|
Rosetta Stone Decree
The Rosetta Stone decree, or the Decree of Memphis, is a Ptolemaic decree issued at Memphis, Egypt, Memphis by a council of priests confirming the royal cult of Ptolemy V in 196 BC. It is one of a series that affirm the royal cult of the king. It was recorded in Egyptian hieroglyphs, Egyptian Demotic and Ancient Greek, on the Rosetta Stone and the Nubayrah Stele, among others. The bilingual and triscriptual nature of the inscription was key to the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs. Context The decree was issued during a turbulent period in Egyptian history. Ptolemy V Epiphanes reigned from 204 to 181 BC, the son of Ptolemy IV Philopator and his wife and sister Arsinoe. He had become ruler at the age of five after the sudden death of both of his parents, who were murdered in a conspiracy that involved Ptolemy IV's mistress Agathoclea (mistress of Ptolemy IV), Agathoclea, according to contemporary sources. The conspirators effectively ruled Egypt as Ptolemy V's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus III The Great
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίοχος ὁ Μέγας ; 3 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 223 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of western Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in April/June 223 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for "Great King"), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against Rome. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermopolis
Hermopolis ( grc, Ἑρμούπολις ''Hermoúpolis'' "the City of Hermes", also ''Hermopolis Magna'', ''Hermoû pólis megálẽ'', egy, ḫmnw , Egyptological pronunciation: "Khemenu"; cop, Ϣⲙⲟⲩⲛ ''Shmun''; ar, الأشمونين) was a major city in antiquity, located near the boundary between Lower and Upper Egypt. A provincial capital since the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Hermopolis developed into a major city of Roman Egypt, and an early Christian center from the third century. It was abandoned after the Muslim conquest but was restored as both a Latin Catholic (meanwhile suppressed) and a Coptic Orthodox titular see. Its remains are located near the modern town of el Ashmunein (from the Coptic name) in Mallawi, Minya Governorate, Egypt. Name ''Khemenu'' ('), the Egyptian language name of the city, means "Eight-Town", after the Ogdoad, a group of eight "primordial" deities whose cult was situated there. The name survived as Coptic ''Shmun'', from which the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demotic (Egyptian)
Demotic (from grc, δημοτικός ''dēmotikós'', 'popular') is the ancient Egyptian script derived from northern forms of hieratic used in the Nile Delta, and the stage of the Egyptian language written in this script, following Late Egyptian and preceding Coptic. The term was first used by the Greek historian Herodotus to distinguish it from hieratic and hieroglyphic scripts. By convention, the word "Demotic" is capitalized in order to distinguish it from demotic Greek. Script The Demotic script was referred to by the Egyptians as ', "document writing," which the second-century scholar Clement of Alexandria called , "letter-writing," while early Western scholars, notably Thomas Young, formerly referred to it as "Enchorial Egyptian." The script was used for more than a thousand years, and during that time a number of developmental stages occurred. It is written and read from right to left, while earlier hieroglyphs could be written from top to bottom, left to right, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assmann
Assmann, Aßmann or Assman is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Aleida Assmann (born 1947), professor of Egyptology, literary and cultural studies * Arno Assmann (1908–1979), German actor and film director * Charles Assmann (born 1972), Canadian football player * Dick Assman (1934–2016), Canadian petrol station owner * Fabián Assmann (born 1986), Argentine football goalkeeper * Hans Assmann (1923–1998), alleged KGB intelligence officer * Hans Erasmus Aßmann (1646–1699), German poet, statesman and translator * Jan Assmann (born 1938), German Egyptologist * Katja Aßmann (born 1971), German art historian * Peter Assmann (born 1963), Austrian writer and visual artist * Richard Assmann (1845–1918), meteorologist * Sarah M. Assmann, American biologist * William F. Assmann (1862–1920), balloonist See also * "The Assman", a working title of "The Fusilli Jerry "The Fusilli Jerry" is the 107th episode of the sitcom ''Seinfeld''. Featuring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adikhalamani
__NOTOC__ Adikhalamani was a Kushite King of Meroe dating to the 2nd century BCE. Adikhalamani was the successor of King Arqamani and was later succeeded by a king whose name has only partially survived: (...)mr(...)t. He is said to be contemporary with an Egyptian revolt dated to ca. 207-186 BCE. During this revolt a ruler, Horwennefer (who may have been a Nubian) took control of Thebes and revolted against Ptolemy IV Philopator. The revolt ended ca. 186 BCE when Ankhwennefer (his successor or more likely Horwennefer with a different nomen) was captured and executed. by Chris Bennett, retrieved June 2, 2010 Titles * |
Hugronaphor
Horwennefer ( egy, ḥr-wnn-nfr "Horus- Onnophris"; grc, Άροννώφρις ) was an Upper Egyptian who led Upper Egypt in secession from the rule of Ptolemy IV Philopator in 205 BC. No monuments are attested to this king but along with his successor Ankhwennefer (also known as ''Chaonnophris'' or ''Ankhmakis''Günther Hölbl, ''History of the Ptolemaic Empire'', Routledge, 2000, pp. 155ff.) he held a large part of Egypt until 186 BC. A graffito dating to about 201 BC on a wall of the mortuary Temple of Seti I at Abydos, in which his name is written (), is an attestation to the extent of his influence. He appears to have died before 197 BC. The Abydene graffito, one of the few documents remaining from his reign, is written in Egyptian using Greek letters, the oldest testimony of a development which would end in the Coptic script replacing the native Egyptian demotic. References Bibliography * ''The Jews of Egypt: From Rameses II to Emperor Hadrian'' by Joseph Mél ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
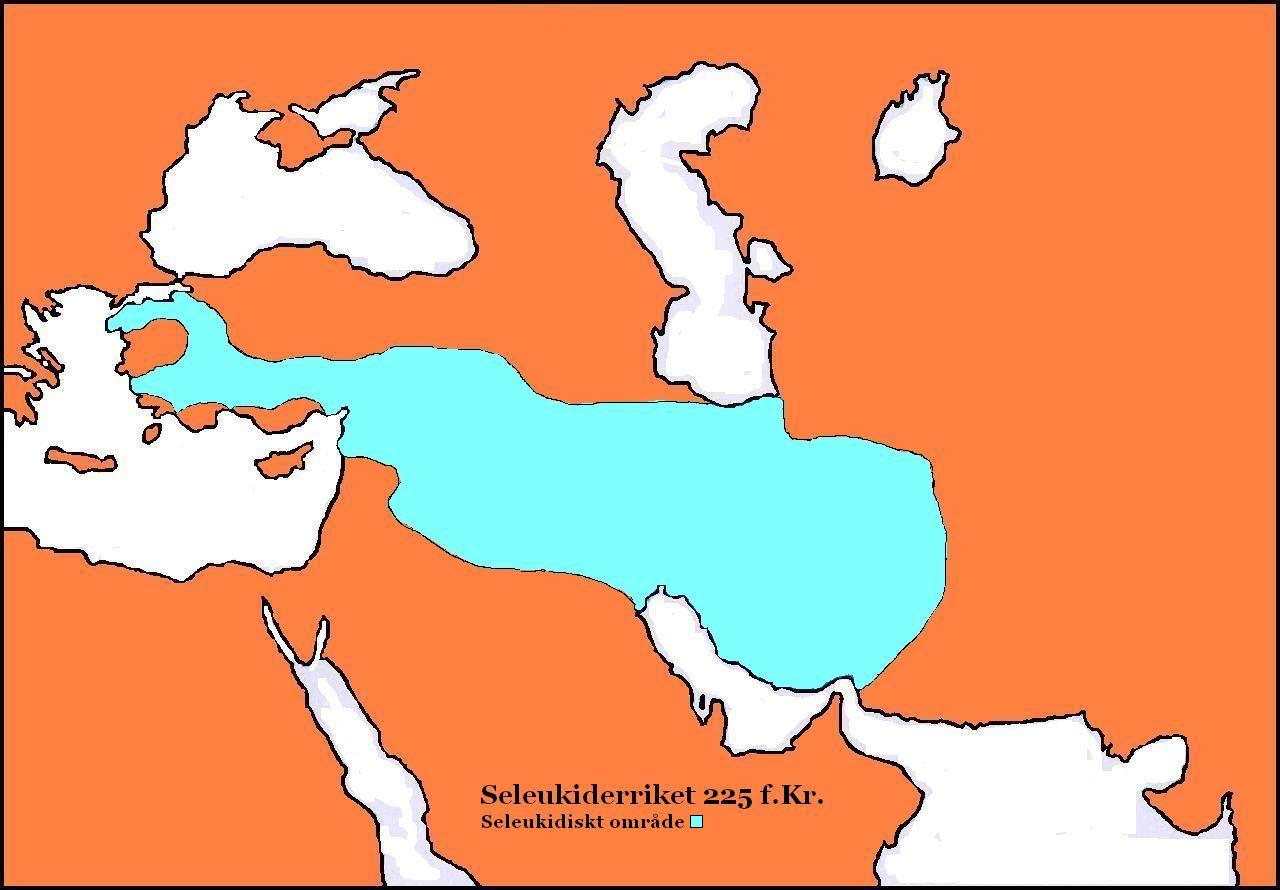
Seleucids
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire originally founded by Alexander the Great. After receiving the Mesopotamian region of Babylonia in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Persian Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that had covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, and what are now modern Iraq, Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide variet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Hebrew language#Modern Hebrew, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian vocalization, Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous southern part of the modern States of State of Palestine, Palestine and Israel. The name originates from the Hebrew name Judah (son of Jacob), Yehudah, a son of the biblical Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch Jacob, Jacob/Israel, with Yehudah's progeny forming the biblical Israelite tribe of Judah (Yehudah) and later the associated Kingdom of Judah. Related nomenclature continued to be used by the Babylonians, Achaemenid Empire, Persian, Hellenistic period, Hellenistic, and Roman Empire, Roman periods as the Yehud (Babylonian province), Babylonian and Yehud (Persian province), Persian Yehud, Hasmonean Kingdom, Hasmonean Kingdom of Judea, and consequently Herodian Kingdom, Herodian and Judea (Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coele-Syria
Coele-Syria (, also spelt Coele Syria, Coelesyria, Celesyria) alternatively Coelo-Syria or Coelosyria (; grc-gre, Κοίλη Συρία, ''Koílē Syría'', 'Hollow Syria'; lat, Cœlē Syria or ), was a region of Syria (region), Syria in classical antiquity. It probably derived from the Aramaic word for all of the Syria (region), region of Syria, but it was most often applied to the Beqaa Valley between the Mount Lebanon, Lebanon and the Anti-Lebanon Mountains, Anti-Lebanon mountain ranges. The area is now part of the modern-day Syria and Lebanon. Name It is widely accepted that the term Coele is a transcription of Aramaic ''kul'', meaning "all, the entire", such that the term originally identified ''all'' of Syria.A History of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
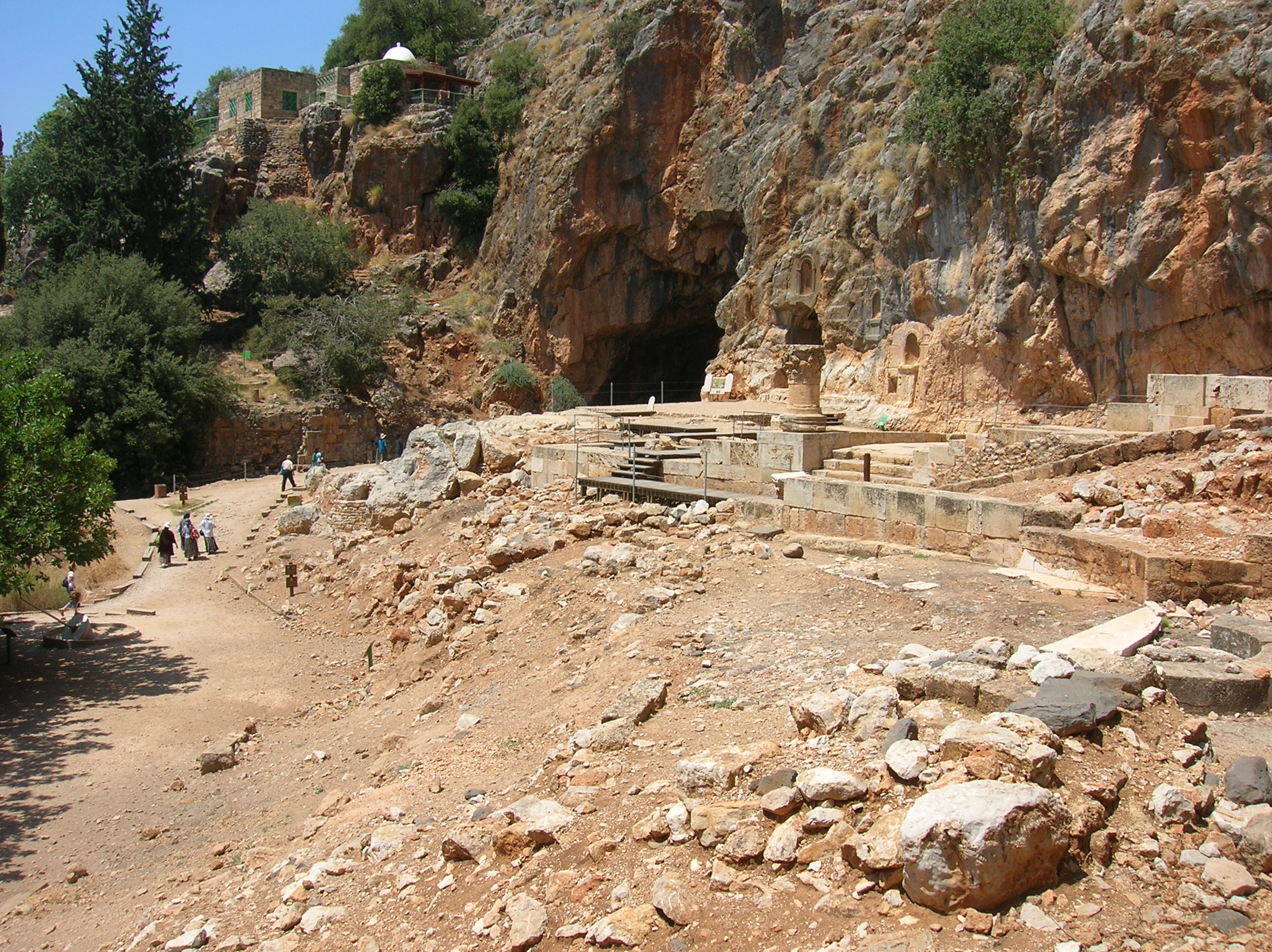
Battle Of Panium
The Battle of Panium (also known as Paneion, grc, Πάνειον, or Paneas, Πανειάς) was fought in 200 BC near Paneas (Caesarea Philippi) between Seleucid and Ptolemaic forces as part of the Fifth Syrian War. The Seleucids were led by Antiochus III the Great, while the Ptolemaic army was led by Scopas of Aetolia. The Seleucids achieved a complete victory, annihilating the Ptolemaic army and conquering the province of Coele-Syria. The Ptolemaic Kingdom never recovered from its defeat at Panium and ceased to be an independent great power. Antiochus secured his southern flank and began to concentrate on the looming conflict with the Roman Republic. Background In 202 BC, Ptolemy son of Thraseas, the Ptolemaic governor of Coele-Syria, defected to the side of Antiochus III the Great, the ruler of the Seleucid Empire. Antiochus invaded and occupied most of the province, including the city of Gaza, by the autumn of 201 BC, when he returned to winter quarters in Syria. The Pt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |