|
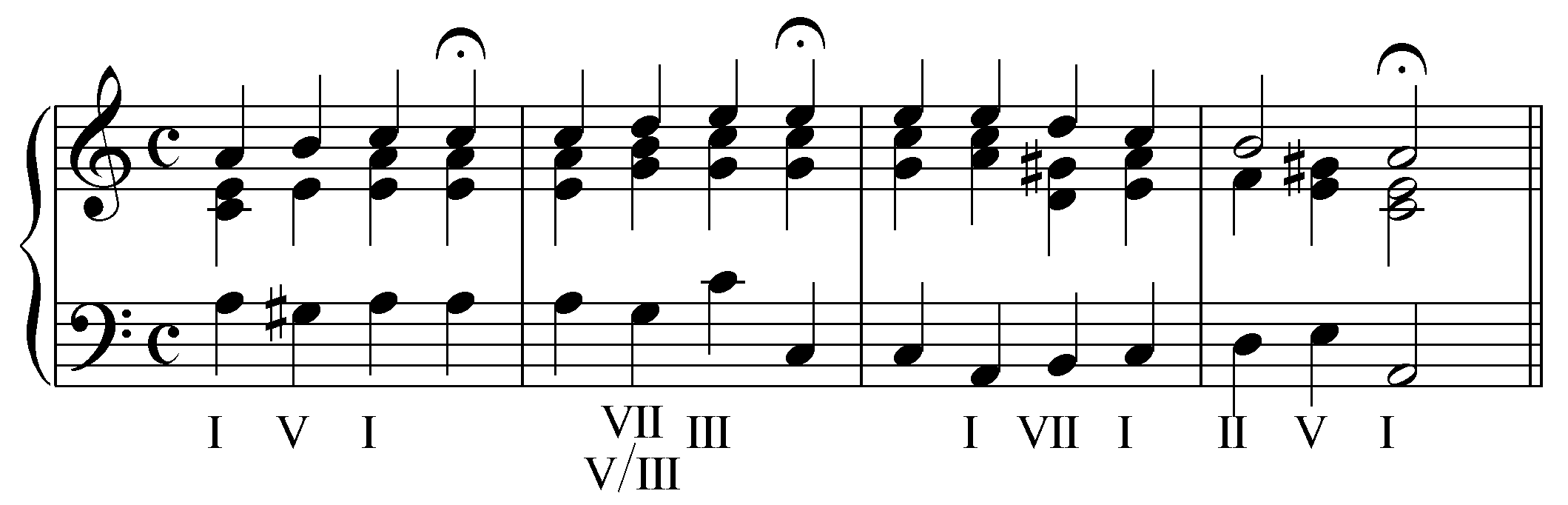
Romanesca
Romanesca is a melodic-harmonic formula popular from the mid–16th to early–17th centuries that was used as an aria formula for singing poetry and as a subject for instrumental variation. The pattern, which is found in an endless collection of compositions labeled ''romanesca'', perhaps named after the Roma, is a descending descant formula within a chordal progression that has a bass which moves by 4ths. The formula was not to be viewed as a fixed tune, but as a framework over which elaborate ornamentation can occur. Gerbino, Giuseppe. (2001). Romanesca. In John Tyrrell and Stanley Sadie (Eds.), The New Grove Dictionary of music and musicians (2nd ed., Vol. 21, pp. 577-578). New York: Grove It was most popular with Italian and Spanish composers of the Renaissance and early Baroque period. It was also used by vihuelistas including Luis de Narváez, Alonso Mudarra, Enríquez de Valderrábano, and Diego Pisador. Origins Scholars are uncertain of the precise origins of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanesca
Romanesca is a melodic-harmonic formula popular from the mid–16th to early–17th centuries that was used as an aria formula for singing poetry and as a subject for instrumental variation. The pattern, which is found in an endless collection of compositions labeled ''romanesca'', perhaps named after the Roma, is a descending descant formula within a chordal progression that has a bass which moves by 4ths. The formula was not to be viewed as a fixed tune, but as a framework over which elaborate ornamentation can occur. Gerbino, Giuseppe. (2001). Romanesca. In John Tyrrell and Stanley Sadie (Eds.), The New Grove Dictionary of music and musicians (2nd ed., Vol. 21, pp. 577-578). New York: Grove It was most popular with Italian and Spanish composers of the Renaissance and early Baroque period. It was also used by vihuelistas including Luis de Narváez, Alonso Mudarra, Enríquez de Valderrábano, and Diego Pisador. Origins Scholars are uncertain of the precise origins of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Griffiths (musician)
John Griffiths (born 2 December 1952, Melbourne) is a musician and musicologist specialised in music for guitar and early plucked instruments, especially the vihuela and lute. He has researched aspects of the sixteenth-century Spanish vihuela, its history and its music. He has also had an international career as a solo lutenist, vihuelist, and guitarist, and as a member of the pioneer Australian early music group La Romanesca. After a thirty-year career at the University of Melbourne (1980–2011), he now works as a freelance scholar and performer. Career Griffiths graduated from Monash University in Melbourne (Australia) with a Bachelor of Arts degree and a PhD in 1984. From childhood he also studied guitar, initially with his father and then with Susan Ellis, Sadie Bishop and Sam Dunn during his school years. After completing his BA, he continued his performance studies in Germany with Siegfried Behrend and in Spain with José Luis Lopátegui. He also studied lute and vihuel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passamezzo Antico
The passamezzo antico is a ground bass or chord progression that was popular during the Italian Renaissance and known throughout Europe in the 16th century. van der Merwe, Peter. 1989. ''Origins of the Popular Style: The Antecedents of Twentieth-Century Popular Music'', p.207. Oxford: Clarendon Press. . The progression is a variant of the double tonic: its major mode variant is known as the passamezzo moderno. The sequence consists of two phrases as follows: ''(For an explanation of this notation see Chord progression)'' Though usually in the key of G minor, in the key of A minor this gives: The romanesca is a variant of the passamezzo antico, where the first chord is the III (e.g., a C major chord in A minor). A famous example is "Greensleeves". The passamezzo antico chord changes are found, knowingly or not, in modern popular music culture: Carrie Underwood Carrie Marie Underwood (born March 10, 1983) is an American singer. She rose to prominence after winning the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melody Type
Melody type or type-melody is a set of melodic formulas, figures, and patterns. Term and typical meanings "Melody type" is a fundamental notion for understanding a nature of Western and non-Western musical modes, according to Harold Powers' seminal article "Mode" in the first edition of the ''New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' . Melody types are used in the composition of an enormous variety of music, especially non-Western and early Western music. Such music is generally composed by a process of centonization, either freely (i.e. improvised) or in a fixed pattern. "Melody type" as used by the ethnomusicologist Mark is defined as a "group of melodies that are related, in that they all contain similar modal procedures and characteristic rhythmic and melodic contours or patterns". Most cultures which compose music in this way organize the patterns into distinct melody types. These are often compared to modern Western scales, but they in fact represent much more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melody
A melody (from Greek language, Greek μελῳδία, ''melōidía'', "singing, chanting"), also tune, voice or line, is a Linearity#Music, linear succession of musical tones that the listener perceives as a single entity. In its most literal sense, a melody is a combination of pitch (music), pitch and rhythm, while more figuratively, the term can include other musical elements such as Timbre, tonal color. It is the foreground to the background accompaniment. A line or part (music), part need not be a foreground melody. Melodies often consist of one or more musical Phrase (music), phrases or Motif (music), motifs, and are usually repeated throughout a musical composition, composition in various forms. Melodies may also be described by their melodic motion or the pitches or the interval (music), intervals between pitches (predominantly steps and skips, conjunct or disjunct or with further restrictions), pitch range, tension (music), tension and release, continuity and coheren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord (music)
A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of pitches/frequencies consisting of multiple notes (also called "pitches") that are heard as if sounding simultaneously. For many practical and theoretical purposes, arpeggios and broken chords (in which the notes of the chord are sounded one after the other, rather than simultaneously), or sequences of chord tones, may also be considered as chords in the right musical context. In tonal Western classical music (music with a tonic key or "home key"), the most frequently encountered chords are triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: the root note, and intervals of a third and a fifth above the root note. Chords with more than three notes include added tone chords, extended chords and tone clusters, which are used in contemporary classical music, jazz and almost any other genre. A series of chords is called a chord progression. One example of a widely used chord progression in Western traditional music and blu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion; or inspires awe or reverence among believers. The property is often ascribed to objects (a " sacred artifact" that is venerated and blessed), or places (" sacred ground"). French sociologist Émile Durkheim considered the dichotomy between the sacred and the profane to be the central characteristic of religion: "religion is a unified system of beliefs and practices relative to ''sacred things'', that is to say, things set apart and forbidden." Durkheim, Émile. 1915. ''The Elementary Forms of the Religious Life''. London: George Allen & Unwin. . In Durkheim's theory, the sacred represents the interests of the group, especially unity, which are embodied in sacred group symbols, or using team work to help get out of trouble. The profane, on the other hand, involve mundane individual concerns. Etymology The word ''sacred'' des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greensleeves
"Greensleeves" is a traditional English folk song. A broadside ballad by the name "A Newe Northen Dittye of ye Ladye Greene Sleves" was registered by Richard Jones at the London Stationer's Company in September 1580,Frank Kidson, ''English Folk-Song and Dance''. READ BOOKS, 2008, p.26. John M. Ward, "'And Who But Ladie Greensleeues?'", in ''The Well Enchanting Skill: Music, Poetry, and Drama in the Culture of the Renaissance: Essays in Honour of F. W. Sternfeld'', edited by John Caldwell, Edward Olleson, and Susan Wollenberg, 181–211 (Oxford:Clarendon Press; New York: Oxford University Press, 1990): 181. . and the tune is found in several late-16th-century and early-17th-century sources, such as ''Ballet's MS Lute Book'' and ''Het Luitboek van Thysius'', as well as various manuscripts preserved in the Seeley Historical Library in the University of Cambridge. Form "Greensleeves" can have a ground either of the form called a ''romanesca''; or its slight variant, the ''passame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominant (music)
In music, the dominant is the fifth scale degree () of the diatonic scale. It is called the ''dominant'' because it is second in importance to the first scale degree, the tonic. In the movable do solfège system, the dominant note is sung as "So(l)". The triad built on the dominant note is called the dominant chord. This chord is said to have dominant function, which means that it creates an instability that requires the tonic for resolution. Dominant triads, seventh chords, and ninth chords typically have dominant function. Leading-tone triads and leading-tone seventh chords may also have dominant function. Dominant chords In music theory, the dominant triad is a major chord, symbolized by the Roman numeral "V" in the major scale. In the natural minor scale, the triad is a minor chord, denoted by "v". However, in a minor key, the seventh scale degree is often raised by a half step ( to ), creating a major chord. These chords may also appear as seventh chords: ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonic (music)
In music, the tonic is the first scale degree () of the diatonic scale (the first note of a scale) and the tonal center or final resolution tone that is commonly used in the final cadence in tonal (musical key-based) classical music, popular music, and traditional music. In the movable do solfège system, the tonic note is sung as ''do''. More generally, the tonic is the note upon which all other notes of a piece are hierarchically referenced. Scales are named after their tonics: for instance, the tonic of the C major scale is the note C. The triad formed on the tonic note, the tonic chord, is thus the most significant chord in these styles of music. In Roman numeral analysis, the tonic chord is typically symbolized by the Roman numeral "I" if it is major and by "i" if it is minor. These chords may also appear as seventh chords: in major, as IM7, or in minor as i7 or rarely iM7: The tonic is distinguished from the root, which is the reference note of a chord, rathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtonic
In music, the subtonic is the degree of a musical scale which is a whole step below the tonic note. In a major key, it is a lowered, or flattened, seventh scale degree (). It appears as the seventh scale degree in the natural minor and descending melodic minor scales but not in the major scale. In major keys, the subtonic sometimes appears in borrowed chords. In the movable do solfège system, the subtonic note is sung as ''te'' (or ''ta''). The subtonic can be contrasted with the leading note, which is a ''half step'' below the tonic. The distinction between leading note and subtonic has been made by theorists since at least the second quarter of the 20th century. Before that, the term ''subtonic'' often referred to the leading tone triad, for example. The word ''subtonic'' is also used as an English translation of ''subtonium'', the Latin term used in Gregorian chant theory for the similar usage of a tone one whole step below the mode final in the Dorian, Phrygian, and Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediant
In music, the mediant (''Latin'': to be in the middle) is the third scale degree () of a diatonic scale, being the note halfway between the tonic and the dominant.Benward & Saker (2003), p.32. In the movable do solfège system, the mediant note is sung as ''mi''. While the fifth scale degree is almost always a perfect fifth, the mediant can be a major or minor third. Schenkerian analysts consider this scale degree as expansion of the tonic since they have two common tones. On the other hand, in German theory derived from Hugo Riemann the mediant in major is considered the dominant parallel, Dp, and in minor the tonic parallel, tP. In Roman numeral analysis, the mediant chord can take several forms. In major scales, the mediant chord is a minor triad and is symbolized with the Roman numeral iii. In natural minor scales, the mediant is a major triad and is symbolized with the Roman numeral III. In harmonic minor scales and ascending melodic minor scales, the seventh scale d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)