|
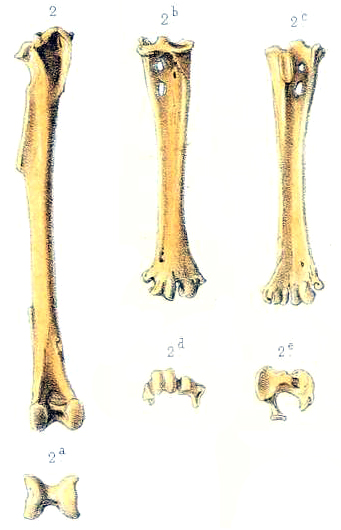
Rodrigues Night Heron
The Rodrigues night heron (''Nycticorax megacephalus'') is an extinct species of heron formerly occurring on the Mascarene island of Rodrigues (island), Rodrigues. Taxonomy It is known from subfossil bones and the 1708 description of François Leguat, Leguat as well as the 1726 report of Julien Tafforet. Description The skull of the Rodrigues night heron was 154 long,the upper mandible was 94 mm and the lower was 147. Behaviour and ecology Little is known about the behaviour of the Rodrigues night heron apart from the two contemporary descriptions. Leguat's 1708 description, wherein he stated the bird fed on endemic ''Phelsuma'' geckos (likely the Rodrigues day gecko), reads as follows: Milne-Edwards suggested in 1874 that the Rodrigues night heron had reduced power of flight, an opinion which Günther and Newton corroborated in 1879 by measuring the known wing-bones and founding all of them except the scapula to have been reduced in size and strength, while retaining the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphonse Milne-Edwards
Alphonse Milne-Edwards (Paris, 13 October 1835 – Paris, 21 April 1900) was a French mammalogist, ornithologist, and carcinologist. He was English in origin, the son of Henri Milne-Edwards and grandson of Bryan Edwards, a Jamaican planter who settled at Bruges (then in France). Milne-Edwards obtained a medical degree in 1859 and became assistant to his father at the ' in 1876. He became the director of the in 1891, devoting himself especially to fossil birds and deep-sea exploration. In 1881, he undertook a survey of the Gulf of Gascony with Léopold de Folin and worked aboard the ''Travailleur'' and the ''Talisman,'' researching the seas off the Canary Islands, the Cape Verde Islands, and the Azores. For this, he received a gold medal of the Royal Geographical Society. His major ornithological works include ' published in two parts in 1867 and 1872, ' 1866–1874 and ' 1868–1874. His study of fossils led to the discovery of tropical birds such as trogons and parrots from p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fat Chicken
In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food. The term often refers specifically to triglycerides (triple esters of glycerol), that are the main components of vegetable oils and of fatty tissue in animals; or, even more narrowly, to triglycerides that are solid or semisolid at room temperature, thus excluding oils. The term may also be used more broadly as a synonym of lipid—any substance of biological relevance, composed of carbon, hydrogen, or oxygen, that is insoluble in water but soluble in non-polar solvents. In this sense, besides the triglycerides, the term would include several other types of compounds like mono- and diglycerides, phospholipids (such as lecithin), sterols (such as cholesterol), waxes (such as beeswax), and free fatty acids, which are usually present in human diet in smaller amounts. Fats are one of the three main macr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodrigues Starling
The Rodrigues starling (''Necropsar rodericanus'') is an extinct species of starling that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Rodrigues. Its closest relatives were the Mauritius starling and the hoopoe starling from nearby islands; all three are extinct and appear to be of Southeast Asian origin. The bird was only reported by French sailor Julien Tafforet, who was marooned on the island from 1725 to 1726. Tafforet observed it on the offshore islet of Île Gombrani. Subfossil remains found on the mainland were described in 1879, and were suggested to belong to the bird mentioned by Tafforet. There was much confusion about the bird and its taxonomic relations throughout the 20th century. The Rodrigues starling was long, and had a stout beak. It was described as having a white body, partially black wings and tail, and a yellow bill and legs. Little is known about its behaviour. Its diet included eggs and dead tortoises, which it processed with its strong bill. Predation by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodrigues Scops Owl
The Rodrigues scops owl (''Otus murivorus''), also known as Rodrigues owl, Rodrigues lizard owl, Leguat's owl, or (somewhat misleadingly) Rodrigues little owl, was a small owl. It lived on the Mascarene island of Rodrigues, but it is nowadays extinct. It is part of the three Mascarene owls, formerly classified in the genus ''Mascarenotus'', although they are now classified in the genus ''Otus''. Like many of the Mascarene land-birds, the genus was a distinct relative to South-East Asian taxa, in this case apparently being a descendant of the direct ancestor of the Oriental scops owl. This insular scops owl had evolved gigantism, becoming twice as large and four times heavier than its continental ancestor.Duhamel, A. ''et al''. (2020) Cranial evolution in the extinct Rodrigues Island owl ''Otus murivorus'' (Strigidae), associated with unexpected ecological adaptations. ''Scientific Reports'', 10:14019. Taxonomy It is sometimes assumed that Leguat mentioned this bird in his 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodrigues Rail
The Rodrigues rail (''Erythromachus leguati''), also known as Leguat's gelinote or Leguat's rail, is an extinct species of the Rallidae, rail family that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Rodrigues, east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. It is generally kept in its own genus, ''Erythromachus'', but has sometimes been assigned to the genus ''Aphanapteryx'' along with its close relative the red rail (''A. bonasia'') of Mauritius; their relationship with other rails is unclear. The Rodrigues rail was about long and weighed at least . It was described as having grey plumage, a red beak, red legs, and a naked red patch around the eye. The beak was long and curved downwards. It was flightless and fed on tortoise eggs. It was described as being attracted to red objects, which humans exploited while hunting it. The Rodrigues rail is believed to have become extinct in the mid-18th century because of predation by introduced cats and destruction of its habitat by tortoise hunters. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton's Parakeet
Newton's parakeet (''Psittacula exsul''), also known as the Rodrigues parakeet or Rodrigues ring-necked parakeet, is an extinct species of parrot that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Rodrigues in the western Indian Ocean. Several of its features diverged from related species, indicating long-term isolation on Rodrigues and subsequent adaptation. The rose-ringed parakeet of the same genus is a close relative and probable ancestor. Newton's parakeet may itself have been ancestral to the endemic parakeets of nearby Mauritius and Réunion. Around long, Newton's parakeet was roughly the size of a rose-ringed parakeet. Its plumage was mostly greyish or slate blue in colour, which is unusual in ''Psittacula'', a genus containing mostly green species. The male had stronger colours than the female and possessed a reddish instead of black beak, but details of a mature male's appearance are uncertain; only one male specimen is known, and it is believed to be immature. Matur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodrigues Parrot
The Rodrigues parrot or Leguat's parrot (''Necropsittacus rodricanus'') is an extinct species of parrot that was endemic to the Mascarene island of Rodrigues in the Indian Ocean, east of Madagascar. It is unclear to which other species it is most closely related, but it is classified as a member of the tribe Psittaculini, along with other Mascarene parrots. The Rodrigues parrot bore similarities to the broad-billed parrot of Mauritius, and may have been related. Two additional species have been assigned to its genus (''N. francicus'' and ''N. borbonicus''), based on descriptions of parrots from the other Mascarene islands, but their identities and validity have been debated. The Rodrigues parrot was green, and had a proportionally large head and beak and a long tail. Its exact size is unknown, but it may have been around long. It was the largest parrot on Rodrigues, and it had the largest head of any Mascarene parrot. It may have looked similar to the great-billed parrot. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodrigues Solitaire
The Rodrigues solitaire (''Pezophaps solitaria'') is an extinct flightless bird that was endemic to the island of Rodrigues, east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. Genetically within the family of pigeons and doves, it was most closely related to the also extinct dodo of the nearby island Mauritius, the two forming the subfamily Raphinae. The Nicobar pigeon is their closest living genetic relative. Rodrigues solitaires grew to the size of swans, and demonstrated pronounced sexual dimorphism. Males were much larger than females and measured up to in length and in weight, contrasting with and for females. Its plumage was grey and brown; the female was paler than the male. It had a black band at the base of its slightly hooked beak, and its neck and legs were long. Both sexes were highly territorial, with large bony knobs on their wings that were used in combat. The Rodrigues solitaire laid a single egg that was incubated in turn by both sexes. Gizzard stones helped digest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the system through photosynthesis and is incorporated into plant tissue. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and microbes. Ecosystems are controlled by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beak
The beak, bill, or rostrum is an external anatomical structure found mostly in birds, but also in turtles, non-avian dinosaurs and a few mammals. A beak is used for eating, preening, manipulating objects, killing prey, fighting, probing for food, courtship, and feeding young. The terms ''beak'' and ''rostrum'' are also used to refer to a similar mouth part in some ornithischians, pterosaurs, cetaceans, dicynodonts, anuran tadpoles, monotremes (i.e. echidnas and platypuses, which have a beak-like structure), sirens, pufferfish, billfishes and cephalopods. Although beaks vary significantly in size, shape, color and texture, they share a similar underlying structure. Two bony projections – the upper and lower mandibles – are covered with a thin keratinized layer of epidermis known as the rhamphotheca. In most species, two holes called ''nares'' lead to the respiratory system. Etymology Although the word "beak" was, in the past, generally restricted to the sharpened bills o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodrigues Giant Day Gecko
The Rodrigues giant day gecko (''Phelsuma gigas'') is an extinct species of day gecko. It lived on the island of Rodrigues and surrounding islands and typically dwelt on trees. The Rodrigues giant day gecko fed on insects and nectar, and, unlike most other day geckos, was apparently nocturnal in habit. Description ''Phelsuma gigas'' was one of the largest known geckoes. It reached a total length of about . The body colour was grayish or grayish brown. On the back there were irregular black spottings. The tail had some striping and was charcoal- or dark grey-coloured. The tongue had a pink colour and the ventral side of the body was light yellow. The original collected specimens that were used to describe this species have been lost. Today, only a few portions of some skeletons remain. Behaviour Leguat described the species: Distribution This species inhabited Rodrigues and surrounding islands. ''P. gigas'' was last collected in 1842 on the offshore islet of Ile aux Fregates. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gecko
Geckos are small, mostly carnivorous lizards that have a wide distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. Belonging to the infraorder Gekkota, geckos are found in warm climates throughout the world. They range from . Geckos are unique among lizards for their vocalisations, which differ from species to species. Most geckos in the family Gekkonidae use chirping or clicking sounds in their social interactions. Tokay geckos (''Gekko gecko'') are known for their loud mating calls, and some other species are capable of making hissing noises when alarmed or threatened. They are the most species-rich group of lizards, with about 1,500 different species worldwide. All geckos, except species in the family Eublepharidae lack eyelids; instead, the outer surface of the eyeball has a transparent membrane, the cornea. They have a fixed lens within each iris that enlarges in darkness to let in more light. Since they cannot blink, species without eyelids generally lick t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |