circular DNA. Gene cassettes can move around within an organism's genome or be transferred to another organism in the environment via horizontal gene transfer. These cassettes often carry antibiotic resistance genes. An example would be the '' kanMX'' cassette which confers kanamycin (an antibiotic) resistance upon bacteria. Integrons Integrons are genetic structures in bacteria which express and are capable of acquiring and exchanging gene cassettes. The integron consists of a promoter, an attachment site, and an integrase gene that encodes a site-specific recombinase There are three classes of integrons described. The mobile units that insert into integrons are gene cassettes. For cassettes that ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synechocystis
''Synechocystis'' is a genus of unicellular, freshwater cyanobacteria in the family Merismopediaceae. It includes a strain, ''Synechocystis'' sp. PCC 6803, which is a well studied model organism. Like all cyanobacteria, ''Synechocystis'' branches on the evolutionary tree from its ancestral root, ''Gloeobacter violaceus''. ''Synechocystis'' is not diazotrophic, and is closely related to another model organism, ''Cyanothece ''Cyanothece'' is a genus of unicellular, diazotrophic, oxygenic photosynthesizing cyanobacteria. Modern organisms and cellular organization In 1976, Jiří Komárek defined the prokaryotic cyanobacteria genus ''Cyanothece'' as distinct from ' ...'' ATCC 51442. It has been suggested that originally ''Synechocystis'' possessed the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen, but lost the genes required for the process. See also * ''Synechocystis'' run-and-tumble References {{Taxonbar, from=Q7662346 Cyanobacteria genera Synechococcales Bacteria genera< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosystem II
Photosystem II (or water-plastoquinone oxidoreductase) is the first protein complex in the light-dependent reactions of oxygenic photosynthesis. It is located in the thylakoid membrane of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. Within the photosystem, enzymes capture photons of light to energize electrons that are then transferred through a variety of coenzymes and cofactors to reduce plastoquinone to plastoquinol. The energized electrons are replaced by oxidizing water to form hydrogen ions and molecular oxygen. By replenishing lost electrons with electrons from the splitting of water, photosystem II provides the electrons for all of photosynthesis to occur. The hydrogen ions (protons) generated by the oxidation of water help to create a proton gradient that is used by ATP synthase to generate ATP. The energized electrons transferred to plastoquinone are ultimately used to reduce to NADPH or are used in non-cyclic electron flow. DCMU is a chemical often used in laboratory sett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phototroph
Phototrophs () are organisms that carry out photon capture to produce complex organic compounds (e.g. carbohydrates) and acquire energy. They use the energy from light to carry out various cellular metabolic processes. It is a common misconception that phototrophs are obligatorily photosynthetic. Many, but not all, phototrophs often photosynthesize: they anabolically convert carbon dioxide into organic material to be utilized structurally, functionally, or as a source for later catabolic processes (e.g. in the form of starches, sugars and fats). All phototrophs either use electron transport chains or direct proton pumping to establish an electrochemical gradient which is utilized by ATP synthase, to provide the molecular energy currency for the cell. Phototrophs can be either autotrophs or heterotrophs. If their electron and hydrogen donors are inorganic compounds (e.g. , as in some purple sulfur bacteria, or , as in some green sulfur bacteria) they can be also called lithot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guillardia Theta
''Guillardia'' is a genus of flagellate cryptomonad algae belonging to the family Geminigeraceae, containing a secondary plastid within a reduced cytoplasmic compartment that contains a vestigial nucleomorph. There is only one characterised member of this genus, ''Guillardia theta''. Genomes ''Guillardia theta'' was the first cryptophyte to have its nuclear genome sequenced. The genome contains 87 Mbp, encoding around 24,840 genes. The complete nucleomorph and plastid genomes have been sequenced, containing 551 kbp and 121 kbp respectively. Optogenetic tools Two anion-conducting channelrhodopsins Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed ... were isolated from ''Guillardia theta'' that hyperpolarize neuronal membrane potential and are potent inhibitors of neural activi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |