|
Robert J. Cotter
Robert J. Cotter (July 15, 1943 – November 12, 2012) was an American chemist and mass spectrometrist. His research contributed to many early advances in the field of time-of-flight mass spectrometry. From 1998 to 2000 he was president of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry. Cotter was also a co-investigator on the Mars Organic Molecule Analyzer (MOMA) project, developing a miniaturized, low power consumption ion trap/time-of-flight mass spectrometer that was to be deployed with the ExoMars rover, now the ''Rosalind Franklin'' rover. Early life and education Cotter was raised in Abington, Massachusetts, and was the oldest of seven children. After being educated at Boston College High School in 1961, he attended the College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, Massachusetts. After graduating in 1965 with a Bachelor of Science (B.S.), he studied under W.S. Koski at Johns Hopkins University. He received his Ph.D. in 1972 and joined the faculty of Towson University and Getty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington, D
Washington commonly refers to: * Washington (state), United States * Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States ** A metonym for the federal government of the United States ** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered on Washington, D.C. * George Washington (1732–1799), the first president of the United States Washington may also refer to: Places England * Washington, Tyne and Wear, a town in the City of Sunderland metropolitan borough ** Washington Old Hall, ancestral home of the family of George Washington * Washington, West Sussex, a village and civil parish Greenland * Cape Washington, Greenland * Washington Land Philippines *New Washington, Aklan, a municipality *Washington, a barangay in Catarman, Northern Samar *Washington, a barangay in Escalante, Negros Occidental *Washington, a barangay in San Jacinto, Masbate *Washington, a barangay in Surigao City United States * Washington, Wisconsin (other) * Fort Washington (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bachelor Of Science
A Bachelor of Science (BS, BSc, SB, or ScB; from the Latin ') is a bachelor's degree awarded for programs that generally last three to five years. The first university to admit a student to the degree of Bachelor of Science was the University of London in 1860. In the United States, the Lawrence Scientific School first conferred the degree in 1851, followed by the University of Michigan in 1855. Nathaniel Southgate Shaler, who was Harvard's Dean of Sciences, wrote in a private letter that "the degree of Bachelor of Science came to be introduced into our system through the influence of Louis Agassiz, who had much to do in shaping the plans of this School." Whether Bachelor of Science or Bachelor of Arts degrees are awarded in particular subjects varies between universities. For example, an economics student may graduate as a Bachelor of Arts in one university but as a Bachelor of Science in another, and occasionally, both options are offered. Some universities follow the Oxford a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometrists
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by measuring the object's weight using a spring scale, rather than balance scale comparing it directly with known masses. An object on the Moon would weigh l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term memory, remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include primary progressive aphasia, problems with language, Orientation (mental), disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and challenging behaviour, behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an alle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Amyloid
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; grc, βῆτα, bē̂ta or ell, βήτα, víta) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiodental fricative while in borrowed words is instead commonly transcribed as μπ. Letters that arose from beta include the Roman letter and the Cyrillic letters and . Name Like the names of most other Greek letters, the name of beta was adopted from the acrophonic name of the corresponding letter in Phoenician, which was the common Semitic word ''*bait'' ('house'). In Greek, the name was ''bêta'', pronounced in Ancient Greek. It is spelled βήτα in modern monotonic orthography and pronounced . History The letter beta was derived from the Phoenician letter beth . Uses Algebraic numerals In the system of Greek numerals, beta has a value of 2. Such use is denoted by a number mark: Β′. Computing Finance Beta is used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma-desorption Mass Spectrometry
An ion source is a device that creates atomic and molecular ions. Ion sources are used to form ions for Mass spectrometry, mass spectrometers, optical emission spectrometers, particle accelerators, Ion implantation, ion implanters and Ion thruster, ion engines. Electron ionization Electron ionization is widely used in mass spectrometry, particularly for organic chemistry, organic molecules. The Phase (matter), gas phase reaction producing electron ionization is :M + e^- -> M^ + 2e^- where M is the atom or molecule being ionized, e^- is the electron, and M^ is the resulting ion. The electrons may be created by an arc discharge between a cathode and an anode. An electron beam ion source (EBIS) is used in atomic physics to produce highly charged ions by bombarding atoms with a powerful electron beam. Its principle of operation is shared by the electron beam ion trap. Electron capture ionization Electron capture ionization (ECI) is the ionization of a gas phase atom or molec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermospray
Thermospray is a soft ionization source by which a solvent flow of liquid sample passes through a very thin heated column to become a spray of fine liquid droplets. As a form of atmospheric pressure ionization in mass spectrometry these droplets are then ionized via a low-current discharge electrode to create a solvent ion plasma. A repeller then directs these charged particles through the skimmer and acceleration region to introduce the aerosolized sample to a mass spectrometer. It is particularly useful in liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). In more technical terms thermospray is the controlled partial vaporization of a liquid as it flows through a heated capillary tube. The nebulization is accomplished by pumping a liquid sample at moderately high pressure through an electrothermally heated capillary tube. When sufficient power is coupled to the flowing sample stream, a partially vaporized mixture is produced consisting of some fraction of vaporized sample and some r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
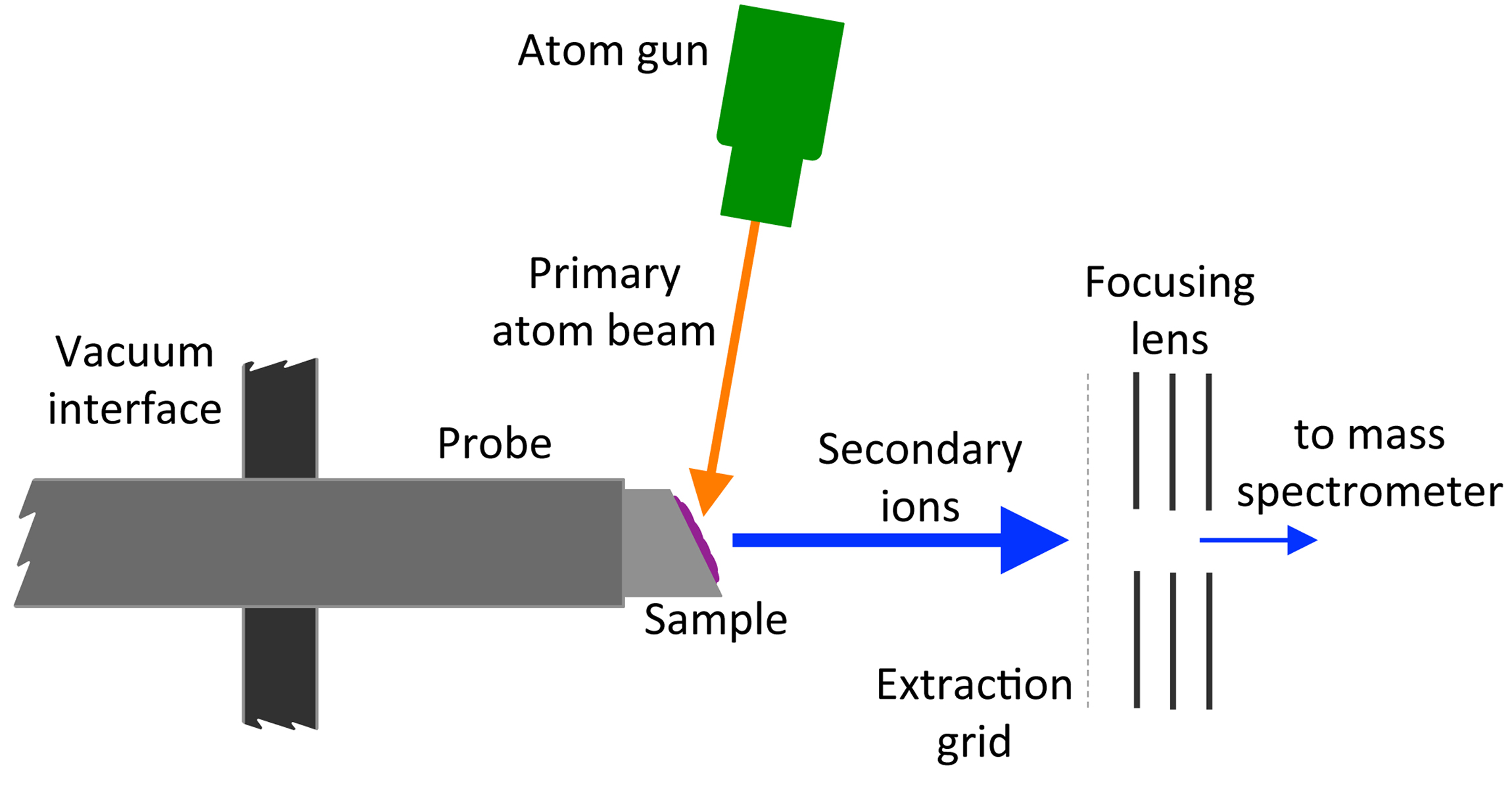
Fast Atom Bombardment
Fast atom bombardment (FAB) is an ionization technique used in mass spectrometry in which a beam of high energy atoms strikes a surface to create ions. It was developed by Michael Barber at the University of Manchester in 1980. When a beam of high energy ions is used instead of atoms (as in secondary ion mass spectrometry), the method is known as liquid secondary ion mass spectrometry (LSIMS). In FAB and LSIMS, the material to be analyzed is mixed with a non-volatile chemical protection environment, called a matrix, and is bombarded under vacuum with a high energy (4000 to 10,000 electron volts) beam of atoms. The atoms are typically from an inert gas such as argon or xenon. Common matrices include glycerol, thioglycerol, 3-nitrobenzyl alcohol (3-NBA), 18-crown-6 ether, 2-nitrophenyloctyl ether, sulfolane, diethanolamine, and triethanolamine. This technique is similar to secondary ion mass spectrometry and plasma desorption mass spectrometry. Ionization mechanism FAB is a rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
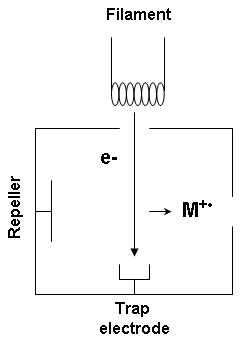
Ion Source
An ion source is a device that creates atomic and molecular ions. Ion sources are used to form ions for mass spectrometers, optical emission spectrometers, particle accelerators, ion implanters and ion engines. Electron ionization Electron ionization is widely used in mass spectrometry, particularly for organic molecules. The gas phase reaction producing electron ionization is :M + e^- -> M^ + 2e^- where M is the atom or molecule being ionized, e^- is the electron, and M^ is the resulting ion. The electrons may be created by an arc discharge between a cathode and an anode. An electron beam ion source (EBIS) is used in atomic physics to produce highly charged ions by bombarding atoms with a powerful electron beam. Its principle of operation is shared by the electron beam ion trap. Electron capture ionization Electron capture ionization (ECI) is the ionization of a gas phase atom or molecule by attachment of an electron to create an ion of the form A−•. The reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collision-induced Dissociation
Collision-induced dissociation (CID), also known as collisionally activated dissociation (CAD), is a mass spectrometry technique to induce fragmentation of selected ions in the gas phase. The selected ions (typically molecular ions or protonated molecules) are usually accelerated by applying an electrical potential to increase the ion kinetic energy and then allowed to collide with neutral molecules (often helium, nitrogen or argon). In the collision some of the kinetic energy is converted into internal energy which results in bond breakage and the fragmentation of the molecular ion into smaller fragments. These fragment ions can then be analyzed by tandem mass spectrometry. CID and the fragment ions produced by CID are used for several purposes. Partial or complete structural determination can be achieved. In some cases identity can be established based on previous knowledge without determining structure. Another use is in simply achieving more sensitive and specific detection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption/ionization
In mass spectrometry, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) is an ionization technique that uses a laser energy absorbing matrix to create ions from large molecules with minimal fragmentation. It has been applied to the analysis of biomolecules ( biopolymers such as DNA, proteins, peptides and carbohydrates) and various organic molecules (such as polymers, dendrimers and other macromolecules), which tend to be fragile and fragment when ionized by more conventional ionization methods. It is similar in character to electrospray ionization (ESI) in that both techniques are relatively soft (low fragmentation) ways of obtaining ions of large molecules in the gas phase, though MALDI typically produces far fewer multi-charged ions. MALDI methodology is a three-step process. First, the sample is mixed with a suitable matrix material and applied to a metal plate. Second, a pulsed laser irradiates the sample, triggering ablation and desorption of the sample and matrix materi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |