|
Robert L. Forward
Robert Lull Forward (August 15, 1932 – September 21, 2002) was an American physicist and science fiction writer. His literary work was noted for its scientific credibility and use of ideas developed from his career as an aerospace engineer. He also made important contributions to gravitational wave detection research. Biography Forward earned his doctorate from the University of Maryland in 1965, with a thesis entitled ''Detectors for Dynamic Gravitational Fields'', for the development of a bar antenna for the detection of gravitational radiation. Career and research He then went to work at the research labs of Hughes Aircraft, where he continued his research on gravity measurement and received 18 patents. He took early retirement in 1987, to focus on his fiction writing and consulting for such clients as NASA and the U.S. Air Force. In 1994, he co-founded the company Tethers Unlimited, Inc. with Robert P. Hoyt, where he served as Chief Scientist and Chairman until 2002. Muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geneva, New York
Geneva is a City (New York), city in Ontario County, New York, Ontario and Seneca County, New York, Seneca counties in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. It is at the northern end of Seneca Lake (New York), Seneca Lake; all land portions of the city are within Ontario County; the water portions are in Seneca County. The population was 13,261 at the 2010 census. The city is supposedly named after the city and canton of Geneva in Switzerland. The main settlement of the Seneca was spelled Zoneshio by early white settlers, and was described as being two miles north of Seneca Lake. The city borders, and was once part of, the town of Geneva (town), New York, Geneva. The city identifies as the "Lake Trout Capital of the World." History The area was long occupied by the Seneca tribe, which had established a major village of ''Kanadaseaga'' here by 1687. The British helped fortify the village against the French of Canada during the Seven Years' War (locally known as the Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Radiation
Gravitational waves are waves of the intensity of gravity generated by the accelerated masses of an orbital binary system that propagate as waves outward from their source at the speed of light. They were first proposed by Oliver Heaviside in 1893 and then later by Henri Poincaré in 1905 as waves similar to electromagnetic waves but the gravitational equivalent. Gravitational waves were later predicted in 1916 by Albert Einstein on the basis of his general theory of relativity as ripples in spacetime. Later he refused to accept gravitational waves. Gravitational waves transport energy as gravitational radiation, a form of radiant energy similar to electromagnetic radiation. Newton's law of universal gravitation, part of classical mechanics, does not provide for their existence, since that law is predicated on the assumption that physical interactions propagate instantaneously (at infinite speed)showing one of the ways the methods of Newtonian physics are unable to explain phe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statite
A statite (from the words ''static'' and ''satellite'') is a hypothetical type of artificial satellite that employs a solar sail to continuously modify its orbit in ways that gravity alone would not allow. Typically, a statite would use the solar sail to "hover" in a location that would not otherwise be available as a stable geosynchronous orbit. Statites have been proposed that would remain in fixed locations high over Earth's poles, using reflected sunlight to counteract the gravity pulling them down. Statites might also employ their sails to change the shape or velocity of more conventional orbits, depending upon the purpose of the particular statite. The concept of the statite was invented independently and at about the same time by Robert L. Forward (who coined the term "statite") and Colin McInnes, who used the term "halo orbit" (not to be confused with the type of halo orbit discovered by Robert Farquhar). Subsequently, the terms "non-Keplerian orbit" and "artificial Lagrange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Matter
There are several proposed types of exotic matter: * Hypothetical particles and states of matter that have "exotic" physical properties that would violate known laws of physics, such as a particle having a negative mass. * Hypothetical particles and states of matter that have not yet been encountered, but whose properties would be within the realm of mainstream physics if found to exist. * Several particles whose existence has been experimentally confirmed that are conjectured to be exotic hadrons and within the Standard Model. * States of matter that are not commonly encountered, such as Bose–Einstein condensates, fermionic condensates, nuclear matter, quantum spin liquid, string-net liquid, supercritical fluid, color-glass condensate, quark–gluon plasma, Rydberg matter, Rydberg polaron, photonic matter, and time crystal but whose properties are entirely within the realm of mainstream physics. * Forms of matter that are poorly understood, such as dark matter and mirror ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Travel
Time travel is the concept of movement between certain points in time, analogous to movement between different points in space by an object or a person, typically with the use of a hypothetical device known as a time machine. Time travel is a widely recognized concept in philosophy and fiction, particularly science fiction. The idea of a time machine was popularized by H. G. Wells' 1895 novel ''The Time Machine''. It is uncertain if time travel to the past is physically possible, and such travel, if at all feasible, may give rise to questions of causality. Forward time travel, outside the usual sense of the perception of time, is an extensively observed phenomenon and well-understood within the framework of special relativity and general relativity. However, making one body advance or delay more than a few milliseconds compared to another body is not feasible with current technology. As for backward time travel, it is possible to find solutions in general relativity that allow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Propulsion
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. In-space propulsion exclusively deals with propulsion systems used in the vacuum of space and should not be confused with space launch or atmospheric entry. Several methods of pragmatic spacecraft propulsion have been developed each having its own drawbacks and advantages. Most satellites have simple reliable chemical thrusters (often monopropellant rockets) or resistojet rockets for orbital station-keeping and some use momentum wheels for attitude control. Soviet bloc satellites have used electric propulsion for decades, and newer Western geo-orbiting spacecraft are starting to use them for north–south station-keeping and orbit raising. Interplanetary vehicles mostly use chemical rockets as well, although a few have used ion thrusters and Hall-effect thrusters (two different types of electric propulsion) to great success. Hypothetical in-space propulsion technologies describe the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimatter Propulsion
An antimatter rocket is a proposed class of rockets that use antimatter as their power source. There are several designs that attempt to accomplish this goal. The advantage to this class of rocket is that a large fraction of the rest mass of a matter/antimatter mixture may be converted to energy, allowing antimatter rockets to have a far higher energy density and specific impulse than any other proposed class of rocket. Methods Antimatter rockets can be divided into three types of application: those that directly use the products of antimatter annihilation for propulsion, those that heat a working fluid or an intermediate material which is then used for propulsion, and those that heat a working fluid or an intermediate material to generate electricity for some form of electric spacecraft propulsion system. The propulsion concepts that employ these mechanisms generally fall into four categories: solid core, gaseous core, plasma core, and beamed core configurations. The alternati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starwisp
Starwisp is a hypothetical unmanned interstellar probe design proposed by the late Robert L. Forward. It is propelled by a microwave sail, similar to a solar sail in concept, but powered by microwaves from a human-made source. It would fly through the target system without slowing down. Description "Starwisp" is a concept for an ultra-low-mass interstellar probe pushed by a microwave beam. It was proposed by scientist and author Robert L. Forward in 1985, and further work was published by Geoffrey A. Landis in 2000.Landis, Geoffrey A. "Microwave Pushed Interstellar Sail: Starwisp Revisited" (paper AIAA-2000-3337, presented at the AIAA 36th Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Huntsville AL, July 17–19, 2000). The proposed device uses beam-powered propulsion in the form of a high-power microwave antenna pushing a sail. The probe itself would consist of a mesh of extremely fine carbon wires about 100 m across, with the wires spaced the same distance apart as the 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Sail
Solar sails (also known as light sails and photon sails) are a method of spacecraft propulsion using radiation pressure exerted by sunlight on large mirrors. A number of spaceflight missions to test solar propulsion and navigation have been proposed since the 1980s. The first spacecraft to make use of the technology was IKAROS, launched in 2010. A useful analogy to solar sailing may be a sailing boat; the light exerting a force on the mirrors is akin to a sail being blown by the wind. High-energy laser beams could be used as an alternative light source to exert much greater force than would be possible using sunlight, a concept known as beam sailing. Solar sail craft offer the possibility of low-cost operations combined with long operating lifetimes. Since they have few moving parts and use no propellant, they can potentially be used numerous times for delivery of payloads. Solar sails use a phenomenon that has a proven, measured effect on astrodynamics. Solar pressure affec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
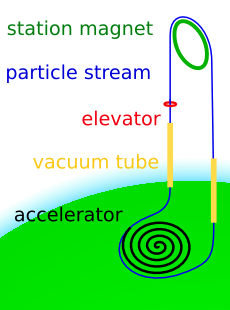
Space Fountain
A space fountain is a proposed form of an extremely tall tower extending into space. As known materials cannot support a static tower with this height, a space fountain has to be an active structure: A stream of pellets is accelerated upwards from a ground station. At the top it is deflected downwards. The necessary force for this deflection supports the station at the top and payloads going up the structure. A spacecraft could launch from the top without having to deal with the atmosphere. This could reduce the cost of placing payloads into orbit. Its largest downside is that the tower will re-enter the atmosphere if the accelerator fails and the stream stops. This risk could be reduced by several redundant streams. The lower part of a pellet stream has to be in a vacuum tube to avoid excessive drag in the atmosphere. Similar to the top station, this tube can be supported by its own system of transferring momentum from a space-bound stream to a surface-bound stream. If the tub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Tether
Space tethers are long cables which can be used for propulsion, momentum exchange, stabilization and attitude control, or maintaining the relative positions of the components of a large dispersed satellite/spacecraft sensor system. Depending on the mission objectives and altitude, spaceflight using this form of spacecraft propulsion is theorized to be significantly less expensive than spaceflight using rocket engines. Main techniques Tether satellites might be used for various purposes, including research into tether propulsion, tidal stabilization and orbital plasma dynamics. Five main techniques for employing space tethers are in development: ;Electrodynamic tethers Electrodynamic tethers are primarily used for propulsion. These are conducting tethers that carry a current that can generate either thrust or drag from a planetary magnetic field, in much the same way as an electric motor does. ;Momentum exchange tethers These can be either rotating tethers, or non-rotating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert P
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of ''Hrōþ, Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use Robert (surname), as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert (name), Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta (given name), Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto (given name), Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |