|
Robert Taylor (architect)
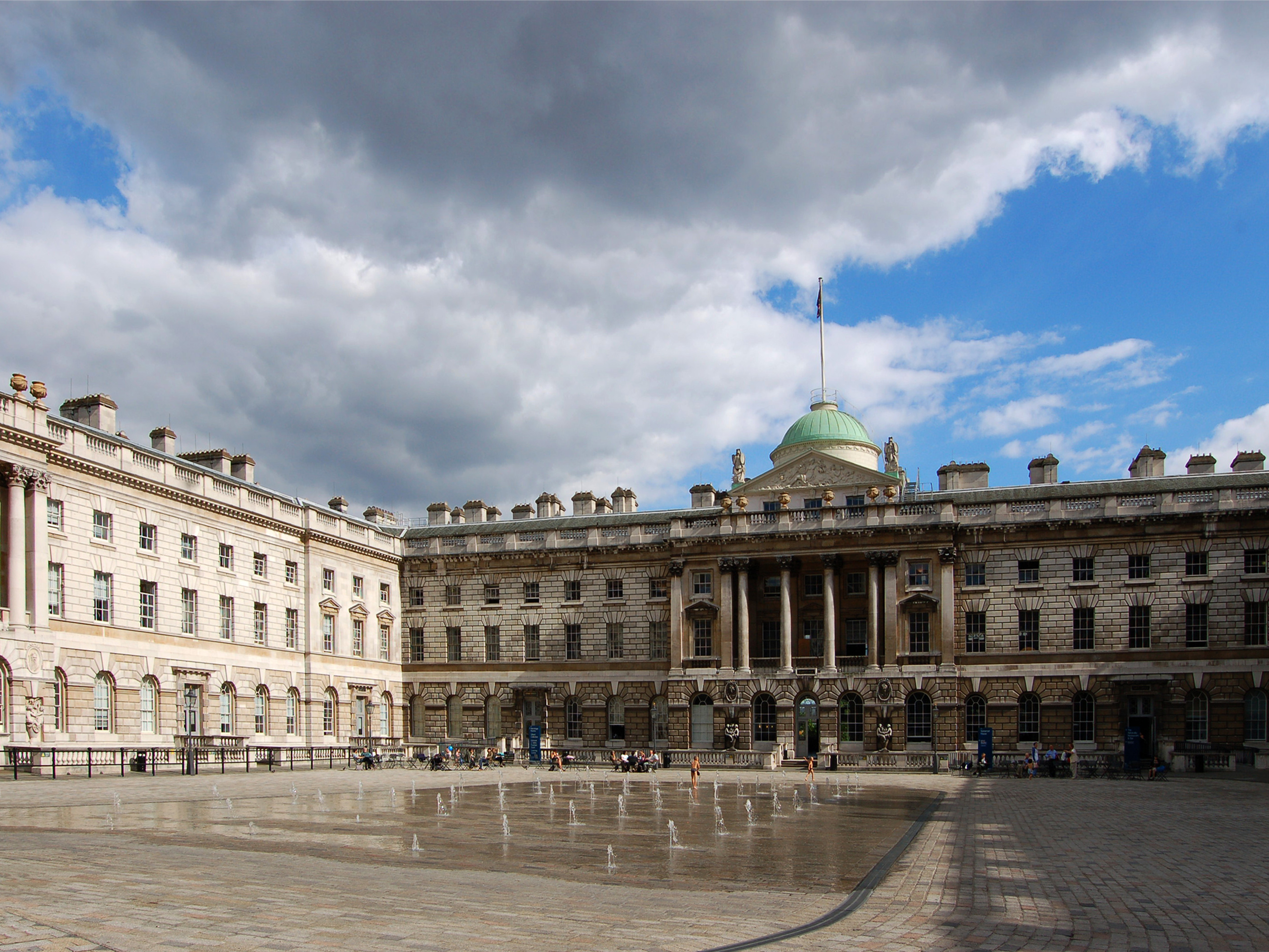
Sir Robert Taylor (1714–1788) was an English architect and sculptor who worked in London and the south of England. Early life Born at Woodford, Essex, Taylor followed in his father's footsteps and started working as a stonemason and sculptor, spending time as a pupil of Sir Henry Cheere.Sir_Robert_Taylor's_Foundation Despite some important commissions, including a bust of London merchant Christopher Emmott (died 1745) today held in the church of St Bartholomew, Colne, Lancashire, and another of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carmarthen Guildhall
Carmarthen Guildhall ( cy, Neuadd y Dref Caerfyrddin) is a municipal structure in Guildhall Square, Carmarthen, Wales. The guildhall, which was the headquarters of Carmarthen Borough Council, is a Grade I listed building. History The building was commissioned to replace a 16th-century guildhall which, by 1765, had become very dilapidated and had to be demolished in 1766. Some £4,000 towards the cost of the new building was donated by the future local Member of Parliament, John Adams. The foundation stone for the new building was laid on 10 April 1767: it was designed by Sir Robert Taylor in the neoclassical style, built in rubble masonry and completed in 1777. The design involved a symmetrical main frontage with three bays facing onto Guildhall Square; it was originally arcaded on the ground floor, so that markets could be held, with assembly rooms on the first floor. The ground floor was rusticated with Tuscan order columns supporting an entablature and a balustrade, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Chambers (architect)
__NOTOC__ Sir William Chambers (23 February 1723 – 10 March 1796) was a Swedish-Scottish architect, based in London. Among his best-known works are Somerset House, and the pagoda at Kew. Chambers was a founder member of the Royal Academy. Biography William Chambers was born on 23 February 1723 in Gothenburg, Sweden, to a Scottish merchant father. Between 1740 and 1749 he was employed by the Swedish East India Company making three voyages to China where he studied Chinese architecture and decoration. Returning to Europe, he studied architecture in Paris (with J. F. Blondel) and spent five years in Italy. Then, in 1755, he moved to London, where he established an architectural practice. In 1757, through a recommendation of Lord Bute, he was appointed architectural tutor to the Prince of Wales, later George III, and in 1766 also, along with Robert Adam, Architect to the King, (this being an unofficial title, rather than an actual salaried post with the Office of Works). He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United Kingdom's most notable religious buildings and since Edward the Confessor, a burial site for English and, later, British monarchs. Since the coronation of William the Conqueror in 1066, all coronations of English and British monarchs have occurred in Westminster Abbey. Sixteen royal weddings have occurred at the abbey since 1100. According to a tradition first reported by Sulcard in about 1080, a church was founded at the site (then known as Thorney Island) in the seventh century, at the time of Mellitus, Bishop of London. Construction of the present church began in 1245 on the orders of Henry III. The church was originally part of a Catholic Benedictine abbey, which was dissolved in 1539. It then served as the cathedral of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
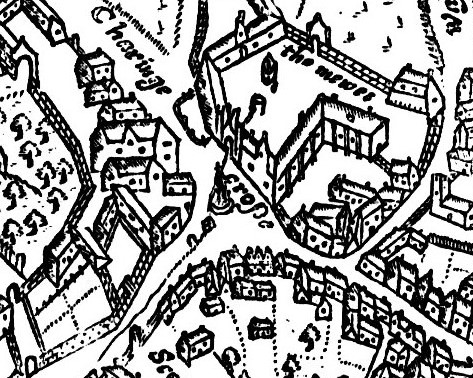
Trafalgar Square
Trafalgar Square ( ) is a public square in the City of Westminster, Central London, laid out in the early 19th century around the area formerly known as Charing Cross. At its centre is a high column bearing a statue of Admiral Nelson commemorating the victory at the Battle of Trafalgar. The battle of 21 October 1805, established the British navy's dominance at sea in the Napoleonic Wars over the fleets of France and Spain. The site around Trafalgar Square had been a significant landmark since the 1200s. For centuries, distances measured from Charing Cross have served as location markers. The site of the present square formerly contained the elaborately designed, enclosed courtyard of the King's Mews. After George IV moved the mews to Buckingham Palace, the area was redeveloped by John Nash, but progress was slow after his death, and the square did not open until 1844. The Nelson's Column at its centre is guarded by four lion statues. A number of commemorative statu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Martin-in-the-Fields
St Martin-in-the-Fields is a Church of England parish church at the north-east corner of Trafalgar Square in the City of Westminster, London. It is dedicated to Saint Martin of Tours. There has been a church on the site since at least the medieval period. It was at that time located in the farmlands and fields beyond the London wall, when it was awarded to Westminster Abbey for oversight. It became a principal parish church west of the old City in the early modern period as Westminster's population grew. When its medieval and Jacobean structure was found to be near failure, the present building was constructed in an influential neoclassical design by James Gibbs in 1722–1726. The church is one of the visual anchors adding to the open-urban space around Trafalgar Square. History Roman era Excavations at the site in 2006 uncovered a grave from about A.D. 410. The site is outside the city limits of Roman London (as was the usual Roman practice for burials) but is particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Whig Party
The Whigs were a political faction and then a political party in the Parliaments of England, Scotland, Ireland, Great Britain and the United Kingdom. Between the 1680s and the 1850s, the Whigs contested power with their rivals, the Tories. The Whigs merged into the new Liberal Party with the Peelites and Radicals in the 1850s, and other Whigs left the Liberal Party in 1886 to form the Liberal Unionist Party, which merged into the Liberals' rival, the modern day Conservative Party, in 1912. The Whigs began as a political faction that opposed absolute monarchy and Catholic Emancipation, supporting constitutional monarchism with a parliamentary system. They played a central role in the Glorious Revolution of 1688 and were the standing enemies of the Roman Catholic Stuart kings and pretenders. The period known as the Whig Supremacy (1714–1760) was enabled by the Hanoverian succession of George I in 1714 and the failure of the Jacobite rising of 1715 by Tory r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poole (UK Parliament Constituency)
Poole is a constituency represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 1997 by Robert Syms, a Conservative. History The first version of the Poole constituency existed from 1455 until 1885. During this period its exact status was a parliamentary borough, sending two burgesses to Westminster per year, except during its last 17 years when its representation was reduced to one member. During its abeyance most of Poole was in the East Dorset seat and since its recreation in 1950 its area has been reduced as the harbour town's population has increased. Boundaries 1950–1983: The Municipal Borough of Poole. 1983–1997: The Borough of Poole wards of Broadstone, Canford Cliffs, Canford Heath, Creekmoor, Hamworthy, Harbour, Newtown, Oakdale, Parkstone, and Penn Hill. 1997–2010: The Borough of Poole wards of Bourne Valley, Canford Cliffs, Hamworthy, Harbour, Newtown, Oakdale, Parkstone, and Penn Hill. 2010–19: The Borough of Poole wards of Branksome West, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Angelo Taylor
Michael Angelo Taylor (1757 – 16 July 1834) was an English politician and MP for Poole. He favored parliamentary reform and was made a privy councillor in 1831. Life He was a son of Sir Robert Taylor (1714–1788), the architect, and his wife Elizabeth, and was educated at Corpus Christi College, Oxford, becoming a barrister at Lincoln's Inn in 1774. He entered the House of Commons as Member of Parliament (MP) for Poole in 1784, and, with the exception of the short period from 1802 to 1806, remained a member of parliament until 1834, although not as the representative of the same constituency. In Parliament Taylor showed himself anxious to curtail the delays in the Court of Chancery, and to improve the lighting and paving of the London streets; and he was largely instrumental in bringing about the abolition of the pillory. At first a supporter of the younger Pitt, he soon veered round to the side of Fox and the Whigs, favored parliamentary reform, and was a personal frie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foundling Hospital
The Foundling Hospital in London, England, was founded in 1739 by the philanthropic sea captain Thomas Coram. It was a children's home established for the "education and maintenance of exposed and deserted young children." The word " hospital" was used in a more general sense than it is in the 21st century, simply indicating the institution's "hospitality" to those less fortunate. Nevertheless, one of the top priorities of the committee at the Foundling Hospital was children's health, as they combated smallpox, fevers, consumption, dysentery and even infections from everyday activities like teething that drove up mortality rates and risked epidemics. With their energies focused on maintaining a disinfected environment, providing simple clothing and fare, the committee paid less attention to and spent less on developing children's education. As a result, financial problems would hound the institution for years to come, despite the growing "fashionableness" of charities like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheriff Of London
Two sheriffs are elected annually for the City of London by the Liverymen of the City livery companies. Today's sheriffs have only nominal duties, but the historical officeholders had important judicial responsibilities. They have attended the justices at the Central Criminal Court, Old Bailey, since its original role as the court for the City and Middlesex. The sheriffs live in the Central Criminal Court, Old Bailey, during their year of service, so that one of them can always be attendant on the judges. In Court No 1 the principal chairs on the bench are reserved for their and the Lord Mayor's use, with the Sword of the City hanging behind the bench. It is an invariable custom that the Lord Mayor of London must previously have served as a sheriff. By a "custom of immemorial usage in the City", Howell et al., p. 191 the two sheriffs are elected at the Midsummer Common Hall by the Liverymen by acclamation, unless a ballot is demanded from the floor, which takes place wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Pilkington (architect)
William Pilkington (1758–1848) was an English architect. Life Born at Hatfield, near Doncaster, Yorkshire, on 7 September 1758, he was elder son of William Pilkington of Hatfield, by his second wife, Elizabeth, daughter of William Barker of Tadcaster. He was a pupil with Sir Robert Taylor, whose assistant he remained until Taylor's death in 1788. Pilkington had a practice as surveyor and architect in London, being employed by the Board of Customs (1782–1810), the parishes of St. Margaret and St. John in Westminster (1784), the Sun Fire Assurance office (1792), and Charterhouse School (1792). He retired about 1842 to his property at Hatfield, where he lived for the remainder of his life. He died in 1848. Works Pilkington was employed as surveyor and architect by Jacob Pleydell-Bouverie, 2nd Earl of Radnor at Salisbury, where he built the Guildhall (1788–97) from Taylor's designs, and at Folkestone, where he built the gaol. He was also employed by Augustus FitzRoy, 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Byfield
George may refer to: People * George (given name) * George (surname) * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Washington, First President of the United States * George W. Bush, 43rd President of the United States * George H. W. Bush, 41st President of the United States * George V, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1910-1936 * George VI, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1936-1952 * Prince George of Wales * George Papagheorghe also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George Harrison, an English musician and singer-songwriter Places South Africa * George, Western Cape ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa * George, Missouri * George, Washington * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Characters * George (Peppa Pig), a 2- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)