|
Rory O'Moore
Sir Rory O'Moore (; c. 1600 – 16 February 1655), also known Sir Roger O'Moore or O'More or Sir Roger Moore, was an Irish landowner, and is most notable for being one of the four principal organisers of the Irish Rebellion of 1641. Early life O'Moore belonged to an ancient Irish noble family descended from Conall Cernach. He was born in either Laois around 1600, or more likely at Balyna, his father's estate in County Kildare, about 4km west of Johnstownbridge. His father was Calvagh O'More, son of nobleman Rory Caoch O'More, and his mother was Margaret Scurlock (Sherlock). O'Moore's uncle Rory Oge O'More, Lord of Laois, had fought against the English during the Tudor conquest of Ireland. In 1556 Queen Mary I confiscated Clan O'Mores' lands and created "Queens County" (modern-day County Laois). Over 180 family members, who were peaceful and had taken no part in any rebellion, were murdered with virtually all of the leaders of Laois and Offaly by the English at a feast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
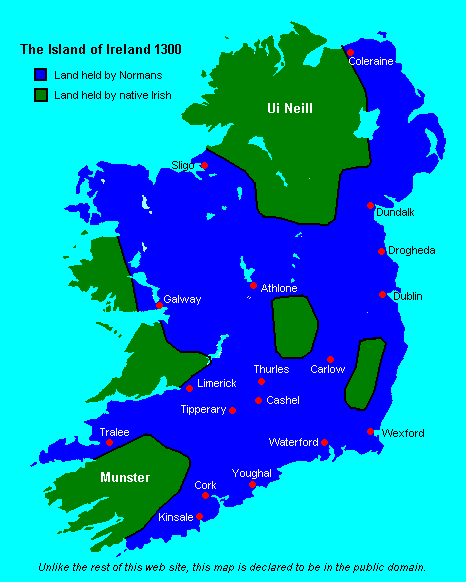
Irish Rebellion Of 1641
The Irish Rebellion of 1641 was an uprising in Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, initiated on 23 October 1641 by Catholic gentry and military officers. Their demands included an end to anti-Catholic discrimination, greater Irish self-governance, and return of plantations of Ireland, confiscated Catholic lands. Planned as a swift ''coup d'état'' to gain control of the Protestant-dominated Dublin Castle administration, central government, instead it led to the 1641–1653 Irish Confederate Wars, part of the wider Wars of the Three Kingdoms. Despite failing to seize Dublin Castle, rebels under Felim O'Neill of Kinard, Felim O'Neill quickly over-ran most of Ulster, centre of the most recent Plantation of Ulster, land confiscations. O'Neill then issued the Proclamation of Dungannon, a forgery claiming he had been authorised by Charles I of England to secure Ireland against his opponents in Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland. Many Cavalier, Royalist Normans in I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
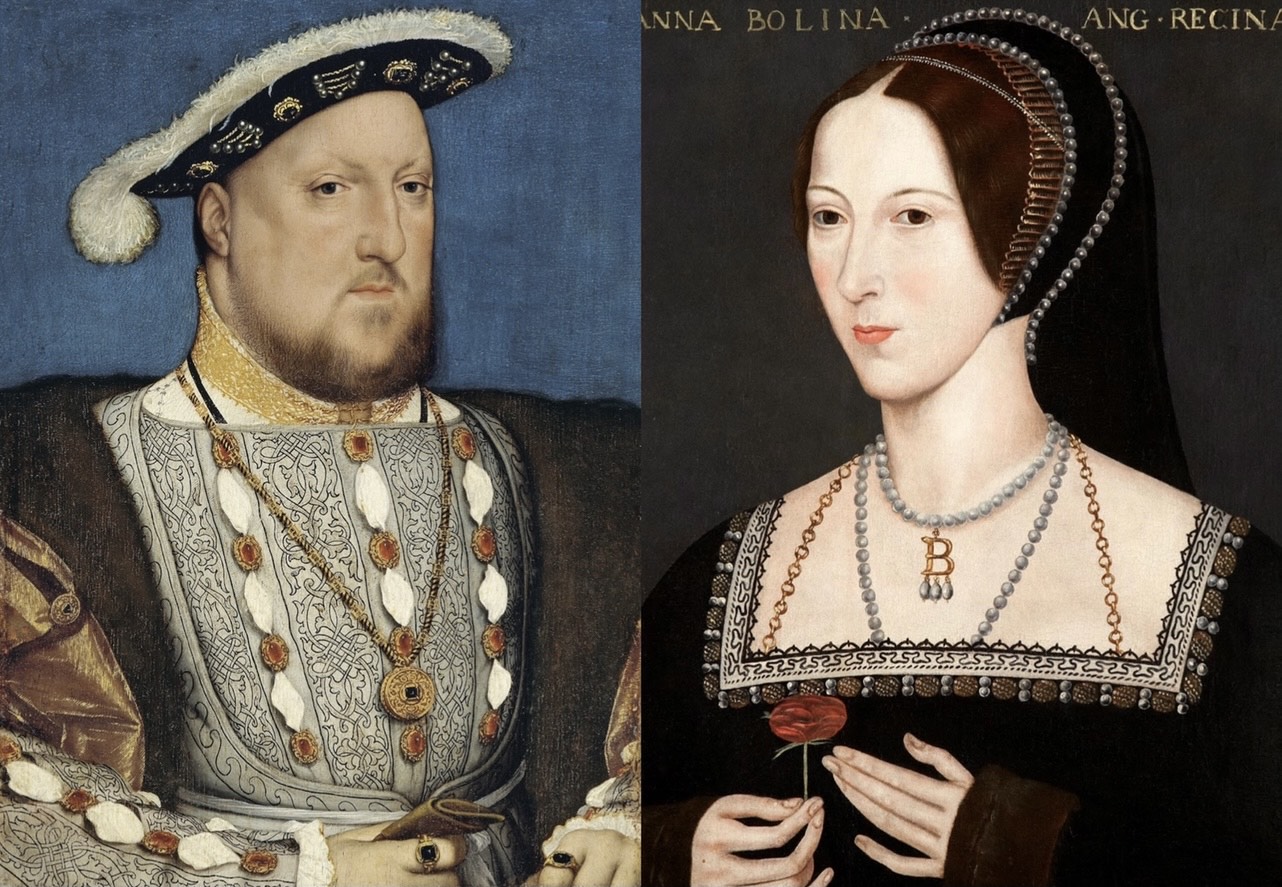
Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudor. Her eventful reign, and its effect on history and culture, gave name to the Elizabethan era. Elizabeth was the only surviving child of Henry VIII and his second wife, Anne Boleyn. When Elizabeth was two years old, her parents' marriage was annulled, her mother was executed, and Elizabeth was declared royal bastard, illegitimate. Henry Third Succession Act 1543, restored her to the line of succession when she was 10. After Henry's death in 1547, Elizabeth's younger half-brother Edward VI ruled until his own death in 1553, bequeathing the crown to a Protestant cousin, Lady Jane Grey, and ignoring the claims of his two half-sisters, Mary I of England, Mary and Elizabeth, despite statutes to the contrary. Edward's will was quickly set aside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Offaly
County Offaly (; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. It is named after the Ancient Ireland, ancient Kingdom of Uí Failghe. It was formerly known as King's County, in honour of Philip II of Spain. Offaly County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority for the county. The county population was 82,668 at the 2022 census. Geography and political subdivisions Offaly is the 18th largest of Ireland's 32 counties by area and the 24th largest in terms of population. It is the fifth largest of Leinster's 12 counties by size and the tenth largest by population. Physical geography Tullamore is the county town and largest town in Offaly and is the List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland, 30th largest in Ireland. Offaly borders seven counties: County Galway, Galway, County Roscommon, Roscommon, County Tipperary, Tippe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Owen Roe O'Neill
Owen Roe O'Neill ( Irish: ''Eoghan Ruadh Ó Néill;'' – 6 November 1649) was a Gaelic Irish soldier and one of the most famous of the O'Neill dynasty of Ulster. O'Neill left Ireland at a young age and spent most of his life as a mercenary in the Spanish Army serving against the Dutch in Flanders during the Eighty Years' War. After the Irish Rebellion of 1641, O'Neill returned and took command of the Irish Confederate Ulster Army. He is known for his victory at the Battle of Benburb in 1646. O'Neill's later years were marked by infighting amongst the Confederates, and in 1647 he led his army to seize power in the capital of Kilkenny. His troops clashed with rival forces of the Confederacy, leading to O'Neill forming a temporary alliance with Charles Coote's English Parliamentary forces in Ulster. He initially rejected a treaty of alliance between the Confederates and the Irish Royalists, but faced with the Cromwellian invasion he changed his mind. O'Neill died shortly a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Confederate Wars
The Irish Confederate Wars, took place from 1641 to 1653. It was the Irish theatre of the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, a series of civil wars in Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, all then ruled by Charles I of England, Charles I. The conflict caused an estimated 200,000 deaths from fighting, as well as war-related famine and disease. It began with the Irish Rebellion of 1641, when local Catholics tried to seize control of the Dublin Castle administration. They wanted an end to anti-Catholic discrimination, to increase Irish self-governance, and to roll back the Plantations of Ireland. They also wanted to prevent an invasion by anti-Catholic Roundhead, English Parliamentarians and Covenanter, Scottish Covenanters, who were defying the king. Rebel leader Felim O'Neill of Kinard, Felim O'Neill claimed to be Proclamation of Dungannon, doing the king's bidding, but Charles condemned the rebellion after it broke out. The rebellio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Julianstown
The Battle of Julianstown was fought on 27 November 1641 near Julianstown in County Louth during the Irish Rebellion of 1641. A force sent by the Dublin government to reinforce the garrison of Drogheda was ambushed by Irish rebels and nearly destroyed. Background At the beginning of the Irish Rebellion in October 1641, the rebels over ran most of Ulster before moving south towards Dublin. On 21 November, they besieged Drogheda and the Dublin government assembled reinforcements to support the garrison. The battle The relief force was hastily put together and its soldiers largely untrained, many being half-starved refugees from the north who had been pressed into service. The detachment was commanded by Sir Patrick Wemyss and was composed of 50 horse and around 600 foot, led by Sergeant Major Roper. The rebel forces were led by Philip O'Reilly and Miles O'Reilly, both Irish leaders from County Cavan. Their force of 3,000 men including 300 horse had experienced commanders an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Drogheda 1641
The siege of Drogheda took place from 21 November 1641 to February 1642 during the Irish Rebellion of 1641. A Catholic force under Féilim Ó Néill laid siege to the town but failed to wrest the garrison from the Royalists. During the siege, the Irish rebels made three attempts to break into and capture the town. All three attempts failed and the town was ultimately relieved by English forces.Quaile.Plant Background After the Irish rebellion began on 22 October 1641, the rebels first attempted to move into Ulster and capture Belfast. When they met stiff resistance from Protestant militias in Ulster, the rebels turned their focus southward with the goal of taking Dublin. En route to attack Dublin, the rebels came upon the town of Drogheda, and laid siege to the Royalist stronghold. Assaults during the siege Early in November, Lord Moore of Mellifont had become concerned about the defense of Drogheda and had stepped in to make preliminary improvements. Among the actions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leinster
Leinster ( ; or ) is one of the four provinces of Ireland, in the southeast of Ireland. The modern province comprises the ancient Kingdoms of Meath, Leinster and Osraige, which existed during Gaelic Ireland. Following the 12th-century Norman invasion of Ireland, the historic "fifths" of Leinster and Meath gradually merged, mainly due to the impact of the Pale, which straddled both, thereby forming the present-day province of Leinster. The ancient kingdoms were shired into a number of counties for administrative and judicial purposes. In later centuries, local government legislation has prompted further sub-division of the historic counties. Leinster has no official function for local-government purposes. However, it is an officially recognised subdivision of Ireland and is listed on ISO 3166-2 as one of the four provinces of Ireland. "IE-L" is attributed to Leinster as its ''country sub-division'' code. Leinster had a population of 2,858,501 according to the prelim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English (Ireland)
Norman Irish or Hiberno-Normans (; ) is a modern term for the descendants of Normans, Norman settlers who arrived during the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland in the 12th century. Most came from Anglo-Normans, England and Cambro-Normans, Wales. They are distinguished from the native Gaelic Ireland, Gaelic Irish; although some Normans eventually became Gaelicised. The Hiberno-Normans were a feudal aristocracy and merchant oligarchy who controlled the Lordship of Ireland. The Hiberno-Normans were associated with the Gregorian Reform of the Catholic Church in Ireland and contributed to the emergence of a Hiberno-English dialect. Some of the most prominent Hiberno-Norman families were the House of Burke, Burkes (de Burghs), Butler dynasty, Butlers, and FitzGerald dynasty, FitzGeralds. One of the most common Irish surnames, Walsh (surname), Walsh, derives from Welsh Normans who arrived in Ireland as part of this group. Some Norman families were said to have become "more Irish than t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felim O'Neill Of Kinard
Sir Phelim Roe O'Neill of Kinard ( Irish: ''Sir Féilim Rua Ó Néill na Ceann Ard''; 1604–1653) was an Irish politician and soldier who started the Irish rebellion in Ulster on 23 October 1641. He joined the Irish Catholic Confederation in 1642 and fought in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms under his cousin, Owen Roe O'Neill, in the Confederate Ulster Army. After the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland O’Neill went into hiding but was captured, tried and executed in 1653. Birth and origins Phelim was born in 1604, the eldest son of Turlough O'Neill and his wife Catherine O'Neill. His father was a member of the Kinard branch of the O'Neills who were descendants of Shane O'Neill of Kinard, a half-brother of Conn Baccach O'Neill. His father and paternal grandfather were killed on 20 June 1608, while defending Kinard against the insurgents during the O'Doherty's Rebellion. This grandfather, Sir Henry Óg O'Neill, had fought for his seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); the remaining three are in the Republic of Ireland. It is the second-largest (after Munster) and second-most populous (after Leinster) of Ireland's four traditional provinces, with Belfast being its biggest city. Unlike the other provinces, Ulster has a high percentage of Protestantism in Ireland, Protestants, making up almost half of its population. English is the main language and Ulster English the main dialect. A minority also speak Irish, and there are (Irish-speaking regions) in County Donegal which is home to a quarter of the total Gaeltacht population of the Republic of Ireland. There are also large Irish-speaking networks in southern County Londonderry and in the Gaeltacht Quarter, Belfast. Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dublin Castle
Dublin Castle () is a major Government of Ireland, Irish government complex, conference centre, and tourist attraction. It is located off Dame Street in central Dublin. It is a former motte-and-bailey castle and was chosen for its position at the highest point of central Dublin. Until 1922 it was the seat of the Dublin Castle administration, British government's administration in Ireland. Many of the current buildings date from the 18th century, though a castle has stood on the site since the days of King John, King of England, John, the first Lordship of Ireland, Lord of Ireland. The Castle served as the seat of English, then later British, government of Ireland under the Lordship of Ireland (1171–1541), the Kingdom of Ireland (1541–1800), and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922). After the signing of the Anglo-Irish Treaty in December 1921, the complex was ceremonially handed over to the newly formed Provisional Government of Ireland (1922), Prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |