|
Robert De Bello Fago
Robert de Beaufeu (died in or before 1219) (List of Latinised names, Latinised to ''de Bello Fago'' or ''de Bello Foco'', meaning "from a beautiful fireplace") was a secular canon of Salisbury Cathedral, Salisbury and a minor poet. Life Educated at the University of Oxford, he gained, at an early age, a reputation for learning, and became the friend of Gerald of Wales, Walter Map, and other scholars. He was granted the prebend of Horton Court, Horton, near Chipping Sodbury, Gloucestershire, where he built a hall house, part of which survives in the structure of the present 16th century Horton Court. Works He is said have written a work entitled ''Encomium topographiae'', after hearing the ''Topographia Hiberniae'' (c.1188) of Gerald of Wales read by the author at a festival at Oxford. His authorship of this piece depends on Gerald of Wales's self-serving story reporting the praise that Robert gave to Gerald's ''Topographia Hiberniae''. A poem in praise of ale, ', in a manuscrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. On 12 July 927, the various Anglo-Saxon kings swore their allegiance to Æthelstan of Wessex (), unifying most of modern England under a single king. In 1016, the kingdom became part of the North Sea Empire of Cnut the Great, a personal union between England, Denmark and Norway. The Norman conquest of England in 1066 led to the transfer of the English capital city and chief royal residence from the Anglo-Saxon one at Winchester to Westminster, and the City of London quickly established itself as England's largest and principal commercial centre. Histories of the kingdom of England from the Norman conquest of 1066 conventionally distinguish periods named after successive ruling dynasties: Norman (1066–1154), Plantagenet (1154–1485), Tudor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
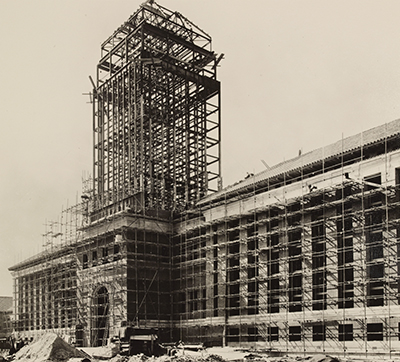
Cambridge University Library
Cambridge University Library is the main research library of the University of Cambridge. It is the largest of the over 100 libraries within the university. The Library is a major scholarly resource for the members of the University of Cambridge and external researchers. It is often referred to within the university as the UL. Thirty three faculty and departmental libraries are associated with the University Library for the purpose of central governance and administration, forming "Cambridge University Libraries". Cambridge University Library is one of the six legal deposit libraries under UK law. The Library holds approximately 9 million items (including maps and sheet music) and, through legal deposit, purchase and donation it receives around 100,000 items every year. The University Library is unique among the legal deposit libraries in keeping a large proportion of its material on open access and in allowing some categories of reader to borrow from its collections. Its or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alumni Of The University Of Oxford
Alumni (singular: alumnus (masculine) or alumna (feminine)) are former students of a school, college, or university who have either attended or graduated in some fashion from the institution. The feminine plural alumnae is sometimes used for groups of women. The word is Latin and means "one who is being (or has been) nourished". The term is not synonymous with "graduate"; one can be an alumnus without graduating (Burt Reynolds, alumnus but not graduate of Florida State, is an example). The term is sometimes used to refer to a former employee or member of an organization, contributor, or inmate. Etymology The Latin noun ''alumnus'' means "foster son" or "pupil". It is derived from PIE ''*h₂el-'' (grow, nourish), and it is a variant of the Latin verb ''alere'' "to nourish".Merriam-Webster: alumnus .. Separate, but from the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century Deaths
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 ( MCCI) through December 31, 1300 ( MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258), the destruction of the House of Wisdom and the weakening of the Mamluks and Rums which, according to historians, caused the decline of the Islamic Golden Age. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The Southern Song dynasty would begin the century as a prosperous kingdom but would eventually be invaded and annexed into the Yuan dynasty of the Mongols. The Kamakura Shogunate of Japan would be invaded by the Mongols. Goryeo resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Death Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Of Avranches
Henry of Avranches (died 1260) was a poet of the first half of the 13th century, writing in Latin. He is sometimes assumed to have been born in Avranches, but is otherwise said to have been of German birth with a Norman father. He is described as an itinerant cleric. He wrote numerous works, in hagiography and in other styles, including a life of Francis of Assisi, on John Blund, and poems on grammar. He wrote in 1228/9 a topographical poem about the Starkenburg Starkenburg is an historical region in the State of Hesse, Germany, comprising the area south of the Main River and east of the Rhine, around the regional capital Darmstadt. Geography The region is named after Starkenburg Castle, above Heppenh .... He took part in a poetry contest against Michael of Cornwall in 1254-55. This was after some earlier contests. References * John Paul Heironimus and Josiah Cox Russell, editors (1929), ''Two types of thirteenth century grammatical poems'' * John Paul Heironimus and Josiah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reginald Of Canterbury
Reginald of Canterbury (died after 1109) was a medieval French writer and Benedictine monk who lived and wrote in England in the very early part of the 12th century. He was the author of a number of Latin poems, including an epic entitled ''Malchus'', which still survives. Born in France around 1050, he arrived in England sometime before 1100. He became a monk at St Augustine's Abbey in Canterbury where most of his poetic works were composed. He is last mentioned in 1109, when he was the recipient of a poem from Thomas the Archbishop of York. Reginald's major work was an epic poem in six books on the life of Malchus, a late antique Syrian saint whose first biographer was Jerome. Reginald's other works included a poem about his native town, a group of poems extolling Canterbury and its saints, and one or two on Anselm of St Saba. Life Reginald, a native of France, was born roughly about 1050 in a place usually called Fagia, which may be the modern Faye-la-Vineuse in Poitou. The l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcuin
Alcuin of York (; la, Flaccus Albinus Alcuinus; 735 – 19 May 804) – also called Ealhwine, Alhwin, or Alchoin – was a scholar, clergyman, poet, and teacher from York, Northumbria. He was born around 735 and became the student of Ecgbert of York, Archbishop Ecgbert at York. At the invitation of Charlemagne, he became a leading scholar and teacher at the Carolingian dynasty, Carolingian court, where he remained a figure in the 780s and 790s. Before that, he was also a court chancellor in Aachen. "The most learned man anywhere to be found", according to Einhard's ''Vita Karoli Magni, Life of Charlemagne'' (–833), he is considered among the most important intellectual architects of the Carolingian Renaissance. Among his pupils were many of the dominant intellectuals of the Carolingian era. During this period, he perfected Carolingian minuscule, an easily read manuscript hand using a mixture of upper- and lower-case letters. Latin paleography in the eighth centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hall House
The hall house is a type of vernacular house traditional in many parts of England, Wales, Ireland and lowland Scotland, as well as northern Europe, during the Middle Ages, centring on a hall. Usually timber-framed, some high status examples were built in stone. Unaltered hall houses are almost unknown. Where they have survived, they have almost always been significantly changed and extended by successive owners over the generations. Origins In Old English, a "hall" is simply a large room enclosed by a roof and walls, and in Anglo-Saxon England simple one-room buildings, with a single hearth in the middle of the floor for cooking and warmth, were the usual residence of a lord of the manor and his retainers. The whole community was used to eating and sleeping in the hall. This is the hall as Beowulf understood it. Over several centuries the hall developed into a building which provided more than one room, giving some privacy to its more important residents. A significant house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poetry
Poetry (derived from the Greek ''poiesis'', "making"), also called verse, is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language − such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre − to evoke meanings in addition to, or in place of, a prosaic ostensible meaning. A poem is a literary composition, written by a poet, using this principle. Poetry has a long and varied history, evolving differentially across the globe. It dates back at least to prehistoric times with hunting poetry in Africa and to panegyric and elegiac court poetry of the empires of the Nile, Niger, and Volta River valleys. Some of the earliest written poetry in Africa occurs among the Pyramid Texts written during the 25th century BCE. The earliest surviving Western Asian epic poetry, the '' Epic of Gilgamesh'', was written in Sumerian. Early poems in the Eurasian continent evolved from folk songs such as the Chinese ''Shijing'', as well as religious hymns (the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chipping Sodbury
Chipping Sodbury is a market town and former civil parish, now in the parish of Sodbury, in the unitary authority area of South Gloucestershire, in the ceremonial county of Gloucestershire, England. It was founded in the 12th century by William le Gros. It is the principal settlement in the civil parish of Sodbury, which also includes the village of Old Sodbury. Little Sodbury is a nearby but separate civil parish. Sodbury parish council has elected to be known as Sodbury Town Council. At the 2011 census the population of Chipping Sodbury was 5,045, but in the last decade the town has become part of a much larger built-up area due to the rapid expansion of nearby Yate, with which it is contiguous to the west. At the census the combined population of Yate and Chipping Sodbury was 26,834. Governance An electoral ward in the same name (not Sodbury) exists. This ward starts in the north at Chipping Sodbury Golf Course and stretches south to Dodington. The total population of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
_(cropped).jpg)