|
Roniviridae
''Okavirus'' is a genus of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which infect crustaceans. Host organisms are mostly shrimp. It is the only genus in the family ''Roniviridae''. Viruses associated with the genus include: gill-associated virus (GAV) which causes reddening, biofouling with exoparasites, emaciation, and massive mortality; and yellow head virus (YHV) which causes yellow head, arrest of feeding, and massive mortality. The name is derived from the 'Oka' or lymphoid organ in which the viruses are commonly detected and in which pathology occurs during acute infections. Lymphoid organs are anatomical structures common to penaeid shrimp. There are three species in this genus. Structure Viruses in the genus ''Okavirus'' are enveloped, with bacilliform geometries, and helical symmetry. The diameter is around 20–30 nm. Genome Genomes are linear and non-segmented, around 26 kb in length. Life cycle Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment to host re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tipravirus
''Okavirus'' is a genus of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which infect crustaceans. Host organisms are mostly shrimp. It is the only genus in the family ''Roniviridae''. Viruses associated with the genus include: gill-associated virus (GAV) which causes reddening, biofouling with exoparasites, emaciation, and massive mortality; and yellow head virus (YHV) which causes yellow head, arrest of feeding, and massive mortality. The name is derived from the 'Oka' or lymphoid organ in which the viruses are commonly detected and in which pathology occurs during acute infections. Lymphoid organs are anatomical structures common to penaeid shrimp. There are three species in this genus. Structure Viruses in the genus ''Okavirus'' are enveloped, with bacilliform geometries, and helical symmetry. The diameter is around 20–30 nm. Genome Genomes are linear and non-segmented, around 26 kb in length. Life cycle Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment to host re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gill-associated Virus
''Okavirus'' is a genus of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which infect crustaceans. Host organisms are mostly shrimp. It is the only genus in the family ''Roniviridae''. Viruses associated with the genus include: gill-associated virus (GAV) which causes reddening, biofouling with exoparasites, emaciation, and massive mortality; and yellow head virus (YHV) which causes yellow head, arrest of feeding, and massive mortality. The name is derived from the 'Oka' or lymphoid organ in which the viruses are commonly detected and in which pathology occurs during acute infections. Lymphoid organs are anatomical structures common to penaeid shrimp Penaeidae is a family of marine crustaceans in the suborder Dendrobranchiata, which are often referred to as penaeid shrimp or penaeid prawns. The Penaeidae contain many species of economic importance, such as the tiger prawn, whiteleg shrimp, .... There are three species in this genus. Structure Viruses in the genus ''Okavirus'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
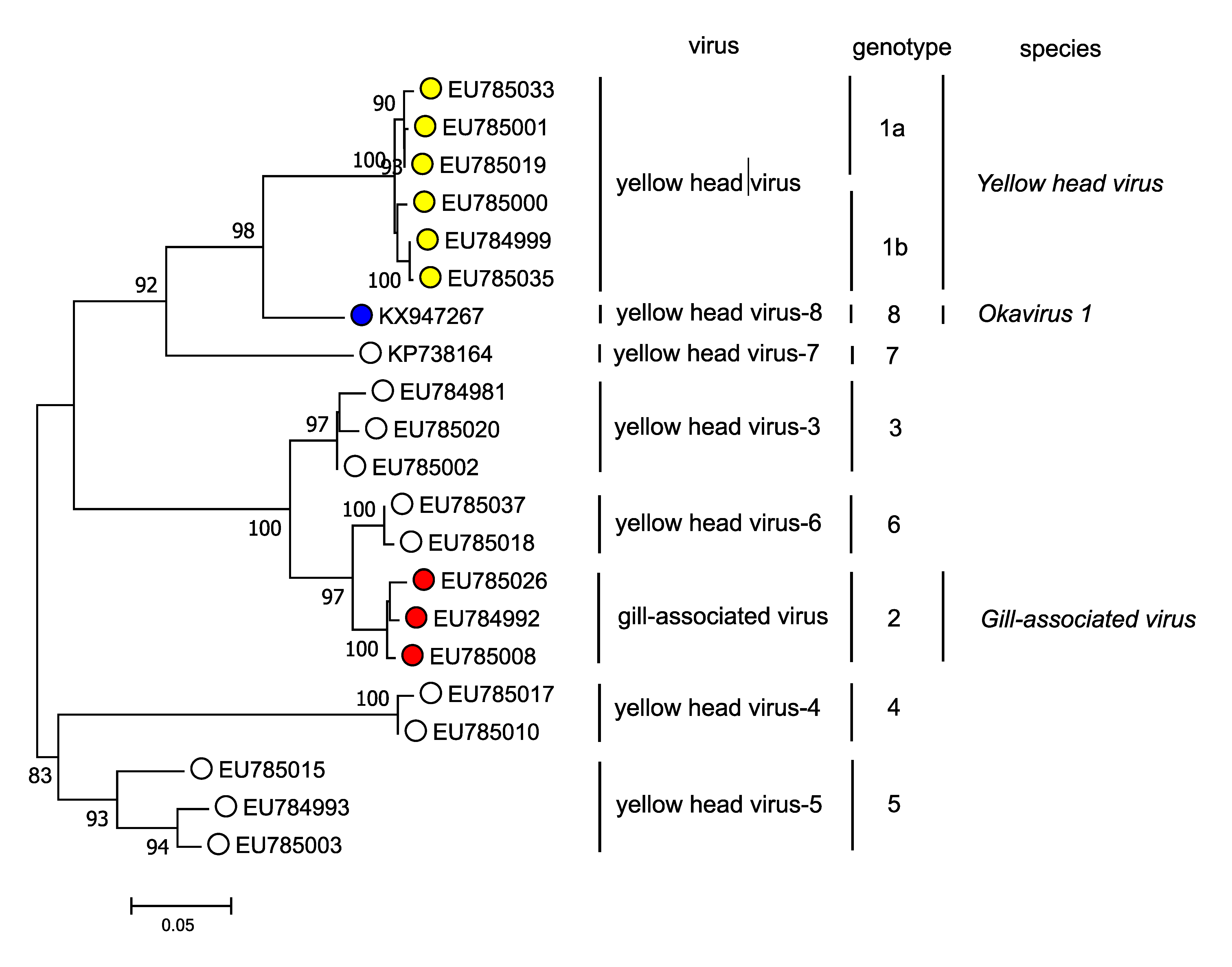
Okavirus 1
''Okavirus'' is a genus of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which infect crustaceans. Host organisms are mostly shrimp. It is the only genus in the family ''Roniviridae''. Viruses associated with the genus include: gill-associated virus (GAV) which causes reddening, biofouling with exoparasites, emaciation, and massive mortality; and yellow head virus (YHV) which causes yellow head, arrest of feeding, and massive mortality. The name is derived from the 'Oka' or lymphoid organ in which the viruses are commonly detected and in which pathology occurs during acute infections. Lymphoid organs are anatomical structures common to penaeid shrimp. There are three species in this genus. Structure Viruses in the genus ''Okavirus'' are enveloped, with bacilliform geometries, and helical symmetry. The diameter is around 20–30 nm. Genome Genomes are linear and non-segmented, around 26 kb in length. Life cycle Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment to host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roniviridae
''Okavirus'' is a genus of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which infect crustaceans. Host organisms are mostly shrimp. It is the only genus in the family ''Roniviridae''. Viruses associated with the genus include: gill-associated virus (GAV) which causes reddening, biofouling with exoparasites, emaciation, and massive mortality; and yellow head virus (YHV) which causes yellow head, arrest of feeding, and massive mortality. The name is derived from the 'Oka' or lymphoid organ in which the viruses are commonly detected and in which pathology occurs during acute infections. Lymphoid organs are anatomical structures common to penaeid shrimp. There are three species in this genus. Structure Viruses in the genus ''Okavirus'' are enveloped, with bacilliform geometries, and helical symmetry. The diameter is around 20–30 nm. Genome Genomes are linear and non-segmented, around 26 kb in length. Life cycle Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment to host re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Head Virus
Yellowhead disease (YHD) is a viral infection of shrimp and prawn, in particular of the giant tiger prawn (''Penaeus monodon''), one of the two major species of farmed shrimp. The disease is caused by the ''Yellow head virus'' (YHV), a positive-strand RNA virus related to coronaviruses and arteriviruses. The disease is highly lethal and contagious, killing shrimp quickly. Outbreaks of this disease have wiped out in a matter of days the entire populations of many shrimp farms that cultivated ''P. monodon'', i.e. particularly Southeast Asian farms. In Thai, the disease is called . A closely related virus is the ''Gill-associated virus'' (GAV). Clinical The cephalothorax of infected shrimp turns yellow after a period of unusually high feeding activity ending abruptly, and the then moribund shrimps congregate near the surface of their pond before dying. YHD leads to death of the animals within two to four days.World Organization for Animal Health (OIE): ''Aquatic Manual'', 4t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Head Virus
Yellowhead disease (YHD) is a viral infection of shrimp and prawn, in particular of the giant tiger prawn (''Penaeus monodon''), one of the two major species of farmed shrimp. The disease is caused by the ''Yellow head virus'' (YHV), a positive-strand RNA virus related to coronaviruses and arteriviruses. The disease is highly lethal and contagious, killing shrimp quickly. Outbreaks of this disease have wiped out in a matter of days the entire populations of many shrimp farms that cultivated ''P. monodon'', i.e. particularly Southeast Asian farms. In Thai, the disease is called . A closely related virus is the ''Gill-associated virus'' (GAV). Clinical The cephalothorax of infected shrimp turns yellow after a period of unusually high feeding activity ending abruptly, and the then moribund shrimps congregate near the surface of their pond before dying. YHD leads to death of the animals within two to four days.World Organization for Animal Health (OIE): ''Aquatic Manual'', 4t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive-strand RNA Viruses
Positive-strand RNA viruses (+ssRNA viruses) are a group of related viruses that have positive-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The positive-sense genome can act as messenger RNA (mRNA) and can be directly translated into viral proteins by the host cell's ribosomes. Positive-strand RNA viruses encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) which is used during replication of the genome to synthesize a negative-sense antigenome that is then used as a template to create a new positive-sense viral genome. Positive-strand RNA viruses are divided between the phyla ''Kitrinoviricota'', ''Lenarviricota'', and ''Pisuviricota'' (specifically classes ''Pisoniviricetes'' and '' Stelpavirictes'') all of which are in the kingdom '' Orthornavirae'' and realm '' Riboviria''. They are monophyletic and descended from a common RNA virus ancestor. In the Baltimore classification system, +ssRNA viruses belong to Group IV. Positive-sense RNA viruses include patho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
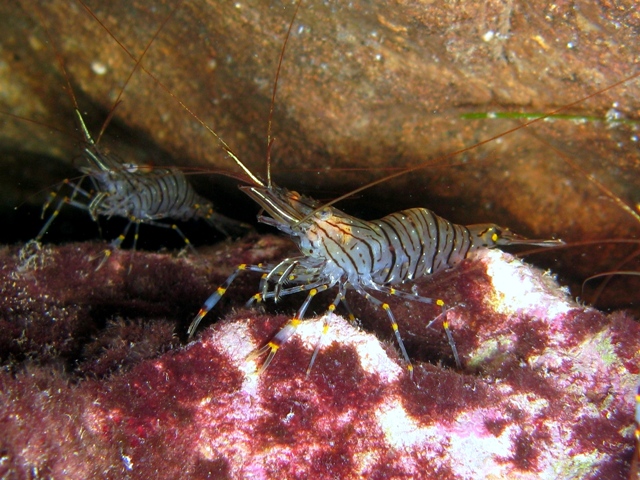
Shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are referred to as "shrimp". More narrow definitions may be restricted to Caridea, to smaller species of either group or to only the marine species. Under a broader definition, ''shrimp'' may be synonymous with prawn, covering stalk-eyed swimming crustaceans with long, narrow muscular tails (abdomens), long whiskers ( antennae), and slender legs. Any small crustacean which resembles a shrimp tends to be called one. They swim forward by paddling with swimmerets on the underside of their abdomens, although their escape response is typically repeated flicks with the tail driving them backwards very quickly. Crabs and lobsters have strong walking legs, whereas shrimp have thin, fragile legs which they use primarily for perching.Rudloe & Rudloe (2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penaeid Shrimp
Penaeidae is a family of marine crustaceans in the suborder Dendrobranchiata, which are often referred to as penaeid shrimp or penaeid prawns. The Penaeidae contain many species of economic importance, such as the tiger prawn, whiteleg shrimp, Atlantic white shrimp, and Indian prawn. Many prawns are the subject of commercial fishery, and farming, both in marine settings, and in freshwater farms. Lateral line–like sense organs on the antennae have been reported in some species of Penaeidae. At , the myelinated giant interneurons of pelagic penaeid shrimp have the world record for impulse conduction speed in any animal. Genera Of the 48 recognised genera in the family Penaeidae, 23 are known only from the fossil record (marked †): * † '' Albertoppelia'' Schweigert & Garassino, 2004 * † ''Ambilobeia'' Garassino & Pasini, 2002 * † ''Antrimpos'' Münster, 1839 * '' Artemesia'' Bate, 1888 * '' Atypopenaeus'' Alcock, 1905 * † '' Bombur'' Münster, 1839 * † ''Bylgia'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes. Numerous human pathogenic viruses in circulation are encased in lipid bilayers, and they infect their target cells by causing the viral envelope and cell membrane to fuse. Although there are effective vaccines against some of these viruses, there is no preventative or curative medicine for the majority of them. In most cases, the known vaccines operate by inducing antibodies that prevent the pathogen from entering cells. This happens in the case of enveloped viruses when the antibodies bind to the viral envelope proteins. The membrane fusion event that triggers viral entrance is caused by the viral fusion protein. Many enveloped viruses only have one protein visible on the surface of the particle, which is required for both mediating adhesion to the cell surface and for the subsequent membrane fusi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus (shape)
A bacillus (), also called a bacilliform bacterium or often just a rod (when the context makes the sense clear), is a rod-shaped bacterium or archaeon. Bacilli are found in many different taxonomic groups of bacteria. However, the name ''Bacillus'', capitalized and italicized, refers to a specific genus of bacteria. The name Bacilli, capitalized but not italicized, can also refer to a less specific taxonomic group of bacteria that includes two orders, one of which contains the genus ''Bacillus''. When the word is formatted with lowercase and not italicized, 'bacillus', it will most likely be referring to shape and not to the genus at all. Bacilliform bacteria are also often simply called rods when the bacteriologic context is clear. Bacilli usually divide in the same plane and are solitary, but can combine to form diplobacilli, streptobacilli, and palisades. * Diplobacilli: Two bacilli arranged side by side with each other. * Streptobacilli: Bacilli arranged in chains. * Coccobac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |