|
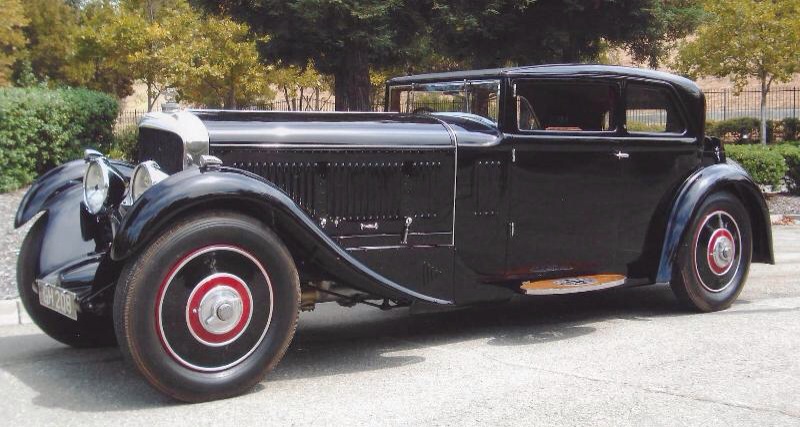
Rover Meteor
The Rover Meteor was a short-lived 2½-litre or 2-litre medium-sized car made by The Rover Company Limited of Meteor Works Coventry. The new 2½-litre model was announced in mid-February 1930 to supplement Rover's Light Twenty which used the same engine and essentially the same chassis. A 2-litre car, a further variant of Rover's Light Twenty was announced in July 1932. Under fiscal rating it was a 16-horsepower car and it was renamed Rover Speed Sixteen in mid-1934 but under either name was out of production before April 1935. The first Meteor was announced a few months into the depression. It is difficult to establish whether models remained in the catalogue from continuing production or they were unsold stock. However it should be remembered it was in this period Rover returned to profit. The name Meteor was abandoned during 1934, the products remaining in Rover's catalogue as Rover Sixteen (a four-door saloon) and Rover Speed Twenty (a four-seater sports tourer), and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
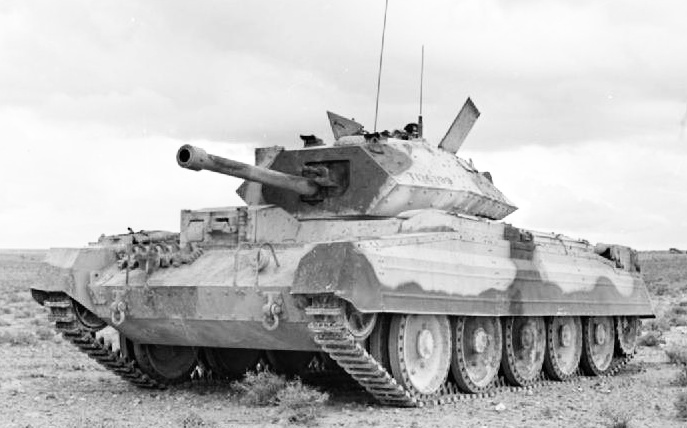
Rolls-Royce Meteor
The Rolls-Royce Meteor later renamed the Rover Meteor is a British tank engine that was developed during the Second World War. It was used in British tanks up to 1964. It was a result of co-operation between Leyland Motors and Rolls-Royce who between them in 1941 had suggested that a specialised de-rated version of the Merlin aero-engine would be highly suitable for use in armoured fighting vehicles. The Meteor was developed from the Merlin by W. A. Robotham and his chassis design and development division at Clan Foundry, Belper, as they were not involved in aero-engine work and his engineers were under-used. With the aid of engineers from Leyland, who were engaged in tank work, he considered RR's two V12s; the Kestrel, while having more power than the existing "Liberty" or Meadows engines, did not provide the desirable 20 bhp per ton (producing only 475 bhp on "pool" petrol) required, so the 1,030 bhp (770 kW) Merlin III was chosen. Also, the Merlin was being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
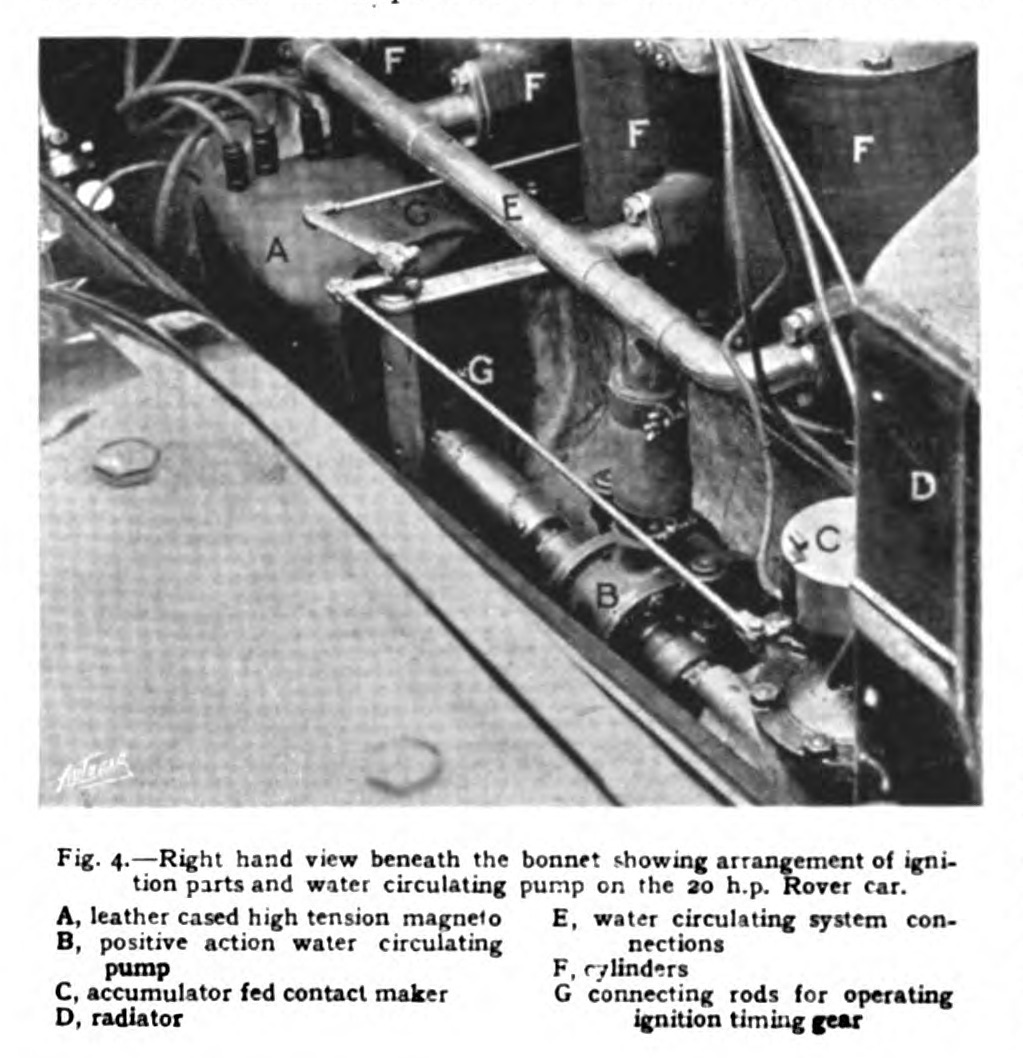
Rover 16
The Rover 16/50 and Rover 16 are mid-sized cars which were produced by Rover from 1926 to 1929 and non-continuously from 1936 to 1947 respectively. Rover initially responding to requests for a more powerful engine for their four-cylinder 14 hp with the 16/50. It remained available into 1929 finishing its run soon after the demise of its smaller bore 14 hp twin. Meanwhile, Rover had begun to provide a six-cylinder 16 hp offering, their 2-litre, in its turn succeeded by their 16 hp ''Meteor''. Production of a considerably revised replacement for Rover's 16 hp ''Meteor'' was resumed under the name Rover 16 in mid 1936 and, with a gap for World War II, the 16 remained in Rover's catalogue until it was replaced by the Rover 75 in early 1948. Rover 16/50 Announced 21 May 1926 to supplement their 14/45 the 16/50 engine had a larger bore and was now rated at 16 rather than 14 hp for tax purposes. Its cubic capacity was 2.4-litres instead of 2.1-litres. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nelson Bohnalite
Nelson-Bohnalite was the name of a piston developed by Adolph Lincoln Nelson in the 1930s and 1940s. The pistons were licensed to Bohn Aluminum and sold to all the major auto manufacturers at the time. These were some of the first pistons to use an aluminum body with a steel strut, allowing for the weight of aluminum and the strength of steel where the piston moves on the piston rod. Many then existing brands of autos used this type of piston in the mid-1930s: Auburn, Graham, Hupmobile Hupmobile was an automobile built from 1909 through 1939 by the Hupp Motor Car Company of Detroit. The prototype was developed in 1908. History Founding In 1909, Bobby Hupp co-founded Hupp Motor Car Company, with Charles Hastings, for ..., Nash, Packard, Pierce-Arrow and Studebaker. (from Motors Handbook, 14th edition, 1937) External links * Engine technology {{Auto-tech-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vauxhall 23-60
The Vauxhall 23-60 is a four or five-seater touring car manufactured by Vauxhall of Luton Luton () is a town and unitary authority with borough status, in Bedfordshire, England. At the 2011 census, the Luton built-up area subdivision had a population of 211,228 and its built-up area, including the adjacent towns of Dunstable a ... that was announced in July 1922. The 23-60's standard tourer Kington body was described as "preserving that greyhound look so characteristic of the Vauxhall car". It shared many parts with Vauxhall's much more powerful 30-98. The 23-60 replaced the Vauxhall 25 which had given sterling service during World War I and from which the 23-60 was developed. Its reliability made Vauxhall's name for dependability. The 23-60 remained in production until the introduction of the ultra-smooth six-cylinder Burt-McCollum type single-sleeve-valve Vauxhall 25-70 was announced in October 1925. General Motors took control of Vauxhall 16 November 1925. Desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balance Shaft
Balance shafts are used in piston engines to reduce vibration by cancelling out unbalanced dynamic forces. The counter balance shafts have eccentric weights and rotate in opposite direction to each other, which generates a net vertical force. The balance shaft was invented and patented by British engineer Frederick W. Lanchester in 1907. It is most commonly used in inline-four and V6 engines used in automobiles and motorcycles. Overview The operating principle of a balance shaft system is that two shafts carrying identical eccentric weights rotate in opposite directions at twice the engine speed. The phasing of the shafts is such that the centrifugal forces produced by the weights cancel the vertical second-order forces (at twice the engine RPM) produced by the engine. The horizontal forces produced by the balance shafts are equal and opposite, and so cancel each other. The balance shafts do not reduce the vibrations experienced by the crankshaft. Applications Two-cylinder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick W
Frederick may refer to: People * Frederick (given name), the name Nobility Anhalt-Harzgerode *Frederick, Prince of Anhalt-Harzgerode (1613–1670) Austria * Frederick I, Duke of Austria (Babenberg), Duke of Austria from 1195 to 1198 * Frederick II, Duke of Austria (1219–1246), last Duke of Austria from the Babenberg dynasty * Frederick the Fair (Frederick I of Austria (Habsburg), 1286–1330), Duke of Austria and King of the Romans Baden * Frederick I, Grand Duke of Baden (1826–1907), Grand Duke of Baden * Frederick II, Grand Duke of Baden (1857–1928), Grand Duke of Baden Bohemia * Frederick, Duke of Bohemia (died 1189), Duke of Olomouc and Bohemia Britain * Frederick, Prince of Wales (1707–1751), eldest son of King George II of Great Britain Brandenburg/Prussia * Frederick I, Elector of Brandenburg (1371–1440), also known as Frederick VI, Burgrave of Nuremberg * Frederick II, Elector of Brandenburg (1413–1470), Margrave of Brandenburg * Frederick William, Elector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagion began around September and led to the Wall Street stock market crash of October 24 (Black Thursday). It was the longest, deepest, and most widespread depression of the 20th century. Between 1929 and 1932, worldwide gross domestic product (GDP) fell by an estimated 15%. By comparison, worldwide GDP fell by less than 1% from 2008 to 2009 during the Great Recession. Some economies started to recover by the mid-1930s. However, in many countries, the negative effects of the Great Depression lasted until the beginning of World War II. Devastating effects were seen in both rich and poor countries with falling personal income, prices, tax revenues, and profits. International trade fell by more than 50%, unemployment in the U.S. rose to 23% and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coventry
Coventry ( or ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city in the West Midlands (county), West Midlands, England. It is on the River Sherbourne. Coventry has been a large settlement for centuries, although it was not founded and given its city status until the Middle Ages. The city is governed by Coventry City Council. Historic counties of England, Formerly part of Warwickshire until 1451, Coventry had a population of 345,328 at the 2021 census, making it the tenth largest city in England and the 12th largest in the United Kingdom. It is the second largest city in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, after Birmingham, from which it is separated by an area of Green belt (United Kingdom), green belt known as the Meriden Gap, and the third largest in the wider Midlands after Birmingham and Leicester. The city is part of a larger conurbation known as the Coventry and Bedworth Urban Area, which in 2021 had a population of 389,603. Coventry is east-south-east of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rover Light Six
The Rover Light Six was a narrower lightweight short wheelbase variant of their Two-litre sports saloon produced from 1929 to 1930 by the Rover Company of Coventry. The following season it was sold with a 2½-litre 20 hp engine under the name Rover Light Twenty. Overview Announced in October 1929 the Rover Light Six was one of the Rover cars manufactured when Spencer and Maurice Wilks, who joined Rover's team in 1929 and 1930, introduced new management practices and engineering techniques to Rover. Engine The Light Six was powered by a watercooled 2 L straight-6 OHV engine with an output of 45 bhp at 3600 rpm designed by Peter Poppe, which provided the Two-litre saloon a maximum speed of 60 mph (97 km/h). The bore of 65 mm put the engine into the 16 hp taxation class. The car was supplied with a three-speed gearbox controlled by a lever in the centre of the car. The lever was flexible, operated in a gate and had a stop to avoid engaging rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corsica Coachworks
Corsica Coachworks was a small British coachbuilding business founded in 1920 just after World War I. They were builders of bespoke car bodies, employing no in-house designer. They realised customers' designs for them. Almost every Corsica body is unique. History Corsica Coachworks was run by Charles Henry Stammers (1884-1945), his brothers-in-law, Joseph and Robert Lee, and Albert Wood. The company name referred to the address of its original premises in Corsica Street, Highbury ( Islington, North London). After a few years the business relocated further out of town to an alleyway off The Broadway, Cricklewood (Northwest London). Throughout its existence Corsica Coachworks remained small, never employing more than 20 people. Products Most Corsica bodies were fitted to the more sporting types of car, with bodies produced for Daimler, Bentley, Bugatti, Alfa Romeo, British Salmson, Frazer Nash, Humber, Lea-Francis, Rolls-Royce and Wolseley models. At least 14 Bugatti T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rover 20
The Rover 20 was a new medium sized car announced by Rover in June 1907. It was a production version of the car which won the Isle of Man Tourist Trophy Race in 1906. However artillery wood wheels were fitted instead of the (still recommended) wire wheels used in the race and the longer wheelbase allowed the engine to be kept out of the passenger area. The prototype's engine came back beneath the petrol tank. With a few breaks Rover kept a premium 20 tax horsepower car in their catalogue until the outbreak of war in 1939. In the early 1950s an equivalent model returned to the market, the 2.6-litre Rover 90 and later Rover's 3-litre. 1907 model Engine The engine was very much based on the Rover 16's but the bore had been increased 2mm. There were a number of minor improvements. The water inlet pipe was now to the other side of the engine to provide better access to the valves and tappets. The oil box (reservoir) was now at the left rear of the engine so a catcher for oil throw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Startix
The Startix automatic engine starting mechanism was a relay in a small box added to the vehicle's electrical system. It automatically started an engine from cold or if stalled. It was supplied to vehicle manufacturers in the mid 1930s and later as an aftermarket accessory — in the USA by Bendix Aviation Corporation Eclipse Machine Division and in UK by Joseph Lucas & Son both of which businesses made electric self-starters. Such devices are now part of the engine management systems which switch off and on to conserve fuel. Operation The switching on of the ignition starts the engine and, in addition, automatically restarts the engine whenever it stalls, as long as the ignition is switched on. As soon as the ignition is switched on current flows to the first ''Startix'' solenoid and current flows from battery to starter. The generator delivers current once the engine starts and part of it goes to a second ''Startix'' solenoid that switches off the current from battery to starter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(15414874475)_(2).jpg)

_031.jpg)