|
Roger Carpenter
Professor Roger Hugh Stephen Carpenter (2 September 1945 – 27 October 2017) was an English neurophysiologist, Professor of Oculomotor Physiology at the University of Cambridge. Early life Carpenter was educated at Gresham's School, Holt, Norfolk, where he was a member of Farfield (1958–1963), and then at Cambridge. Career Before being appointed as Professor of Oculomotor Physiology in the University of Cambridge, Carpenter was a Director of Studies in Medicine at Caius College. In his principal field, mechanisms of consciousness, his position can be described as a one-way Cartesian. He was the creator of EPIC (the Experimental Physiology Instrumentation Computer) and NeuroLab, a set of interactive demonstrations on the working of the human brain. In his spare time, he ran the CUDOS project (Cambridge University Distributed Opportunity Systems), aimed at using medical students' gap year between school and university. He directed the musical ensembles the Susato Consort and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Cambridge
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts. Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge. , established = , other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Scholars of the University of Cambridge , type = Public research university , endowment = £7.121 billion (including colleges) , budget = £2.308 billion (excluding colleges) , chancellor = The Lord Sainsbury of Turville , vice_chancellor = Anthony Freeling , students = 24,450 (2020) , undergrad = 12,850 (2020) , postgrad = 11,600 (2020) , city = Cambridge , country = England , campus_type = , sporting_affiliations = The Sporting Blue , colours = Cambridge Blue , website = , logo = University of Cambridge logo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Professor
Professor (commonly abbreviated as Prof.) is an Academy, academic rank at university, universities and other post-secondary education and research institutions in most countries. Literally, ''professor'' derives from Latin as a "person who professes". Professors are usually experts in their field and teachers of the highest rank. In most systems of List of academic ranks, academic ranks, "professor" as an unqualified title refers only to the most senior academic position, sometimes informally known as "full professor". In some countries and institutions, the word "professor" is also used in titles of lower ranks such as associate professor and assistant professor; this is particularly the case in the United States, where the unqualified word is also used colloquially to refer to associate and assistant professors as well. This usage would be considered incorrect among other academic communities. However, the otherwise unqualified title "Professor" designated with a capital let ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurophysiology
Neurophysiology is a branch of physiology and neuroscience that studies nervous system function rather than nervous system architecture. This area aids in the diagnosis and monitoring of neurological diseases. Historically, it has been dominated by electrophysiology—the electrical recording of neural activity ranging from the molar (the electroencephalogram, EEG) to the cellular (intracellular recording of the properties of single neurons), such as patch clamp, voltage clamp, extracellular single-unit recording and recording of local field potentials. However, since the neurone is an electrochemical machine, it is difficult to isolate electrical events from the metabolic and molecular processes that cause them. Thus, neurophysiologists currently utilise tools from chemistry (calcium imaging), physics (functional magnetic resonance imaging, Functional magnetic resonance imaging, fMRI), and molecular biology (site directed mutations) to examine brain activity. The word originates f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gresham's School
Gresham's School is a Public school (United Kingdom), public school (English Independent school (United Kingdom), independent Day school, day and boarding school) in Holt, Norfolk, Holt, Norfolk, England, one of the top thirty International Baccalaureate schools in England. The school was founded in 1555 by John Gresham, Sir John Gresham as a free grammar school for forty boys, following Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII's Dissolution of the Monasteries, dissolution of Priory of St Mary in the Meadow, Beeston Regis, Beeston Priory. The founder left the school's endowments in the hands of the Worshipful Company of Fishmongers of the City of London, who are still the school's trustees. In the 1890s, an increase in the rental income of property in the City of London led to a major expansion of the school, which built many new buildings on land it owned on the eastern edge of Holt, including several new Boarding school, boarding house system, houses as well as new teaching bui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holt, Norfolk
Holt is a market town, civil parish and electoral ward in the English county of Norfolk. The town is north of the city of Norwich, west of Cromer and east of King's Lynn. The town has a population of 3,550, rising and including the ward to 3,810 at the 2011 census. Holt is within the area covered by North Norfolk District Council. Holt has a heritage railway station; it is the south-western terminus of the preserved North Norfolk Railway, known as the ''Poppy Line''. History Origins The most likely derivation of the name Holt is from an Anglo-Saxon word for woodland,Brooks, Peter, ''Holt, Georgian Market Town'', (Cromer: Poppyland Publishing, second edition 2001, ) and Holt is located on wooded high ground of the Cromer-Holt ridge at the crossing point of two ancient by-ways and as such was a natural point for a settlement to grow. The town has a mention in the great survey of 1086 known as the Domesday Book. In the survey it is described as a market town and a port with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farfield
Farfield is one of the seven boarding houses at Gresham's, an English public school at Holt, Norfolk. Farfield is currently home to approximately fifty boys. History and traditions Farfield was the third new boarding house to be built at the school, following its move from the town centre to the Cromer Road at the beginning of the 20th century, in a surge of renewal and expansion at Gresham's led by George Howson. Completed in 1911, it was shortly followed by a new school chapel. The first housemaster, Major J. C. Miller, and boys were transferred from a smaller house called Bengal Lodge.Farfield House Archive greshams.com, accessed 15 December 2022 The school magazine noted that a useful donkey was being kept in an outbuilding at Farfield. The young |
Gonville And Caius College, Cambridge
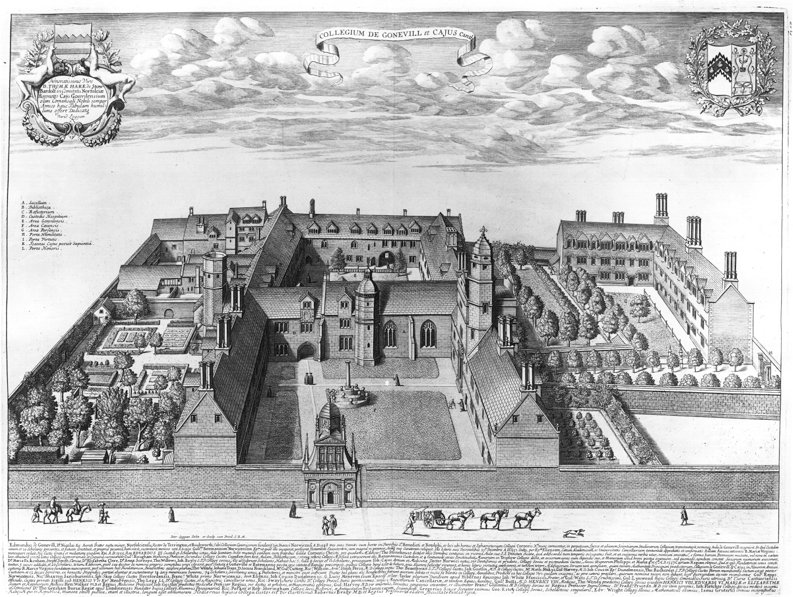
Gonville and Caius College, often referred to simply as Caius ( ), is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1348, it is the fourth-oldest of the University of Cambridge's 31 colleges and one of the wealthiest. The college has been attended by many students who have gone on to significant accomplishment, including fifteen Nobel Prize winners, the second-highest of any Oxbridge college after Trinity College, Cambridge. The college has long historical associations with the teaching of medicine, especially due to its prominent alumni in the medical profession. It also has globally-recognized and prestigious academic programmes in law, economics, English literature, and history. Famous Gonville and Caius alumni include physicians John Caius (who gave the college the caduceus in its insignia) and William Harvey. Other alumni in the sciences include Francis Crick (joint discoverer of the structure of DNA with James Watson), James Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gap Year
A gap year, also known as a sabbatical year, is typically a year-long break before or after college/university during which students engage in various educational and developmental activities, such as travel or some type of regular work. Gap years usually occur between high school and college, or after graduating from college and before entry into graduate school. Students undertaking a gap year might, for example, take advanced courses in mathematics or language studies, learn a trade, study art, volunteer, travel, take internships, play sports, or participate in cultural exchanges. Studies indicate that students who take a gap year perform better academically than those who do not, however, many parents worry that their children will defer continuation of their education. Many students have even decided against going to university after taking time to reflect during their gap year. Description A gap year is described as “a semester or year of experiential learning, typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute For Learning And Teaching In Higher Education
The Institute for Learning and Teaching in Higher Education (ILT) was a UK organisation set up as "the professional body for higher education staff involved in teaching and the support of learning". It was founded in 2000 as a result of the reports of the National Committee of Inquiry into Higher Education (the "Dearing Report").Helen Beebee (2003) ''Times Higher Education'' 28 March 2003 The ILT was located on . The founding Chief Executive was Dr Paul Clark.Sally Brown (1999) ''Active Learning'' 10 pp 67–8 "Introducing the Institute for Learning and Teaching" ISSN 1357-1125 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellows Of Gonville And Caius College, Cambridge
{{disambiguation ...
Fellows may refer to Fellow, in plural form. Fellows or Fellowes may also refer to: Places *Fellows, California, USA *Fellows, Wisconsin, ghost town, USA Other uses *Fellows Auctioneers, established in 1876. *Fellowes, Inc., manufacturer of workspace products *Fellows, a partner in the firm of English canal carriers, Fellows Morton & Clayton *Fellows (surname) See also *North Fellows Historic District, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Wapello County, Iowa *Justice Fellows (other) Justice Fellows may refer to: * Grant Fellows (1865–1929), associate justice of the Michigan Supreme Court * Raymond Fellows (1885–1957), associate justice of the Maine Supreme Judicial Court {{disambiguation, tndis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Educated At Gresham's School
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_1938.jpg)