|
Rosais Islets
The Rosais Islets ( pt, Ilhéus dos Rosais; literally, ''Islets of the Rosaries'') are two uninhabited rocky islets located just off the extreme northwestern coast of the island of São Jorge in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. Geography The Rosais Islets are two small, basaltic volcanic stacks located immediately off Ponta dos Rosais, the extreme northwestern point of São Jorge. The islets arise from an oceanic plateau called Baixa da Ponta dos Rosais, which itself is part of the Terceira Rift. Rosais, a civil parish within the larger municipality of Velas, is the settlement nearest the islets. Biome The waters around the Rosais Islets and Baixa da Ponta dos Rosais are biodiverse. They are home to various fish including anchovy, Atlantic bonito, Atlantic goliath grouper, bluefish, European hake, frigate tuna, longfin yellowtail, needlefish, red scorpionfish, sawfish, skipjack tuna, vadigo, and yellowmouth barracuda. Common bottlenose dolphins and logg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
São Jorge Island
São Jorge () is an island in the central group of the Azores archipelago and part of the autonomous region of Portugal. Separated from its nearest neighbours (Pico and Faial islands) by the Pico-São Jorge Channel, the central group is often referred colloquially as part of the ''Triângulo'' ("Triangle") group or just "The Triangle". São Jorge is a relatively long thin island with tall cliffs, whose 8,381 inhabitants are concentrated on various geological debris fields (''fajãs'') along the north and south coasts; from east to west, the island is long and, north to south, wide: its area is . History It is unclear when the first explorers discovered the island of São Jorge; as part of the politics of human occupation, the Azores were populated after 1430 (probably 1439) through the initiative of Prince Henry the Navigator. 23 April, known as the feast day of Saint George, has been cited by historians as the reason for the island's name, although this is likely conjec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') level. Biodiversity is not distributed evenly on Earth; it is usually greater in the tropics as a result of the warm climate and high primary productivity in the region near the equator. Tropical forest ecosystems cover less than 10% of earth's surface and contain about 90% of the world's species. Marine biodiversity is usually higher along coasts in the Western Pacific, where sea surface temperature is highest, and in the mid-latitudinal band in all oceans. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity. Biodiversity generally tends to cluster in hotspots, and has been increasing through time, but will be likely to slow in the future as a primary result of deforestation. It encompasses the evolutionary, ecological, and cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphyraena Viridensis
''Sphyraena viridensis'', the yellowmouth barracuda or yellow barracuda is a predatory ray finned fish from the family Sphyraenidae, the barracudas, which is found in the warmer waters of the western Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It is often confused with the European barracuda ''Sphyraena sphyraena''. Description ''Sphyraena viridensis'' has a long, wikt:fusiform, fusiform body with a long, streamlined pointed snout which has a long mouth lined with two rows of sharp, fang-like teeth and a jutting lower jaw. There are no scales on the Operculum (fish), preoperculum, unlike the Sphyraena sphyraena, Mediterranean Barracuda which has scales on both the anterior and posterior margins of the preoperculum. There are numerous transverse dark bars on the dorsum and these are longer, extending below the lateral line, towards the head while in ''S. sphyraena'' they do not extend to the lateral line. Generally the colouration is a countershaded dark above, silvery below and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vadigo
The vadigo, ''Campogramma glaycos'' (also known as the big-toothed pompano, zippered pompano, lexa and lexola), is a species of medium-sized coastal marine fish in the jack family, Carangidae. The species is distributed throughout the eastern Atlantic Ocean from the British Isles in the north to Senegal in the south, also entering the western Mediterranean Sea. The vadigo is similar in form to both the leatherjacks and the queenfish, but can be distinguished by its scaleless chest and a broad, rounded upper jaw. It is a predatory fish, preying mostly on smaller schooling fishes. The species was initially classified under the genus ''Centronotus'' before being transferred to its own monotypic genus of ''Campogramma''. The vadigo is of minor commercial importance throughout its range, and is also considered to be a game fish. Taxonomy and naming The vadigo is the only species classified in the monotypic genus ''Campogramma'', which itself is one of 31 genera in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skipjack Tuna
The skipjack tuna (''Katsuwonus pelamis'') is a medium-sized perciform fish in the tuna family, Scombridae. It is otherwise known as the balaya (Sri Lanka), bakulan/kayu (North Borneo), tongkol/aya (Malay Peninsula/Indonesia), aku (Hawaii), cakalang (Indonesia), katsuo, arctic bonito, mushmouth, oceanic bonito, striped tuna or victor fish. It grows up to 1 m (3 ft) in length. It is a cosmopolitan pelagic fish found in tropical and warm-temperate waters. It is a very important species for fisheries. Description It is a streamlined, fast-swimming pelagic fish, common in tropical waters throughout the world, where it inhabits surface waters in large shoals (up to 50,000 fish), feeding on fish, crustaceans, cephalopods, and mollusks. It is an important prey species for sharks and large pelagic fishes and is often used as live bait when fishing for marlin. It has no scales, except on the lateral line and the corselet (a band of large, thick scales forming a circle around th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawfish
Sawfish, also known as carpenter sharks, are a family of rays characterized by a long, narrow, flattened rostrum, or nose extension, lined with sharp transverse teeth, arranged in a way that resembles a saw. They are among the largest fish with some species reaching lengths of about . They are found worldwide in tropical and subtropical regions in coastal marine and brackish estuarine waters, as well as freshwater rivers and lakes. They are endangered. They should not be confused with sawsharks (order Pristiophoriformes) or the extinct sclerorhynchoids (order Rajiformes) which have a similar appearance, or swordfish (family Xiphiidae) which have a similar name but a very different appearance. Sawfishes are relatively slow breeders and the females give birth to live young. They feed on fish and invertebrates that are detected and captured with the use of their saw. They are generally harmless to humans, but can inflict serious injuries with the saw when captured and defend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpaena Scrofa
''Scorpaena scrofa'', the red scorpionfish, bigscale scorpionfish, large-scaled scorpion fish, or rascasse is a venomous marine species of ray-finned fish in the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes. It is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the western Indian Ocean. Taxonomy ''Scorpaena scrofa'' was first formally described in 1758 by Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of his ''Systema Naturae'' in which he gave the type localities as the Mediterranean Sea at Rome and Marseille. The specific name ''scrofa'' means "a breeding sow" in Latin, presumed to derive from ''scrofano'' and ''scrofanello'', which are Italian names for the black scorpionfish (''S. porcus'') and this species, similar to the Old English "hogfish", possible an allusion to Renaissance mistranslations of Athenaeus' observation that scorpionfishes fed on algae or weed, that led to the belief that these fishes live and feed on mud. Description ''Scorpaena scrofa'' is the largest eastern Atlantic scorpion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Needlefish
Needlefish (family Belonidae) or long toms are piscivorous fishes primarily associated with very shallow marine habitats or the surface of the open sea. Some genera include species found in marine, brackish, and freshwater environments (e.g., ''Strongylura''), while a few genera are confined to freshwater rivers and streams, including '' Belonion'', '' Potamorrhaphis'', and ''Xenentodon''. Needlefish closely resemble North American freshwater gars (family Lepisosteidae) in being elongated and having long, narrow jaws filled with sharp teeth, and some species of needlefishes are referred to as gars or garfish despite being only distantly related to the true gars. In fact, the name "garfish" was originally used for the needlefish ''Belone belone'' in Europe and only later applied to the North American fishes by European settlers during the 18th century. Description Needlefish are slender, ranging from in length. They have a single dorsal fin, placed far back on the body, almost o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longfin Yellowtail
The longfin yellowtail (''Seriola rivoliana''), also known as the almaco or silvercoat jack, deep-water, falcate, European or highfin amberjack, rock salmon, longfin or yellow kingfish, is a game fish of the family Carangidae; they are in the same family as yellowtail and amberjack. They are carnivorous and feed, both day and night, on other, smaller fish such as baitfish and small squid. The flesh is thick and dense, like tuna, and easily may be passed off for white albacore if prepared as sushi. Taxonomy Achille Valenciennes, and Georges Cuvier published the first description of this species in 1833, although Cuvier died in 1832. Valenciennes and Cuvier together described many fish species, most notably in the 22-volume, ''Histoire naturelle des poissons'', (Natural History of Fish). Description The longfin yellowtail has a less elongated, more flattened body than most jack species. Their dorsal fin and anal fins are elongated, and their outer edges have a definite sic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigate Tuna
The frigate tuna, frigate mackerel or alagaduwa (''Auxis thazard'') is a species of tuna, in the family Scombridae, found around the world in tropical oceans. The eastern Pacific population is now regarded as a separate species by some authorities, ''Auxis brachydorax''. Parasites As most fishes, the frigate tuna harbours a number of parasites Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha .... Among these are a series of digeneans, which are parasititic within the intestine. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q1145632 frigate tuna Pantropical fish frigate tuna Taxa named by Bernard Germain de Lacépède ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
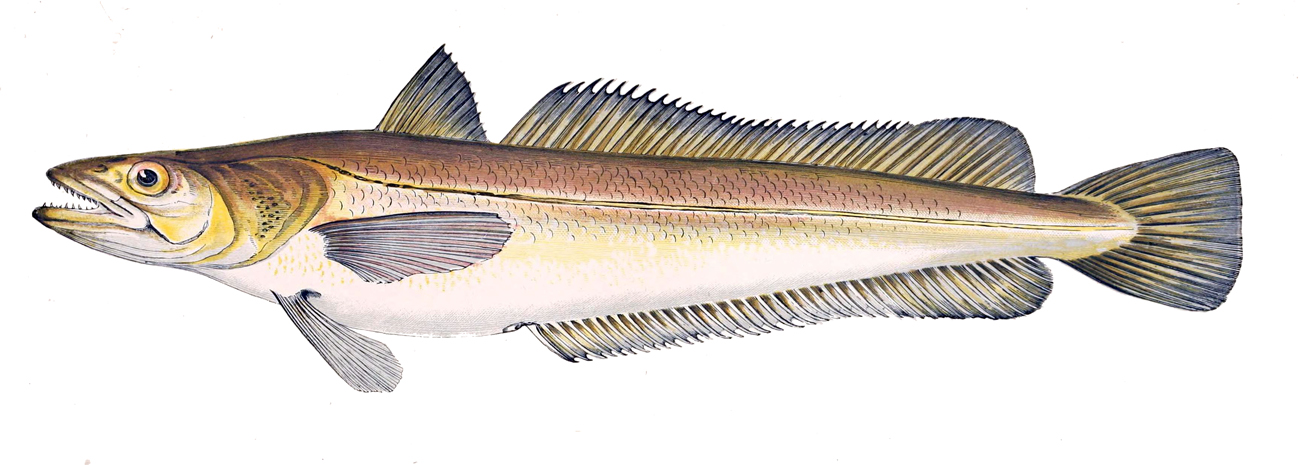
Merluccius Merluccius
''Merluccius merluccius'', the European hake, is a merluccid hake of the genus ''Merluccius''. Other vernacular names include Cornish salmon and herring hake. It is a predatory species which was often netted alongside one of its favoured prey, the Atlantic herring, thus the latter common name. It is found in the eastern Atlantic from the Norway and Iceland south to Mauritania and into the Mediterranean Sea. It is an important species in European fisheries and is heavily exploited with some populations thought to be being fished unsustainably. Description ''Merluccius merluccius'' is a slim-bodied fish with a large head and large jaws on which are set a number of large curved teeth, the lower jaw has two rows of teeth and the upper jaw has one row. The inside of the mouth and the branchial cavity are black. The body is at its widest just behind its head. It has two dorsal fins; the first is triangular in shape, high with a short base, while the second is long, nearly the same leng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bluefish
The bluefish (''Pomatomus saltatrix'') is the only extant species of the family Pomatomidae. It is a marine pelagic fish found around the world in temperate and subtropical waters, except for the northern Pacific Ocean. Bluefish are known as tailor in Australia and New Zealand, elf and shad in South Africa. It is a popular gamefish and food fish. The bluefish is a moderately proportioned fish, with a broad, forked tail. The spiny first dorsal fin is normally folded back in a groove, as are its pectoral fins. Coloration is a grayish blue-green dorsally, fading to white on the lower sides and belly. Its single row of teeth in each jaw is uniform in size, knife-edged, and sharp. Bluefish commonly range in size from seven-inch (18-cm) "snappers" to much larger, sometimes weighing as much as 40 lb (18 kg), though fish heavier than 20 lb (9 kg) are exceptional. Systematics The bluefish is the only extant species now included in the family Pomatomidae. At one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |