|
Ripa (rione Of Rome)
Ripa is the 12th ''rione'' of Rome, identified by the initials R. XII, and it is located in the Municipio I. The coat of arms of the ''rione'' depicts a white rudder on a red background, to remind the port of Ripa Grande, that was placed in Trastevere, but faced the ''rione''. History The borough has always been urbanized, although not intensively, since the Ancient Rome: at that time, the area included three ''regiones'', ''Circus Maximus'', ''Piscina Publica'' and ''Aventinus''. As of 4th century, the bank of the River Tiber in the ''rione'' was called ''Ripa Graeca'', after a Greek community that settled there and increased during the following centuries, particularly in 8th century, when the area was inhabited by Greek and Latin people escaped from the iconoclastic persecutions led by Leo III the Isaurian. During the Middle Ages, the northern part of the ''rione'' remained unpopulated, with the only exceptions of some fortified monastery and a baronial castle, the ''Rocc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Italy
The regions of Italy ( it, regioni d'Italia) are the first-level administrative divisions of the Italian Republic, constituting its second NUTS administrative level. There are twenty regions, five of which have higher autonomy than the rest. Under the Italian Constitution, each region is an autonomous entity with defined powers. With the exception of the Aosta Valley (since 1945) and Friuli-Venezia Giulia (since 2018), each region is divided into a number of provinces (''province''). History During the Kingdom of Italy, regions were mere statistical districts of the central state. Under the Republic, they were granted a measure of political autonomy by the 1948 Italian Constitution. The original draft list comprised the Salento region (which was eventually included in Apulia); ''Friuli'' and ''Venezia Giulia'' were separate regions, and Basilicata was named ''Lucania''. Abruzzo and Molise were identified as separate regions in the first draft, but were later merged into ''Abru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo III The Isaurian
Leo III the Isaurian ( gr, Λέων ὁ Ἴσαυρος, Leōn ho Isauros; la, Leo Isaurus; 685 – 18 June 741), also known as the Syrian, was Byzantine Emperor from 717 until his death in 741 and founder of the Isaurian dynasty. He put an end to the Twenty Years' Anarchy, a period of great instability in the Byzantine Empire between 695 and 717, marked by the rapid succession of several emperors to the throne. He also successfully defended the Empire against the invading Umayyads and forbade the veneration of icons. Early life Of Syrian extraction, Leo was born in Germanikeia, Commagene (modern Kahramanmaraş in Turkey). His original name was Konon ( gr, Κόνων; la, Conon or ''Cononus''). Some, including the Byzantine chronicler Theophanes, have claimed that Konon's family had been resettled in Thrace, where he entered the service of Emperor Justinian II, when the latter was advancing on Constantinople with an army of loyalist followers, and horsemen provided by Terve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celio (rione Of Rome)
Celio () is the 19th ''rione'' of Rome, identified by the initials R. XIX, and is located within the Municipio I. Its coat of arms depicts the bust of an African, with an elephant headdress with golden tusks on a silver background, in memory of an African bust that was found in Via Capo d'Africa. History Up to 1870, the area was moderately inhabited, with some major religious building and many archaeological remains appearing in the vast filed and vineyards. Following to the unification of Italy, the district was among the first to be urbanized, between 1872 and 1873, with new service buildings and residences for the newcomers. Particularly, a military hospital was built on the summit of the Caelian hill between 1885 and 1891, close to the medieval site of Santo Stefano in Formis, an ancient monastery with an annexed hospital. Up until the postwar period, the road scheme has been reworked in the lower part of the ''rione'', near the Colosseo, and in 1968 a big public housing com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porta Capena
Porta Capena was a gate in the Servian Wall in Rome, Italy. The gate was located in the area of Piazza di Porta Capena, where the Caelian, Palatine and Aventine hills meet. Probably its exact position was between the entrance of Via di Valle delle Camene and the beginning of Via delle Terme di Caracalla (known as the "Archaeological Walk"), facing the curved side of the Circus Maximus. Nowadays Piazza di Porta Capena hosts the FAO Headquarters. Between 1937 and 2004, it was home to the obelisk of Axum. History The valley around what is now the avenue of the Baths of Caracalla was in ancient times covered with woods, caves and water springs. In this area (called the valley of the '' Camenae''), considered sacred and mysterious, it is said (and Livy punctually reports) that the peaceful king Numa Pompilius, the first successor of Romulus, had his nocturnal encounters with the goddess (or nymph) Egeria, who on those occasions provided him with all the necessary information for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campitelli
Campitelli is the 10th ''rioni of Rome, rione'' of Rome, identified by the initials R. X, and is located in the Municipio I. Its emblem consists of a black dragon's head on a white background. This symbol comes from the legend that Pope Silvester I threw out a dragon staying in the Forum Romanum. History Some of the major vestiges of the Ancient Rome are located in the area, such as the Palatine Hill, the Campidoglio and the Roman Forum. When in the Middle Ages the new administrative subdivision of the city was adopted, Campitelli was the 12th and last ''rione''. It was called ''Campitelli in Sancti Adriani'', after the deconsecrated church of Sant'Adriano al Foro. Since the 12th century, the Palazzo Senatorio became the seat of the ''Senatore di Roma'' (Senator of Rome), the principal civic authority of the city in the Middle Ages. The Palazzo Senatorio and the basilica of Santa Maria in Ara Coeli are the only remaining features of the medieval construction industry in the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lungotevere Dei Pierleoni
Lungotevere dei Pierleoni is the stretch of lungotevere which links piazza di Monte Savello to ponte Palatino, in Rome, in rione Ripa. This lungotevere is named after the ancient Roman family of the Pierleoni, which owned houses, towers and a fortress on the shore of the Tevere; it was instituted with law of 20 July 1887. Note Sources *{{cite book, last1=Rendina , first1=Claudio, last2=Paradisi , first2=Donatella , title = Le strade di Roma. 3rd volume P-Z, year= 2004, publisher = Newton Compton Editori, Rome, isbn=88-541-0209-1 Pierleoni The family of the Pierleoni, meaning "sons of Peter Leo", was a great Roman patrician clan of the Middle Ages, headquartered in a tower house in the quarter of Trastevere that was home to a larger number of Roman Jews. The heads of the family ofte ... Streets in Rome R. XII Ripa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sant'Angelo (rione Of Rome)
Sant'Angelo is the 11th ''rioni of Rome, rione'' of Rome, Italy, located in Municipio I. Often written as ''rione XI - Sant'Angelo'', it has a coat of arms with an angel on a red background, holding a palm branch in its left hand. In another version, the angel holds a sword in its right hand and a Weighing scale, scale in its left. Sant'Angelo, the smallest of Rome's rioni, lies along the Tiber river east of Isola Tiberina, Tiber Island. Rioni bordering this district, clockwise from north to south, include Regola (rione of Rome), Regola, Sant'Eustachio (rione of Rome), Sant'Eustachio, Pigna (rione of Rome), Pigna, Campitelli, and Ripa (rione of Rome), Ripa. Sant'Angelo's western border is the river. The rione's terrain is low and flat and, until the construction of the Lungotevere, particularly susceptible to flooding from the river. The historical significance of Sant'Angelo is mainly the result of the presence here of the Roman Ghetto. History Roman Age: ''Circus Flamini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
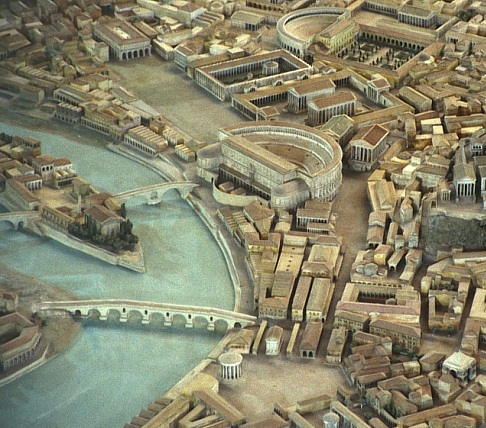
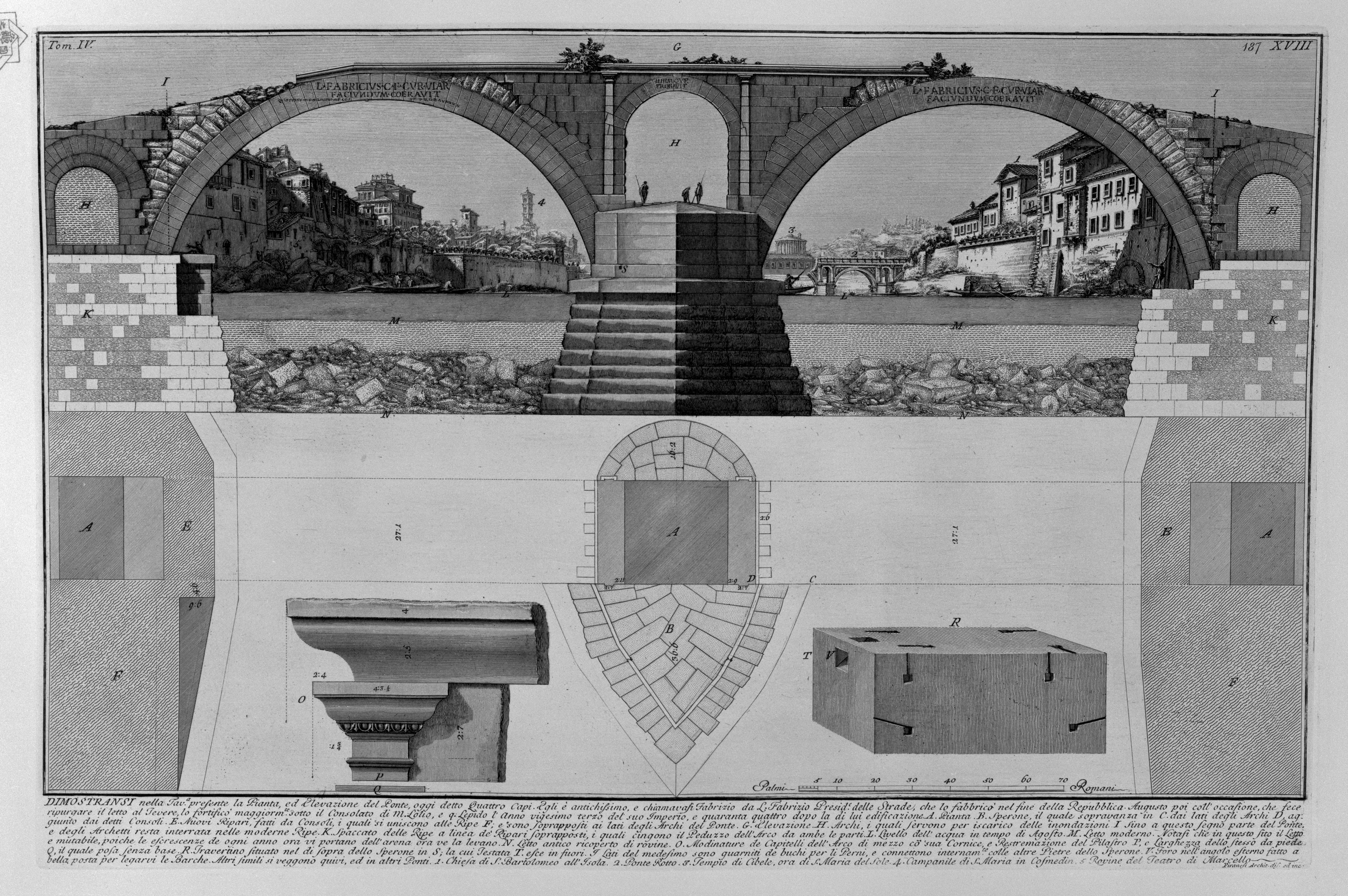
Ponte Fabricio
The Pons Fabricius ( it, Ponte Fabricio, "Fabrician Bridge") or Ponte dei Quattro Capi, is the oldest Roman bridge in Rome, Italy, still existing in its original state. Built in 62 BC, it spans half of the Tiber River, from the Campus Martius on the east side to Tiber Island in the middle (the Pons Cestius is west of the island). ''Quattro Capi'' ("four heads") refers to the two marble pillars of the two-faced Janus herms on the parapet, which were moved here from the nearby Church of St Gregory (Monte Savello) in the 14th century.Claridge, Amanda (1998). Rome: An Oxford Archaeological Guide'. Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press Bridge According to Dio Cassius, the bridge was built in 62 BC, the year after Cicero was consul, to replace an earlier wooden bridge destroyed by fire. It was commissioned by Lucius Fabricius, the curator of the roads and a member of the gens Fabricia of Rome. Completely intact from Roman antiquity, it has been in continuous use ever since. The Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ponte Garibaldi
Ponte Garibaldi is a bridge that links Lungotevere De' Cenci to Piazza Giuseppe Gioachino Belli in Rome (Italy), in the Rioni Regola and Trastevere. Description The bridge was designed by architect Angelo Vescovali and built between 1884 and 1888; it was dedicated to Giuseppe Garibaldi, "Hero of Two Worlds" and one of the fathers of Italian unification. The bridge, enlarged in 1959, was released to facilitate the expansion of the town towards Trastevere.. It has two metal spans, which lie on a central shaft and on two smaller shafts covered with travertine Travertine ( ) is a form of terrestrial limestone deposited around mineral springs, especially hot springs. It often has a fibrous or concentric appearance and exists in white, tan, cream-colored, and even rusty varieties. It is formed by a pro ...; it is long. Transports The bridge is crossed by tram 8 and buses H, 780 e 781. Notes Bibliography * * Bridges in Rome Bridges completed in 1888 Road bridges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiber Island
The Tiber Island ( it, Isola Tiberina, Latin: ''Insula Tiberina'') is the only river island in the part of the Tiber which runs through Rome. Tiber Island is located in the southern bend of the Tiber. The island is boat-shaped, approximately long and wide, and has been connected with bridges to both sides of the river since antiquity. Being a seat of the ancient temple of Asclepius and later a hospital, the island is associated with medicine and healing. The Fatebenefratelli Hospital founded in the 16th century, and the church of San Bartolomeo all'Isola dating from the 10th century, are located on the island. History The island has been linked to the rest of Rome by two bridges since antiquity, and was once called ''Insula Inter-Duos-Pontes'' which means "the island between the two bridges". The Ponte Fabricio, the only original bridge in Rome, connects the island from the northeast to the Field of Mars in the rione Sant'Angelo (left bank). The Ponte Cestio, of which o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regola
Regola is the 7th ''rione'' of Rome, Italy, identified by the initials R. VII, and belongs to the Municipio I. The name comes from ''Arenula'' (the name is recognizable in the modern ''Via Arenula''), which was the name of the soft sand (''rena'' in Italian) that the river Tiber left after the floods, and that built strands on the left bank. The inhabitants of the ''rione'' are called ''Regolanti''. They were nicknamed ''mangiacode'' ('tail-eaters'), after the typical dish ''coda alla vaccinara'', which was a specialty of the many ''vaccinari'' ('butchers') of the ''rione''. The seal of the ''rione'' represents a rampant deer with a turquoise background. History During the Roman empire, the area belonged to the ''Campus Martius''. In particular, in the modern Regola there was the Trigarium, the stadium where the riders of the ''triga'' (a cart with three horses) used to train. When Emperor Augustus divided Rome into 14 regions, the modern Regola belonged was included in the I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testaccio
Testaccio is the 20th ''rione'' of Rome, identified by the initials R. XX, deriving its name from Monte Testaccio. It is located within the Municipio I. Its coat of arms depicts an ''amphora'', referencing to the broken vessels that Monte Testaccio is made of. History In antiquity, much of the Tiber trade took place here, and the remains of broken clay vessels (amphorae) were stacked creating the artificial Testaccio hill, which today is a source of much archaeological evidence as to the history of ancient everyday Roman life. Until the urban recovery that took place after 1870, which destined a huge area to industrial and manufacturing purposes, the borough was chiefly inhabited by poor farmers and shepherds, it was vulnerable to the Tiber floods and infested by malaria. The zone between Monte Testaccio and the city walls (Prati di Testaccio) was public and commonly used by the citizens as a recreation ground, traditional destination of holiday trips and of the typical ''ott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |