|
Rosary Of The Philosophers
''The Rosary of the Philosophers'' (''Rosarium philosophorum sive pretiosissimum donum Dei'') is a 16th-century alchemical treatise. It was published in 1550 as part II of ''De Alchimia Opuscula complura veterum philosophorum'' (Frankfurt). The term ''rosary'' in the title is unrelated to the Catholic prayer beads; it refers to a "rose garden", metaphoric of an anthology or collection of wise sayings. The 1550 print includes a series of 20 woodcuts with German-language captions, plus a title page showing a group of philosophers disputing about the production of the '' lapis philosophorum''. Some of the woodcut images have precedents in earlier (15th-century) German alchemical literature, especially in the '' Buch der heiligen Dreifaltigkeit'' (ca. 1410) which has the direct precedents of woodcuts 10, 17 and 19, allegorical of the complete ''hieros gamos'', nrs. 10 and 17 in the form of the "Hermetic androgyne" and nr. 19 in terms of Christian iconography, showing Mary flanked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winged Sun Alchemical
A wing is a type of fin that produces both Lift (force), lift and drag while moving through air. Wings are defined by two shape characteristics, an airfoil section and a planform (aeronautics), planform. Wing efficiency is expressed as lift-to-drag ratio, which compares the benefit of lift with the air resistance of a given wing shape, as it flies. Aerodynamics is the study of wing performance in air. Equivalent Foil (fluid mechanics), foils that move through water are found on Hydrofoil, hydrofoil power vessels and Sailing hydrofoil, foiling sailboats that lift out of the water at speed and on submarines that use diving planes to point the boat upwards or downwards, while running submerged. Hydrodynamics is the study of foil performance in water. Etymology and usage The word "wing" from the Old Norse ''vængr'' for many centuries referred mainly to the foremost limb (anatomy), limbs of birds (in addition to the architectural aisle). But in recent centuries the word's meaning ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
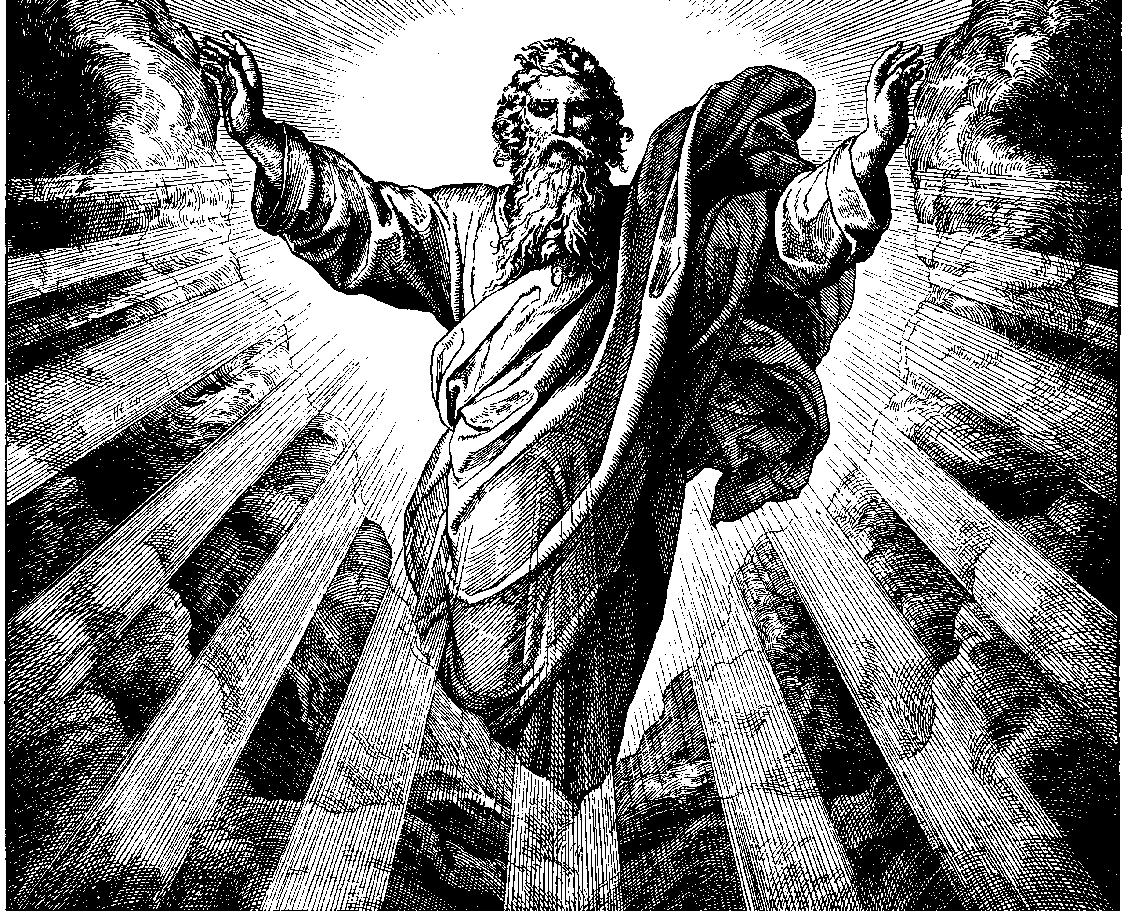
God The Son
God the Son (, ; ) is the second Person of the Trinity in Christian theology. According to Christian doctrine, God the Son, in the form of Jesus Christ, is the incarnation of the eternal, pre-existent divine ''Logos'' (Koine Greek for "word") through whom all things were created. Although the precise term "God the Son" does not appear in the Bible, it serves as a theological designation expressing the understanding of Jesus as a part of the Trinity, distinct yet united in essence with God the Father and God the Holy Spirit (the first and third Persons of the Trinity respectively). Sources The phrase "God the Son" does not appear in the Bible but is found in later Christian writings. It mistakenly appears in a medieval manuscript, MS No.1985, where Galatians 2:20 has "Son of God" changed to "God the Son". In English, this term comes from Latin usage, as seen in the Athanasian Creed and other early church texts. In Greek, "God the Son" is written as ''ho Theos ho huios'' (ὁ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Glasgow
The University of Glasgow (abbreviated as ''Glas.'' in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals; ) is a Public university, public research university in Glasgow, Scotland. Founded by papal bull in , it is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, fourth-oldest university in the English-speaking world and one of Scotland's four Ancient universities of Scotland, ancient universities. Along with the universities of University of St Andrews, St Andrews, University of Aberdeen, Aberdeen, and University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, the university was part of the Scottish Enlightenment during the 18th century. Glasgow is the List of universities in Scotland, second largest university in Scotland by total enrolment and -largest in the United Kingdom. In common with universities of the pre-modern era, Glasgow originally educated students primarily from wealthy backgrounds; however, it became a pioneer in British higher education in the 19th century by also providing for the needs o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The Czech Republic has a hilly landscape that covers an area of with a mostly temperate Humid continental climate, continental and oceanic climate. The capital and largest city is Prague; other major cities and urban areas include Brno, Ostrava, Plzeň and Liberec. The Duchy of Bohemia was founded in the late 9th century under Great Moravia. It was formally recognized as an Imperial Estate of the Holy Roman Empire in 1002 and became Kingdom of Bohemia, a kingdom in 1198. Following the Battle of Mohács in 1526, all of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown were gradually integrated into the Habsburg monarchy. Nearly a hundred years later, the Protestantism, Protestant Bohemian Revolt led to the Thirty Years' War. After the Battle of White ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its Prague metropolitan area, metropolitan area is home to approximately 2.3 million people. Prague is a historical city with Romanesque architecture, Romanesque, Czech Gothic architecture, Gothic, Czech Renaissance architecture, Renaissance and Czech Baroque architecture, Baroque architecture. It was the capital of the Kingdom of Bohemia and residence of several Holy Roman Emperors, most notably Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV (r. 1346–1378) and Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor, Rudolf II (r. 1575–1611). It was an important city to the Habsburg monarchy and Austria-Hungary. The city played major roles in the Bohemian Reformation, Bohemian and the Protestant Reformations, the Thirty Years' War and in 20th-century history a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaroš Griemiller
Jaroš Griemiller of Třebsko was a Czech alchemist, remembered for his illuminated manuscript '' Rosarium philosophorum''. He worked under Wilhelm von Rosenberg in the 1570s, and dedicated the ''Rosarium'' to him. He completed work on the manuscript in 1578 while he was working in Český Krumlov. References Year of birth unknown Year of death unknown Alchemists from Bohemia Czech male writers 16th-century writers from Bohemia 16th-century alchemists 16th-century scientists from the Holy Roman Empire {{CzechRepublic-scientist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow University Library
Glasgow University Library in the main library of the University of Glasgow. At the turn of the 21st century, the main library building itself held 1,347,000 catalogued print books, and 53,300 journals. In total, the university library system including branch libraries now holds approximately 2.5 million books and journals, along with access to 1,853,000 e-books, and over 50,000 e-journals. The University also holds extensive archival material in a separate building. This includes the Scottish Business Archive, which alone amounts to 6.2 kilometres of manuscripts. The current 12-storey building was opened in 1968 and is a prominent landmark in Glasgow's West End. In 2014, there were over 1.7 million visits made to the library. History The first explicit mention of the Library is dated November 1475, when the first donations by the University's Chancellor, Bishop John Laing, were recorded. After the Reformation the University of Glasgow and its Library were reinvigorate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Daniel Mylius
Johann Daniel Mylius (c. 15831642) was a composer for the lute, and writer on alchemy. Born at Wetter in present-day Hesse, Germany, he went on to study theology and medicine at the University of Marburg The Philipps University of Marburg () is a public research university located in Marburg, Germany. It was founded in 1527 by Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse, which makes it one of Germany's oldest universities and the oldest still operating Prote .... He was the brother-in-law and pupil of Johann Hartmann (1568–1613). In 1616, while still a medical student, Mylius published Duncan Burnet's ''Iatrochymicus''. The ', Mylius' own alchemical work, was published two years later. He is known for the collection ' (1622) of pieces for the lute. In the same year his ' was published. Mylius was the personal physician of Moritz of Hessen and his patrons included Maurice and Frederick Henry of Nassau. Works *''Opus medico-chymicum.'' 1618. *''Antidotarium.'' 1620. *''Philosophia r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Spirit
The Holy Spirit, otherwise known as the Holy Ghost, is a concept within the Abrahamic religions. In Judaism, the Holy Spirit is understood as the divine quality or force of God manifesting in the world, particularly in acts of prophecy, creation and guidance. In Nicene Christianity, this conception expanded in meaning to represent the third person of the Trinity, co-equal and co-eternal with God the Father and God the Son. In Islam, the Holy Spirit acts as an agent of divine action or communication. In the Baha’i Faith, the Holy Spirit is seen as the intermediary between God and man and "the outpouring grace of God and the effulgent rays that emanate from His Manifestation". Comparative religion The Hebrew Bible contains the term " spirit of God" (') which by Jews is interpreted in the sense of the might of a unitary God. This interpretation is different from the Nicene Christian conception of the Holy Spirit as one person of the Trinity. The Christian concept ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
God The Father
God the Father is a title given to God in Christianity. In mainstream trinitarian Christianity, God the Father is regarded as the first Person of the Trinity, followed by the second person, Jesus Christ the Son, and the third person, God the Holy Spirit. Since the second century, Christian creeds included affirmation of belief in "God the Father ( Almighty)", primarily in his capacity as "Father and creator of the universe". Christians take the concept of God as the father of Jesus Christ metaphysically further than the concept of God as the creator and father of all people, as indicated in the Apostles' Creed where the expression of belief in the "Father almighty, creator of heaven and earth" is immediately, but separately followed by in "Jesus Christ, his only Son, our Lord", thus expressing both senses of fatherhood. Christianity Overview In much of modern Christianity, God is addressed as the Father, in part because of his active interest in human affairs on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alchemy
Alchemy (from the Arabic word , ) is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practised in China, India, the Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first attested in a number of pseudepigraphical texts written in Greco-Roman Egypt during the first few centuries AD.. Greek-speaking alchemists often referred to their craft as "the Art" (τέχνη) or "Knowledge" (ἐπιστήμη), and it was often characterised as mystic (μυστική), sacred (ἱɛρά), or divine (θɛíα). Alchemists attempted to purify, mature, and perfect certain materials. Common aims were chrysopoeia, the transmutation of " base metals" (e.g., lead) into "noble metals" (particularly gold); the creation of an elixir of immortality; and the creation of panaceas able to cure any disease. The perfection of the human body and soul was thought to result from the alchemical ''magnum opus'' ("Great Work"). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blessed Virgin Mary
Mary was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Saint Joseph, Joseph and the mother of Jesus. She is an important figure of Christianity, venerated under titles of Mary, mother of Jesus, various titles such as Perpetual virginity of Mary, virgin or Queen of Heaven, queen, many of them mentioned in the Litany of Loreto. The Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern and Oriental Orthodox, Catholic, Anglican, Methodist, Reformed Christianity, Reformed, Baptist, and Lutheran churches believe that Mary, as mother of Jesus, is the Theotokos, Mother of God. The Church of the East historically regarded her as Christotokos, a term still used in Assyrian Church of the East liturgy. Other Protestant views on Mary vary, with some holding her to have lesser status. She has the Mary in Islam, highest position in Islam among all women and is mentioned numerous times in the Quran, including in a chapter Maryam (surah), named after her.Jestice, Phyllis G. ''Holy people of the world: a cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |