|
Risograph
Risograph is a brand of digital duplicators manufactured by the Riso Kagaku Corporation, that are designed mainly for high-volume photocopying and printing. It was released in Japan in 1980. It is sometimes called a printer-duplicator, as newer models can be used as a network printer as well as a stand-alone duplicator. When printing or copying many duplicates (generally more than 100) of the same content, it is typically far less expensive per page than a conventional photocopier, laser printer, or inkjet printer. Process The underlying technology is very similar to a mimeograph. It brings together several processes which were previously carried out manually, for example using the Riso Print Gocco system or the Gestetner system. This simple technology is highly reliable compared to a standard photocopier and can achieve both very high speed (typically 150 pages per minute) and very low costs per copy when copying more than 100 copies. A good lifespan for a risograph might i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimeograph
A mimeograph machine (often abbreviated to mimeo, sometimes called a stencil duplicator) is a low-cost duplicating machine that works by forcing ink through a stencil onto paper. The process is called mimeography, and a copy made by the process is a mimeograph. Mimeographs, along with spirit duplicators and hectographs, were common technologies for printing small quantities of a document, as in office work, classroom materials, and church bulletins. Early fanzines were printed by mimeograph because the machines and supplies were widely available and inexpensive. Beginning in the late 1960s and continuing into the 1970s, photocopying gradually displaced mimeographs, spirit duplicators, and hectographs. For even smaller quantities, up to about five, a typist would use carbon paper. Origins Use of stencils is an ancient art, butthrough chemistry, papers, and pressestechniques advanced rapidly in the late nineteenth century: Papyrograph A description of the Papyrograph m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riso Kagaku Corporation
is a Japanese corporation which is the inventor, manufacturer, and distributor of the RISO Printer-Duplicator, a.k.a. Risograph. This device automatically creates a stencil-type master (from a paper original or digital file), thereby enabling it reproduce single-colour documents at high speed and low cost, in a machine that has a small footprint and a relatively low purchase price. The firm was established in Tokyo, Japan, where it continues to maintain its headquarters today. With sales in over 150 countries, Riso is a billion-dollar company. The company maintains a foundation that donates equipment around the world primarily to educational institutions. In Japanese, 'Riso' means 'ideal' and the word 'Kagaku' means 'science.' Noboru Hayama, the company's founder, started his business by mixing inks at his kitchen sink just after World War II, and in 1946 established a mimeograph printing company, whose first product was its signature duplicator. Over the next few y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photocopier
A photocopier (also called copier or copy machine, and formerly Xerox machine, the generic trademark) is a machine that makes copies of documents and other visual images onto paper or plastic film quickly and cheaply. Most modern photocopiers use a technology called ''xerography'', a dry process that uses electrostatic charges on a light-sensitive photoreceptor to first attract and then transfer toner particles (a powder) onto paper in the form of an image. The toner is then fused onto the paper using heat, pressure, or a combination of both. Copiers can also use other technologies, such as inkjet, but xerography is standard for office copying. Commercial xerographic office photocopying was introduced by Xerox in 1959, and it gradually replaced copies made by Verifax, Photostat, carbon paper, mimeograph machines, and other duplicating machines. Photocopying is widely used in the business, education, and government sectors. While there have been predictions that photocopiers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
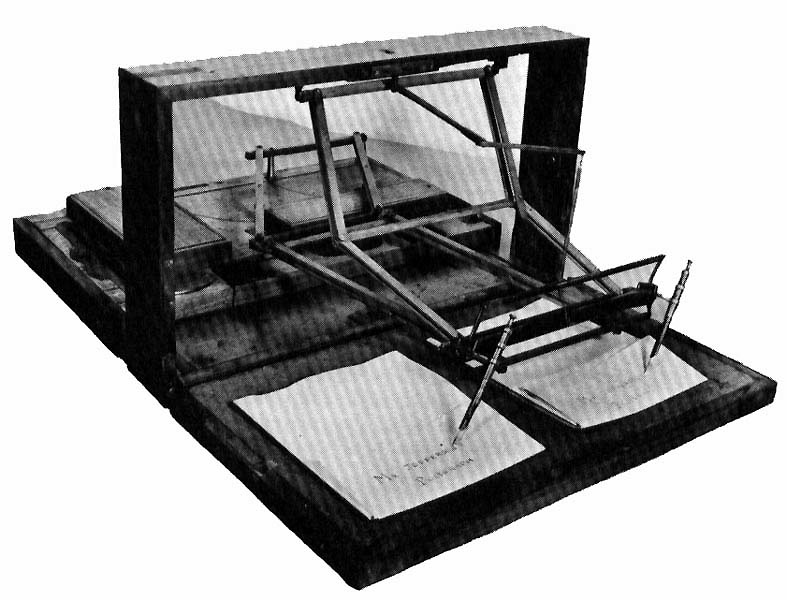
Duplicating Machines
Duplicating machines were the predecessors of modern document-reproduction technology. They have now been replaced by digital duplicators, scanners, laser printers and photocopiers, but for many years they were the primary means of reproducing documents for limited-run distribution. The duplicator was pioneered by Thomas Edison and David Gestetner, with Gestetner dominating the market up until the late 1990s. Like the typewriter, these machines were products of the second phase of the industrial revolution which started near the end of the 19th century (also called the Second Industrial Revolution). This second phase brought to mass markets technologies like the small electric motors and the products of industrial chemistry without which the duplicating machines would not have been economical. By bringing greatly increased quantities of paperwork to daily life, the duplicating machine and the typewriter gradually changed the forms of the office desk and transformed the nature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riso EZ200 (1946–2012), author of several books on the Enneagram of Personality
{{disambig ...
Riso may refer to: Architecture and museums * Palazzo Riso, a contemporary art museum in Palermo, Italy Institutions and corporations * Riso Kagaku Corporation, a Japanese manufacturer of duplicating machines * Risø National Laboratory, a scientific research organization in Denmark People * Don Richard Riso Don Richard Riso (17 January 1946 – August 30, 2012) was an American teacher of the Enneagram of Personality who wrote and co-wrote a number of books on the subject. Early life and education Riso grew up in New Orleans, Louisiana. He studied En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offset Printing
Offset printing is a common printing technique in which the inked image is transferred (or "offset") from a plate to a rubber blanket and then to the printing surface. When used in combination with the lithographic process, which is based on the repulsion of oil and water, the offset technique employs a flat ( planographic) image carrier. Ink rollers transfer ink to the image areas of the image carrier, while a water roller applies a water-based film to the non-image areas. The modern "web" process feeds a large reel of paper through a large press machine in several parts, typically for several meters, which then prints continuously as the paper is fed through. Development of the offset press came in two versions: in 1875 by Robert Barclay of England for printing on tin and in 1904 by Ira Washington Rubel of the United States for printing on paper. History Lithography was initially created to be an inexpensive method of reproducing artwork.Carter, Rob, Ben Day, Philip Meg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The earliest known form of printing as applied to paper was woodblock printing, which appeared in China before 220 AD for cloth printing. However, it would not be applied to paper until the seventh century.Shelagh Vainker in Anne Farrer (ed), "Caves of the Thousand Buddhas", 1990, British Museum publications, Later developments in printing technology include the movable type invented by Bi Sheng around 1040 AD and the printing press invented by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century. The technology of printing played a key role in the development of the Renaissance and the Scientific Revolution and laid the material basis for the modern knowledge-based economy and the spread of learning to the masses. History Woodblock printing Wood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Brands
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japonicum * Japonicus This list of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names is intended to help those unfamiliar with classical languages to understand and remember the scientific names of organisms. The binomial nomenclature used for animals and plants i ... * Japanese studies {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offset Printing
Offset printing is a common printing technique in which the inked image is transferred (or "offset") from a plate to a rubber blanket and then to the printing surface. When used in combination with the lithographic process, which is based on the repulsion of oil and water, the offset technique employs a flat ( planographic) image carrier. Ink rollers transfer ink to the image areas of the image carrier, while a water roller applies a water-based film to the non-image areas. The modern "web" process feeds a large reel of paper through a large press machine in several parts, typically for several meters, which then prints continuously as the paper is fed through. Development of the offset press came in two versions: in 1875 by Robert Barclay of England for printing on tin and in 1904 by Ira Washington Rubel of the United States for printing on paper. History Lithography was initially created to be an inexpensive method of reproducing artwork.Carter, Rob, Ben Day, Philip Meg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nashuatec
Nashuatec was one of the main brands used by parent company Ricoh to sell office equipment within Europe. It was particularly strong in Germany and the Netherlands where it had the biggest share. Along with Rex Rotary and Gestetner, it was one of the three brands of the NRG Group. NRG Group has now been merged into Ricoh Europe as of 1 April 2007. See also * Photocopying A photocopier (also called copier or copy machine, and formerly Xerox machine, the generic trademark) is a machine that makes copies of documents and other visual images onto paper or plastic film quickly and cheaply. Most modern photocopiers ... External links Nashuatec {{Ricoh Companies acquired by Ricoh Companies with year of establishment missing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ricoh
is a Japanese multinational imaging and electronics company. It was founded by the now-defunct commercial division of the Institute of Physical and Chemical Research (Riken) known as the ''Riken Concern'', on 6 February 1936 as . Ricoh's headquarters are located in Ota, Tokyo. Ricoh produces electronic products, primarily cameras and office equipment such as printers, photocopiers, fax machines, offers Software as a Service (SaaS) document management applications such as DocumentMall, RicohDocs, GlobalScan, Print&Share and also offers Projectors. In the late 1990s through early 2000s, the company grew to become the largest copier manufacturer in the world. During this time, Ricoh acquired Savin, Gestetner, Lanier, Rex-Rotary, Monroe, Nashuatec, IKON and most recently IBM Printing Systems Division / Infoprint Solutions Company. Although the Monroe brand was discontinued, products continue to be marketed worldwide under the remaining brand names. In 2006, Ricoh acqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toshiba
, commonly known as Toshiba and stylized as TOSHIBA, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure systems, elevators and escalators, electronic components, semiconductors, hard disk drives (HDD), printers, batteries, lighting, as well as IT solutions such as quantum cryptography which has been in development at Cambridge Research Laboratory, Toshiba Europe, located in the United Kingdom, now being commercialised. It was one of the biggest manufacturers of personal computers, consumer electronics, home appliances, and medical equipment. As a semiconductor company and the inventor of flash memory, Toshiba had been one of the top 10 in the chip industry until its flash memory unit was spun off as Toshiba Memory, later Kioxia, in the late 2010s. The Toshiba name is derived from its former name, Tokyo Shibaura Denki K.K. (Tokyo Shibaura Electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |