|
Ririe Reservoir
The Ririe Reservoir is a reservoir located near Ririe, Idaho. It allows for irrigation, flood control, and provides recreational opportunities. In 1972 the Ririe Dam, built on Willow Creek (Snake River), Willow Creek by the United States Army Corps of Engineers, was the site of the first practical application of steel fibrous shotcrete, which was used to build a tunnel adit. The dam's total capacity is more than 100,000 acre-feet of water. On October 14, 1976, the Corps of Engineers formally transferred control of the dam to the United States Bureau of Reclamation. Ecology The area surrounding the dam is hilly shrub-stepped and features the Artemisia tridentata, sagebrush and bunch grass typical of the area. The reservoir itself contains rainbow trout, kokanee salmon, cutthroat trout, smallmouth bass, and yellow perch. Possibility of failure If the Ririe Dam failed catastrophically, either from a natural disaster or a human initiated event, it would reach the first population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willow Creek (Snake River)
Willow Creek is a long tributary of the Snake River in the U.S. state of Idaho. Beginning at an elevation of east of the Blackfoot Mountains in southeastern Bingham County, Idaho, Bingham County, it flows generally north into Bonneville County, Idaho, Bonneville County and past Bone, Idaho, Bone. South of the town of Ririe, Idaho, Ririe, the creek is impounded by Ririe Dam, forming Ririe Reservoir. It then turns southwest, passing between Iona, Idaho, Iona and Ucon, Idaho, Ucon, before river bifurcation, bifurcating into two distributary, distributaries, North Fork Willow Creek and South Fork Willow Creek, at an elevation of . Both forks reach the Snake River north of Idaho Falls, Idaho, Idaho Falls. Willow Creek has significant populations of brown trout. See also *List of rivers of Idaho *List of longest streams of Idaho References Rivers of Idaho Rivers of Bingham County, Idaho Rivers of Bonneville County, Idaho {{Idaho-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunch Grass
Tussock grasses or bunch grasses are a group of grass species in the family Poaceae. They usually grow as singular plants in clumps, tufts, hummocks, or bunches, rather than forming a sod or lawn, in meadows, grasslands, and prairies. As perennial plants, most species live more than one season. Tussock grasses are often found as forage in pastures and ornamental grasses in gardens. Many species have long roots that may reach or more into the soil, which can aid slope stabilization, erosion control, and soil porosity for precipitation absorption. Also, their roots can reach moisture more deeply than other grasses and annual plants during seasonal or climatic droughts. The plants provide habitat and food for insects (including Lepidoptera), birds, small animals and larger herbivores, and support beneficial soil mycorrhiza. The leaves supply material, such as for basket weaving, for indigenous peoples and contemporary artists. Tussock and bunch grasses occur in almost any habitat w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dams In Idaho
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees (also known as dikes) are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. The earliest known dam is the Jawa Dam in Jordan, dating to 3,000 BC. The word ''dam'' can be traced back to Middle English, and before that, from Middle Dutch, as seen in the names of many old cities, such as Amsterdam and Rotterdam. History Ancient dams Early dam building took place in Mesopotamia and the Middle East. Dams were used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reservoirs In Idaho
A reservoir (; from French language, French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to water storage, store fresh water or it may be a natural formation. Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of water, interrupting a watercourse to form an Bay, embayment within it, through excavation, or building any number of retaining walls or levees. In other contexts, "reservoirs" may refer to storage spaces for various fluids; they may hold liquids or gasses, including hydrocarbons. ''Tank reservoirs'' store these in ground-level, elevated, or buried storage tanks, tanks. Tank reservoirs for water are also called cisterns. Most underground reservoirs are used to store liquids, principally either water or petroleum. Types Dammed valleys Dammed reservoirs are artificial lakes created and controlled by a dam constructed across a valley, and rely on the natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Bonneville County, Idaho
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakes Of Bonneville County, Idaho
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Perch
The yellow perch (''Perca flavescens''), commonly referred to as perch, striped perch, American perch, American river perch or preacher is a freshwater perciform fish native to much of North America. The yellow perch was described in 1814 by Samuel Latham Mitchill from New York. It is closely related, and morphologically similar to the European perch (''Perca fluviatilis''); and is sometimes considered a subspecies of its European counterpart. Other common names for yellow perch include American perch, coontail, lake perch, raccoon perch, ring-tail perch, ringed perch, and striped perch. Another nickname for the perch is the Dodd fish. Latitudinal variability in age, growth rates, and size have been observed among populations of yellow perch, likely resulting from differences in day length and annual water temperatures. In many populations, yellow perch often live 9 to 10 years, with adults generally ranging from in length. The world record yellow perch (; ) was caught in May 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutthroat Trout
The cutthroat trout is a fish species of the family Salmonidae native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean, Rocky Mountains, and Great Basin in North America. As a member of the genus '' Oncorhynchus'', it is one of the Pacific trout, a group that includes the widely distributed rainbow trout. Cutthroat trout are popular gamefish, especially among anglers who enjoy fly fishing. The common name "cutthroat" refers to the distinctive red coloration on the underside of the lower jaw. The specific name ''clarkii'' was given to honor explorer William Clark, coleader of the Lewis and Clark Expedition. Cutthroat trout usually inhabit and spawn in small to moderately large, clear, well- oxygenated, shallow rivers with gravel bottoms. They reproduce in clear, cold, moderately deep lakes. They are native to the alluvial or freestone streams that are typical tributaries of the rivers of the Pacific Basin, Great Basin and Rocky Mountains. Cutthroat trout spawn in the spring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokanee Salmon
The kokanee salmon (''Oncorhynchus nerka''), also known as the kokanee trout, little redfish, silver trout, kikanning, Kennerly's salmon, Kennerly's trout, or Walla, is the non-anadromous form of the sockeye salmon (meaning that they do not migrate to the sea, instead living out their entire lives in freshwater). There is some debate as to whether the kokanee and its sea-going relative are separate species; geographic isolation, failure to interbreed, and genetic distinction point toward a recent divergence in the history of the two groups. The divergence most likely occurred around 15,000 years ago when a large ice melt created a series of freshwater lakes and rivers across the northern part of North America. While some members of the salmon and trout family (salmonids) went out to sea (anadromous), others stayed behind in fresh water (non-anadromous). The separation of the sockeye and the kokanee created a unique example of sympatric speciation that is relatively new in evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
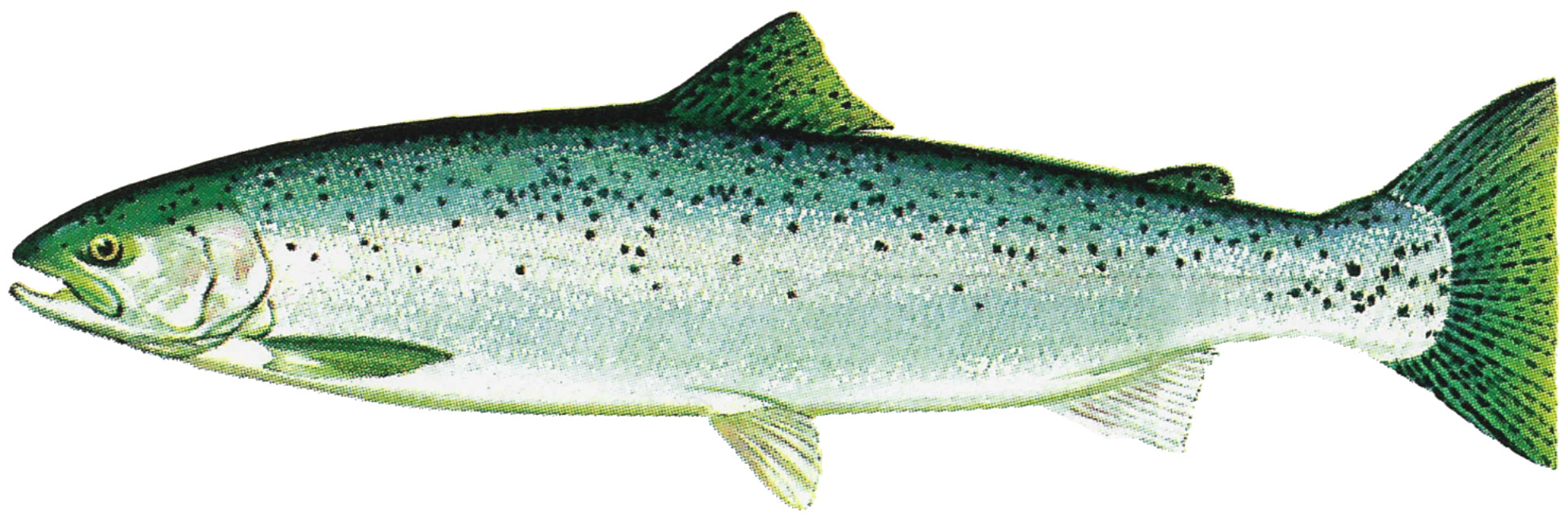
Rainbow Trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coastal rainbow trout or Columbia River redband trout that usually returns to freshwater to spawn after living two to three years in the ocean. Freshwater forms that have been introduced into the Great Lakes and migrate into tributaries to spawn are also called steelhead. Adult freshwater stream rainbow trout average between , while lake-dwelling and anadromous forms may reach . Coloration varies widely based on subspecies, forms, and habitat. Adult fish are distinguished by a broad reddish stripe along the lateral line, from gills to the tail, which is most vivid in breeding males. Wild-caught and hatchery-reared forms of the species have been transplanted and introduced for food or sport in at least 45 countries and every continent except ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
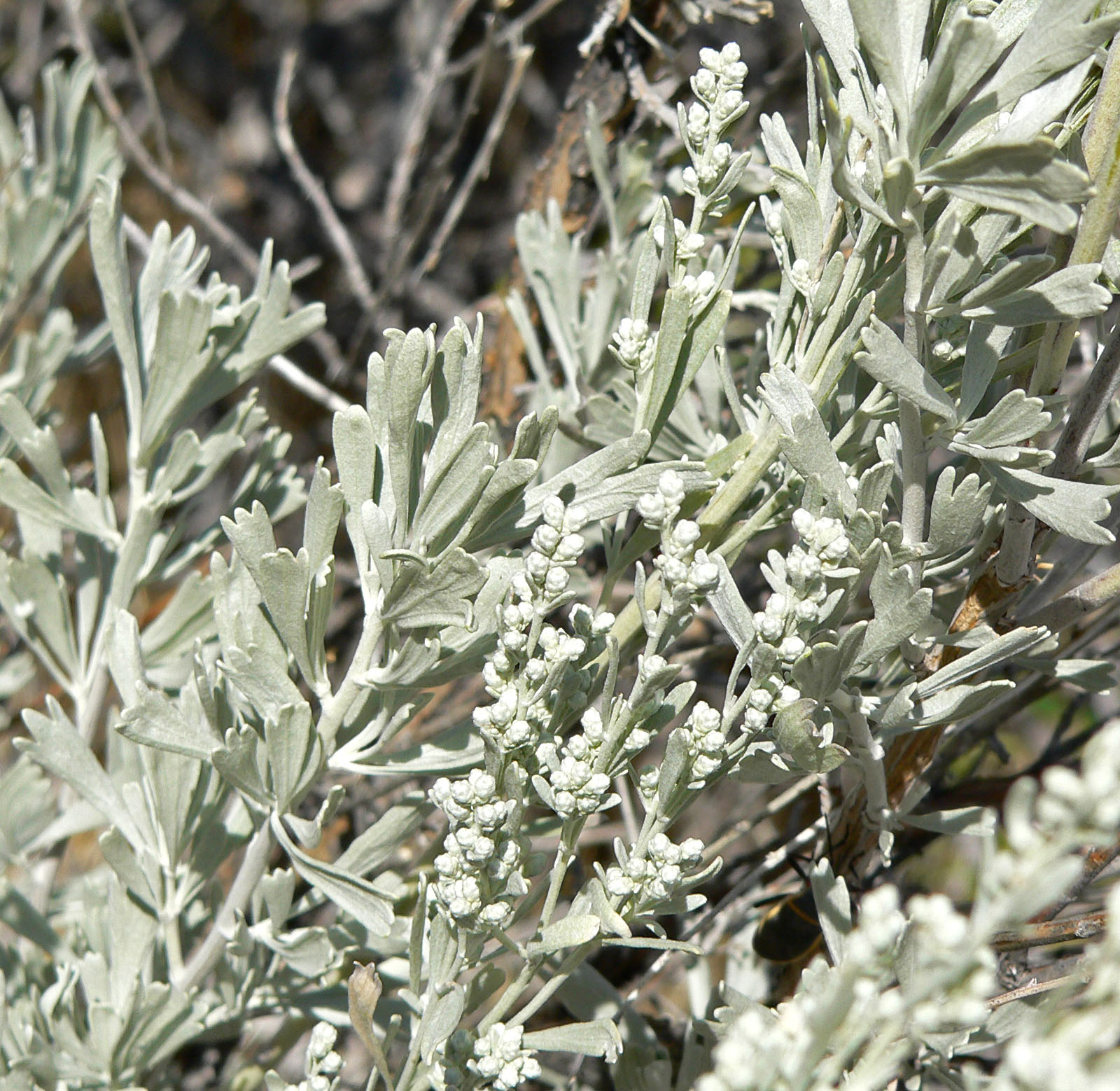
Artemisia Tridentata
''Artemisia tridentata'', commonly called big sagebrush,MacKay, Pam (2013), ''Mojave Desert Wildflowers'', 2nd ed., , p. 264. Great Basin sagebrush or (locally) simply sagebrush, is an aromatic shrub from the family Asteraceae, which grows in arid and semi-arid conditions, throughout a range of cold desert, steppe, and mountain habitats in the Intermountain West of North America. The vernacular name "sagebrush" is also used for several related members of the genus ''Artemisia'', such as California sagebrush (''Artemisia californica''). Big sagebrush and other ''Artemisia'' shrubs are the dominant plant species across large portions of the Great Basin. The range extends northward through British Columbia's southern interior, south into Baja California, and east into the western Great Plains of New Mexico, Colorado, Nebraska, and the Dakotas. Several major threats exist to sagebrush ecosystems, including human settlements, conversion to agricultural land, livestock grazing, inva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)