|
Rosendo Balinas
Rosendo Carreon Balinas Jr. (September 10, 1941 – September 24, 1998) was a chess grandmaster from the Philippines. FIDE awarded him the International Master title in 1975 and the International Grandmaster title in 1976. He was Philippines' second chess grandmaster. Balinas was a lawyer by profession, as well as an award winning chess writer and journalist. Chess career Balinas was considered the strongest Asian player during the 1960s and 1970s, before the emergence of compatriot Eugenio Torre. Balinas won international chess tournaments in Hong Kong, Singapore, Manila, and Odessa, USSR during the period. At the 1966 17th Chess Olympiad in Havana, Cuba, Balinas scored 15½ points out of 20 games (.775) and was awarded the individual silver medal award, behind gold medalist, former world champion Mikhail Tal, who scored 11 points out of 13 games (.846). In the 1967 Meralco "Beat Bobby Fischer" match series in Manila, of the top 10 Filipino players, Balinas was the only then Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to distinguish it from related games, such as xiangqi (Chinese chess) and shogi (Japanese chess). The recorded history of chess goes back at least to the emergence of a similar game, chaturanga, in seventh-century India. The rules of chess as we know them today emerged in Europe at the end of the 15th century, with standardization and universal acceptance by the end of the 19th century. Today, chess is one of the world's most popular games, played by millions of people worldwide. Chess is an abstract strategy game that involves no hidden information and no use of dice or cards. It is played on a chessboard with 64 squares arranged in an eight-by-eight grid. At the start, each player controls sixteen pieces: one king, one queen, two rooks, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lev Polugaevsky
Lev Abramovich Polugaevsky ( rus, Лев Абрамович Полугаевский, p=pəlʊɡɐˈjefskʲɪj; 20 November 1934 – 30 August 1995) was a Soviet chess player. He was awarded the title of International Grandmaster by FIDE in 1962 and was a frequent contender for the World Championship, although he never achieved that title. He was one of the strongest players in the world from the early 1960s until the late 1980s, as well as a distinguished author and opening theorist whose contributions in this field remain important to the present day. Career Lev Polugaevsky was born in Mogilev, in the Soviet Union (now Mahilyow, Belarus), and, after being evacuated during the Second World War, grew up in Kuybyshev (modern Samara). He began playing chess around the age of 10. In 1948, he attracted the attention of Candidate Master Alexy Ivashin, who became his first teacher. International Master Lev Aronin, who lived in Moscow but had family in Kuybyshev, eventually becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Opening
A chess opening or simply an opening is the initial stage of a chess game. It usually consists of established theory; the other phases are the middlegame and the endgame. Many opening sequences have standard names such as the "Sicilian Defense". ''The Oxford Companion to Chess'' lists 1,327 named openings and variants, and there are many others with varying degrees of common usage. Opening moves that are considered standard are referred to as "book moves", or simply "book". When a game begins to deviate from known opening theory, the players are said to be "out of book". In some openings, "book" lines have been worked out for over 30 moves, as in the classical King's Indian Defense and in the Najdorf variation of the Sicilian Defense. Professional chess players spend years studying openings, and continue doing so throughout their careers, as opening theory continues to evolve. Players at the club level also study openings but the importance of the opening phase is smaller t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
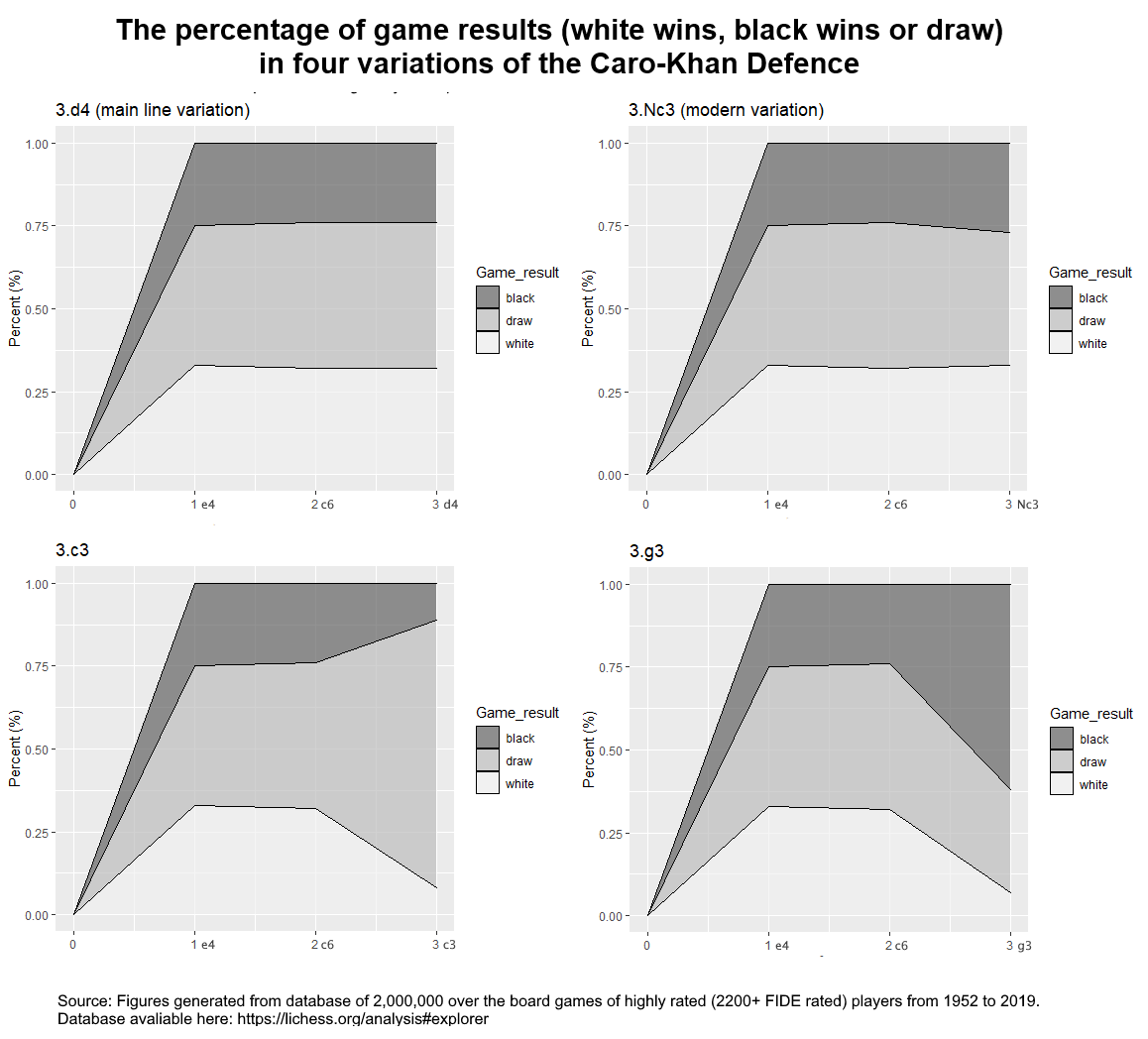
Caro–Kann Defence
The Caro–Kann Defence is a chess opening characterised by the moves: :1. b:Chess Opening Theory/1. e4, e4 b:Chess Opening Theory/1. e4/1...c6, c6 The Caro–Kann is a common defence against the King's Pawn Opening. It is classified as a Semi-Open Game, like the Sicilian Defence and French Defence, although it is thought to be more solid and less dynamic than either of those openings. It often leads to good chess endgame, endgames for Black, who has the better pawn structure. It allows Black to circumvent enormous bodies of theory in 1.e4 openings such as the Ruy Lopez and the Sicilian Defence. Unlike its sister opening, the French Defence, the Caro–Kann does not hinder the development of Black's light-squared bishop. However, it comes at the cost of a Tempo (chess), tempo because Black has to play 1...c6 before pushing the pawn to c5, whereas Black can push c7–c5 in one move in the French Defence. White can combat the Caro–Kann in several different ways, often gaining a sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), is the second-largest city in Russia. It is situated on the Neva River, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea, with a population of roughly 5.4 million residents. Saint Petersburg is the fourth-most populous city in Europe after Istanbul, Moscow and London, the most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's northernmost city of more than 1 million residents. As Russia's Imperial capital, and a historically strategic port, it is governed as a federal city. The city was founded by Tsar Peter the Great on 27 May 1703 on the site of a captured Swedish fortress, and was named after apostle Saint Peter. In Russia, Saint Petersburg is historically and culturally associated with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reuben Fine
Reuben C. Fine (October 11, 1914 – March 26, 1993) was an American chess player, psychologist, university professor, and author of many books on both chess and psychology. He was one of the strongest chess players in the world from the mid-1930s until his retirement from chess in 1951. He was granted the title of International Grandmaster by FIDE in 1950, when titles were introduced. Fine's best result was his equal first place in the 1938 AVRO tournament, one of the strongest tournaments of all time. After the death of world champion Alexander Alekhine in 1946, Fine was one of six players invited to compete for the World Championship in 1948. He declined the invitation, however, and virtually retired from serious competition around that time, although he did play a few events until 1951. Fine won five medals (four gold) in three Chess Olympiads. He won the US Open all seven times he entered (1932, 1933, 1934, 1935, 1939, 1940, 1941). He was the author of several ches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow 1936 Chess Tournament
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow grew to become a prosperous and powerful city that served as the capital of the Grand Duchy that bears its name. When the Grand Duchy of Moscow evolved into the Tsardom of Russia, Moscow remained the political and economic center for most of the Tsardom's history. When the Ts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Raúl Capablanca
José Raúl Capablanca y Graupera (19 November 1888 – 8 March 1942) was a Cuban chess player who was world chess champion from 1921 to 1927. A chess prodigy, he is widely renowned for his exceptional endgame skill and speed of play. Capablanca was born in 1888 in Havana. He beat Cuban champion Juan Corzo in a match on 17 November 1901, two days before his 13th birthday. His victory over Frank Marshall in a 1909 match earned him an invitation to the 1911 San Sebastian tournament, which he won ahead of players such as Akiba Rubinstein, Aron Nimzowitsch and Siegbert Tarrasch. Over the next several years, Capablanca had a strong series of tournament results. After several unsuccessful attempts to arrange a match with then world champion Emanuel Lasker, Capablanca finally won the world chess champion title from Lasker in 1921. Capablanca was undefeated from 10 February 1916 to 21 March 1924, a period that included the world championship match with Lasker. Capablanca lost the ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgi Tringov
Georgi Petrov Tringov ( bg, Георги Пеев Трингов) (7 March 1937 – 2 July 2000) was a Grandmaster (chess), Grandmaster of chess from Bulgaria. He won the Bulgarian Chess Championship, Bulgarian national chess championship in 1963, the year he was awarded the Grandmaster title, only the second Bulgarian player thus honored (after Milko Bobotsov). He was active mainly during the 1960s and 1970s and qualified for the 1964 Interzonal stage of the process for selecting a challenger for the World Chess Championship, but finished fifteenth in the World Chess Championship 1966#1964 Interzonal Tournament, Interzonal held in Amsterdam, so did not advance to the World Chess Championship 1966#1965 Candidates matches, Candidates matches held in 1965. Tringov had numerous successes in international tournaments to his credit, including first place at Vrsac 1973. Tringov placed fifth in the 1955 World Junior Chess Championship, World Junior Championship. He played for Bulgaria in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Bronstein
David Ionovich Bronstein (russian: Дави́д Ио́нович Бронште́йн; February 19, 1924 – December 5, 2006) was a Soviet and Ukrainian chess player. Awarded the title of International Grandmaster by FIDE in 1950, he narrowly missed becoming World Chess Champion in 1951. Bronstein was one of the world's strongest players from the mid-1940s into the mid-1970s, and was described by his peers as a creative genius and master of tactics. Also a renowned chess writer, his book ''Zurich International Chess Tournament 1953'' is widely considered one of the greatest chess books ever written. Early life David Bronstein was born in Bila Tserkva, Ukrainian SSR, Soviet Union, to Jewish parents. Growing up in a poor family, he learned chess at age six from his grandfather. As a youth in Kyiv, he was trained by the renowned International Master Alexander Konstantinopolsky. He finished second in the Kyiv Championship when he was only 15, and achieved the Soviet Master t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Tseitlin
Mark Tseitlin ( he, מארק צייטלין; russian: Марк Данилович Цейтлин, translit=Mark Danilovich Tseitlin; 23 September 1943 – 25 January 2022) was a Soviet-born Israeli chess player. He was awarded the title of International Master in 1978 and that of Grandmaster in 1997. Tseitlin was a four-time European seniors champion. Career Tseitlin got acquainted with chess in Leningrad's Pioneers Palace. He was self-taught, having studied without a coach. He was Leningrad champion in 1970, 1975, 1976, and jointly in 1978. During his playing career he defeated Viktor Korchnoi four times and beat many famous grandmasters. His best tournament achievements include first place at Polanica Zdroj 1978 (ahead of Andersson), and second at Trnava 1979 (after Plachetka). Tseitlin was the many-time Beer-Sheva chess club champion. Tseitlin won the European Seniors Championship four times: in 2004 in Arvier, 2005 in Bad Homburg, 2008 in Dresden and 2013 in Plovdiv. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Savon
Vladimir Andreyevich Savon ( ua, Володи́мир Андрійович Саво́н; 26 September 1940 – 1 June 2005) was a Ukrainian chess player. He was awarded the title of Grandmaster by FIDE in 1973. Savon shared the Ukrainian Chess Championship in 1969 and won the USSR Championship in 1971. He competed in the 1972 Chess Olympiad. Biography Born in Chernihiv, he learned how to play at the age of 13. Savon competed in the Soviet championship eleven times, from 1961 (at age 21) to the last championship in 1991. His best result was his first place in the 1971 championship with an undefeated 15/21. Only an international master, he finished 1.5 points ahead of former world champions Mikhail Tal and Vasily Smyslov. Future world champion Anatoly Karpov finished another half point back.Cafferty and Taimanov, p. 154. Taimanov and Bernard Cafferty, in their book on the Soviet championships, described Savon's win "the least plausible result for decades". One possible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |