|
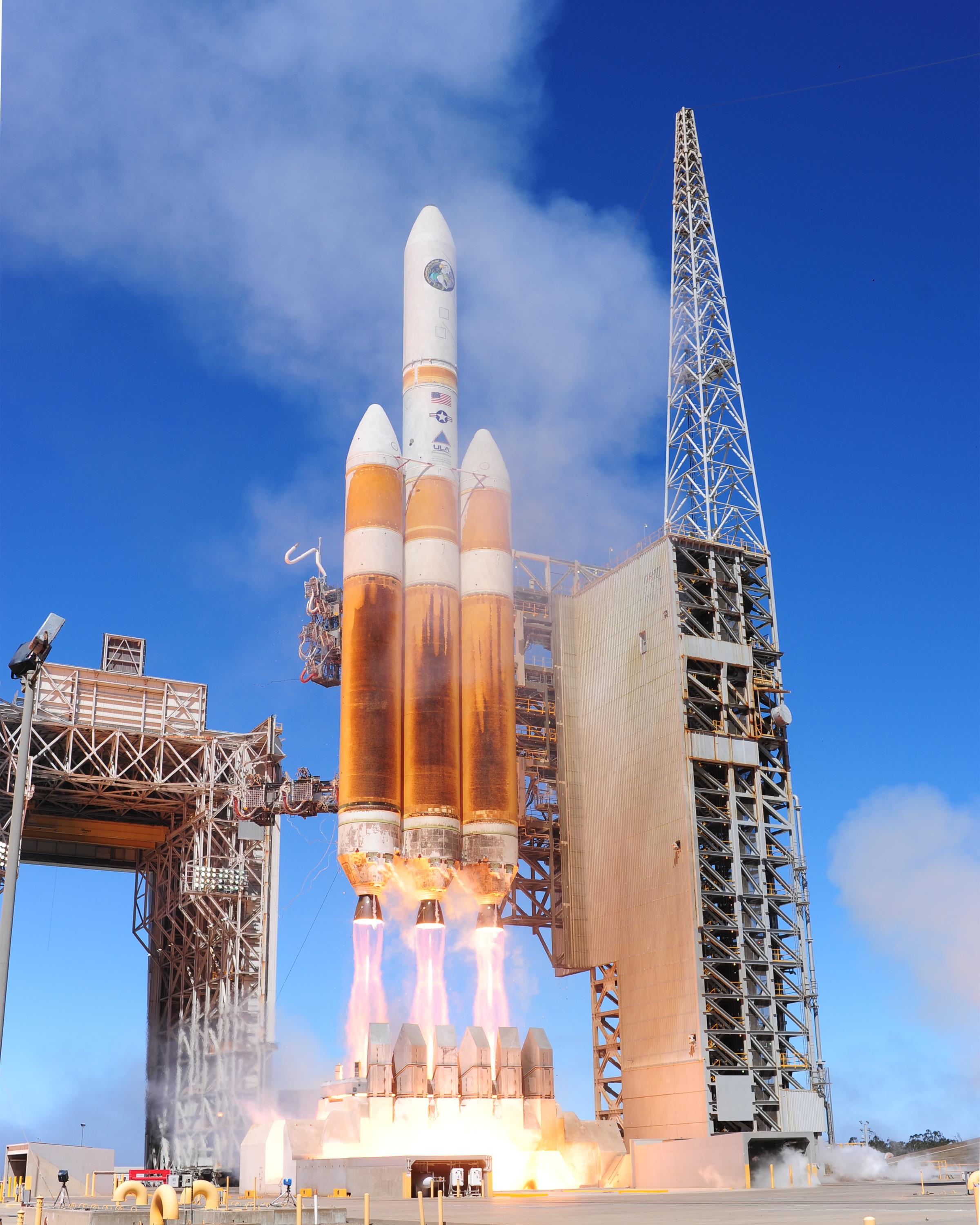
Rocket Ship
A space vehicle is the combination of a spacecraft and its launch vehicle which carries it into space. The earliest space vehicles were expendable launch systems, using a single or multistage rocket to carry a relatively small spacecraft in proportion to the total vehicle size and mass. An early exception to this, the Space Shuttle, consisted of a reusable orbital vehicle carrying crew and payload, supported by an expendable external propellant tank and two reusable solid-fuel booster rockets. Reusable launch systems are currently being developed by private industry. Early spacecraft or space vehicles were sometimes hyped as " spaceships", a term which comes from science fiction to designate a hypothetical vehicle which travels beyond low Earth orbit and is 100% reusable, needing only to be refueled like an airplane. History In the 1865 Jules Verne novel '' From the Earth to the Moon'', successful attempts are made to launch three people in a projectile with the goa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo 11 Launch - GPN-2000-000630
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label=genitive, , ; , is one of the Olympian deities in classical Greek and Roman religion and Greek and Roman mythology. The national divinity of the Greeks, Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, music and dance, truth and prophecy, healing and diseases, the Sun and light, poetry, and more. One of the most important and complex of the Greek gods, he is the son of Zeus and Leto, and the twin brother of Artemis, goddess of the hunt. Seen as the most beautiful god and the ideal of the '' kouros'' (ephebe, or a beardless, athletic youth), Apollo is considered to be the most Greek of all the gods. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as ''Apulu''. As the patron deity of Delphi (''Apollo Pythios''), Apollo is an or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash Gordon
Flash Gordon is the protagonist of a space adventure comic strip created and originally drawn by Alex Raymond. First published January 7, 1934, the strip was inspired by, and created to compete with, the already established '' Buck Rogers'' adventure strip. Creation The ''Buck Rogers'' comic strip had been commercially very successful, spawning novelizations and children's toys, and King Features Syndicate decided to create its own science fiction comic strip to compete with it. At first, King Features tried to purchase the rights to the '' John Carter of Mars'' stories by Edgar Rice Burroughs. However, the syndicate was unable to reach an agreement with Burroughs. King Features then turned to Alex Raymond, one of their staff artists, to create the story. One source for Flash Gordon was the Philip Wylie novel '' When Worlds Collide'' (1933). The themes of an approaching planet threatening the Earth, and an athletic hero, his girlfriend, and a scientist traveling to the new p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of reducing space transportation costs to enable the colonization of Mars. The company manufactures the Falcon 9, Falcon Heavy, and Starship launch vehicles, several rocket engines, Cargo Dragon and Crew Dragon spacecraft, and Starlink communications satellites. SpaceX is developing a satellite internet constellation named Starlink to provide commercial internet service. In January 2020, the Starlink constellation became the largest satellite constellation ever launched, and as of December 2022 comprises over 3,300 small satellites in orbit. The company is also developing Starship, a privately funded, fully reusable, super heavy-lift launch system for interplanetary and orbital spaceflight. It is intended to become SpaceX's prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suborbital Spaceflight
A sub-orbital spaceflight is a spaceflight in which the spacecraft reaches outer space, but its trajectory intersects the atmosphere or surface of the gravitating body from which it was launched, so that it will not complete one orbital revolution (it does not become an artificial satellite) or reach escape velocity. For example, the path of an object launched from Earth that reaches the Kármán line (at ) above sea level), and then falls back to Earth, is considered a sub-orbital spaceflight. Some sub-orbital flights have been undertaken to test spacecraft and launch vehicles later intended for orbital spaceflight. Other vehicles are specifically designed only for sub-orbital flight; examples include crewed vehicles, such as the X-15 and SpaceShipOne, and uncrewed ones, such as ICBMs and sounding rockets. Flights which attain sufficient velocity to go into low Earth orbit, and then de-orbit before completing their first full orbit, are not considered sub-orbital. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
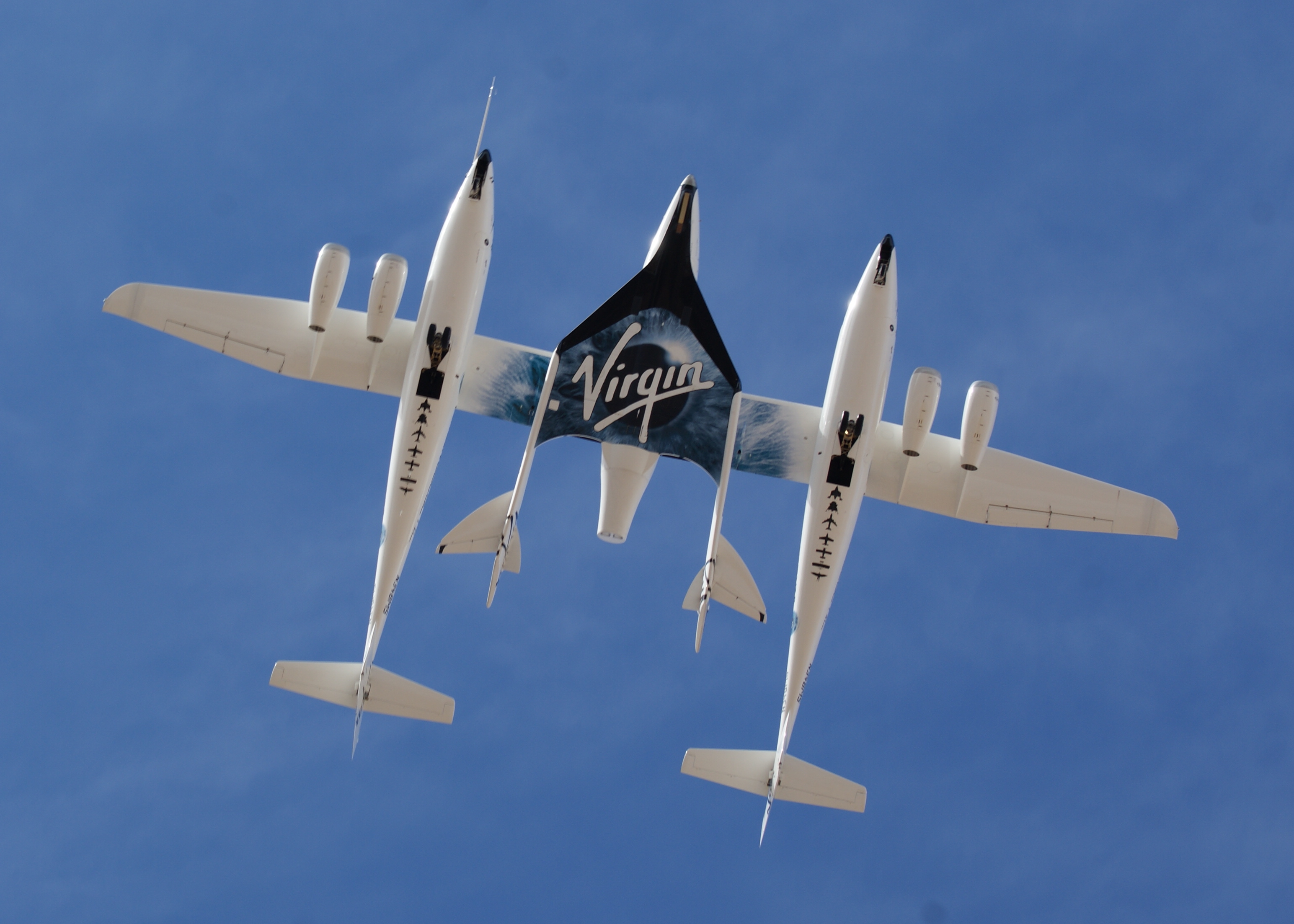
SpaceShipTwo
The Scaled Composites Model 339 SpaceShipTwo (SS2) is an air-launched suborbital spaceplane type designed for space tourism. It is manufactured by The Spaceship Company, a California-based company owned by Virgin Galactic. SpaceShipTwo is carried to its launch altitude by a Scaled Composites White Knight Two, before being released to fly on into the upper atmosphere powered by its rocket engine. It then glides back to Earth and performs a conventional runway landing. The spaceship was officially unveiled to the public on 7 December 2009 at the Mojave Air and Space Port in California. On 29 April 2013, after nearly three years of unpowered testing, the first one constructed successfully performed its first powered test flight. Virgin Galactic plans to operate a fleet of five SpaceShipTwo spaceplanes in a private passenger-carrying service and has been taking bookings for some time, with a suborbital flight carrying an updated ticket price of US$250,000. The spaceplane coul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Shepard
New Shepard is a fully reusable suborbital launch vehicle developed by Blue Origin for space tourism. The vehicle is named after Alan Shepard, the first American astronaut in space. The vehicle is capable of vertical takeoff and vertical landing, and can carry a crew. The first uncrewed test flight of the New Shepard vehicle was in 2015. Blue Origin began testing prototype engines and vehicles in 2006 and completed full-scale engine development in 2015. Testing continued in 2016 and 2017, and Blue Origin planned its first crewed test flight for 2018, but it was delayed until 2021. As of 4 August 2022, New Shepard has flown 32 passengers into space. Tickets for commercial flights began to be sold on May 5, 2021, for flights carrying up to six people. New Shepard is a one-stage rocket consisting of a crew capsule and a booster rocket. The capsule can seat six passengers. The booster rocket, powered by a BE-3 liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen engine, propels the capsule to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Propellant
Rocket propellant is the reaction mass of a rocket. This reaction mass is ejected at the highest achievable velocity from a rocket engine to produce thrust. The energy required can either come from the propellants themselves, as with a chemical rocket, or from an external source, as with ion engines. Overview Rockets create thrust by expelling mass rear-ward, at high velocity. The thrust produced can be calculated by multiplying the mass flow rate of the propellants by their exhaust velocity relative to the rocket (specific impulse). A rocket can be thought of as being accelerated by the pressure of the combusting gases against the combustion chamber and nozzle, not by "pushing" against the air behind or below it. Rocket engines perform best in outer space because of the lack of air pressure on the outside of the engine. In space it is also possible to fit a longer nozzle without suffering from flow separation. Most chemical propellants release energy through redox chemistry, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skylon (spacecraft)
Skylon is a series of concept designs for a reusable single-stage-to-orbit spaceplane by the British company Reaction Engines Limited (Reaction), using SABRE, a combined-cycle, air-breathing rocket propulsion system. The vehicle design is for a hydrogen-fuelled aircraft that would take off from a specially built reinforced runway, and accelerate to Mach 5.4 at altitude (compared to typical airliner's ) using the atmosphere's oxygen before switching the engines to use the internal liquid oxygen (LOX) supply to take it into orbit. It could carry of cargo to an equatorial low Earth orbit (LEO); up to to the International Space Station, almost 45% more than the capacity of the European Space Agency's Automated Transfer Vehicle; or to Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO), over 24% more than SpaceX Falcon 9 launch vehicle in reusable mode (). The relatively light vehicle would then re-enter the atmosphere and land on a runway, being protected from the conditions of re-ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McDonnell Douglas DC-X
The DC-X, short for Delta Clipper or Delta Clipper Experimental, was an uncrewed prototype of a reusable single-stage-to-orbit launch vehicle built by McDonnell Douglas in conjunction with the United States Department of Defense's Strategic Defense Initiative Organization (SDIO) from 1991 to 1993. Starting 1994 until 1995, testing continued through funding of the US civil space agency NASA. In 1996, the DC-X technology was completely transferred to NASA, which upgraded the design for improved performance to create the DC-XA. Background According to writer Jerry Pournelle: "DC-X was conceived in my living room and sold to National Space Council Chairman Dan Quayle by General Graham, Max Hunter and me." According to Max Hunter, however, he had tried hard to convince Lockheed Martin of the concept's value for several years before he retired. Hunter had written a paper in 1985 entitled "The Opportunity", detailing the concept of a Single-Stage-To-Orbit spacecraft built with l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotary Rocket
Rotary Rocket Company was an aerospace company in the late 1990s. Its founders were among the first to recognize that the end of the Cold War represented a significant shift away from the militarization of space, to a new civilian-led, commercial space industry. In 1996, Rotary Rocket Company was formed to address this emerging market. The company developed the Roton launch vehicle as a fully reusable single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO) piloted spacecraft. The design was initially conceived by Bevin McKinney, who shared it with Gary Hudson. The Roton was intended to reduce costs of launching payloads into low earth orbit by a factor of ten. Rotary attracted considerable media attention, as well as venture capital from angel investors and opened an engineering design and test center in a facility at Mojave Air and Space Port in Mojave, California. The fuselage for their vehicles was made by Scaled Composites, at the same airport, while the company developed the novel engine design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
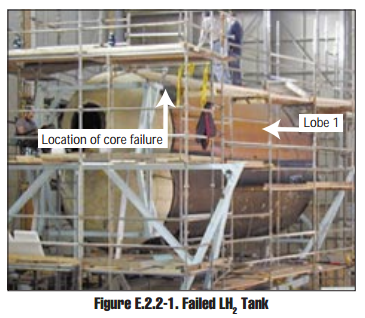
X-33
The Lockheed Martin X-33 was a proposed uncrewed, sub-scale technology demonstrator suborbital spaceplane that was developed for a period in the 1990s. The X-33 was a technology demonstrator for the VentureStar orbital spaceplane, which was planned to be a next-generation, commercially operated reusable launch vehicle. The X-33 would flight-test a range of technologies that NASA believed it needed for single-stage-to-orbit reusable launch vehicles (SSTO RLVs), such as metallic thermal protection systems, composite cryogenic fuel tanks for liquid hydrogen, the aerospike engine, autonomous (uncrewed) flight control, rapid flight turn-around times through streamlined operations, and its lifting body aerodynamics. Failures of its 21-meter wingspan and multi-lobed, composite-material fuel tank during pressure testing ultimately led to the withdrawal of federal support for the program in early 2001. Lockheed Martin has conducted unrelated testing, and has had a single success afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-stage-to-orbit
A single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO) vehicle reaches orbit from the surface of a body using only propellants and fluids and without expending tanks, engines, or other major hardware. The term usually, but not exclusively, refers to reusable vehicles. To date, no Earth-launched SSTO launch vehicles have ever been flown; orbital launches from Earth have been performed by either fully or partially expendable multi-stage rockets. The main projected advantage of the SSTO concept is elimination of the hardware replacement inherent in expendable launch systems. However, the non-recurring costs associated with design, development, research and engineering (DDR&E) of reusable SSTO systems are much higher than expendable systems due to the substantial technical challenges of SSTO, assuming that those technical issues can in fact be solved. SSTO vehicles may also require a significantly higher degree of regular maintenance. It is considered to be marginally possible to launch a single-stage- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |