|
Rintatolimod
Rintatolimod, sold under the tradename Ampligen, is a medication intended for treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). There is some evidence it may improve some CFS symptoms. It is an immunomodulatory RNA#Double-stranded RNA, double-stranded RNA drug similar to the prototypical RNA Polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid, poly I:C, first synthesized in the 1970s and manufactured by Hemispherx Biopharma, which was later renamed AIM ImmunoTech. Although Ampligen was initially cleared for use in Canada in 1997, and obtained orphan drug status for treatment of CFS in the European Union in 2000, it is approved for use only in Argentina. Its status in Canada, per later information, is as a Special Use Program. Rintatolimod has not yet been approved as a legally-prescriptible medication to treat any formally-defined health conditions, diseases, or symptoms in the United States of America as it's still classified by the Food and Drug Administration (United States), U.S. Food and Drug Admini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), also called myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME) or ME/CFS, is a complex, debilitating, long-term medical condition. The causes and mechanisms of the disease are not fully understood. Distinguishing core symptoms are lengthy exacerbations or flare-ups of the illness following ordinary minor physical or mental activity, known as post-exertional malaise (PEM); greatly diminished capacity to accomplish tasks that were routine before the illness; and sleep disturbances. Orthostatic intolerance (difficulty sitting and standing upright) and cognitive dysfunction are also diagnostic. Frequently and variably, other common symptoms occur involving numerous body systems, and chronic pain is common. The unexplained and often incapacitating fatigue in CFS is different from that caused by normal strenuous ongoing exertion, is not significantly relieved by rest, and is not due to a previous medical condition. Diagnosis is based on the person's symptoms because no c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutropenia
Neutropenia is an abnormally low concentration of neutrophils (a type of white blood cell) in the blood. Neutrophils make up the majority of circulating white blood cells and serve as the primary defense against infections by destroying bacteria, bacterial fragments and immunoglobulin-bound viruses in the blood. People with neutropenia are more susceptible to bacterial infections and, without prompt medical attention, the condition may become life-threatening (neutropenic sepsis). Neutropenia can be divided into congenital and acquired, with severe congenital neutropenia (SCN) and cyclic neutropenia (CyN) being autosomal dominant and mostly caused by heterozygous mutations in the ELANE gene (neutrophil elastase). Neutropenia can be acute (temporary) or chronic (long lasting). The term is sometimes used interchangeably with "leukopenia" ("deficit in the number of white blood cells"). Decreased production of neutrophils is associated with deficiencies of vitamin B12 and folic aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DuPont
DuPont de Nemours, Inc., commonly shortened to DuPont, is an American multinational chemical company first formed in 1802 by French-American chemist and industrialist Éleuthère Irénée du Pont de Nemours. The company played a major role in the development of Delaware and first arose as a major supplier of gunpowder. DuPont developed many polymers such as Vespel, neoprene, nylon, Corian, Teflon, Mylar, Kapton, Kevlar, Zemdrain, M5 fiber, Nomex, Tyvek, Sorona, Corfam and Lycra in the 20th century, and its scientists developed many chemicals, most notably Freon (chlorofluorocarbons), for the refrigerant industry. It also developed synthetic pigments and paints including ChromaFlair. In 2015, DuPont and the Dow Chemical Company agreed to a reorganization plan in which the two companies would merge and split into three. As a merged entity, DuPont simultaneously acquired Dow and renamed itself to DowDuPont on August 31, 2017, and after 18 months spin off the merged entity' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DsRNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, nucleic acids constitute one of the four major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA, RNA is found in nature as a single strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (''mRNA'') to convey genetic information (using the nitrogenous bases of guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine, denoted by the letters G, U, A, and C) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome. Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University (Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1876, Johns Hopkins is the oldest research university in the United States and in the western hemisphere. It consistently ranks among the most prestigious universities in the United States and the world. The university was named for its first benefactor, the American entrepreneur and Quaker philanthropist Johns Hopkins. Hopkins' $7 million bequest to establish the university was the largest Philanthropy, philanthropic gift in U.S. history up to that time. Daniel Coit Gilman, who was inaugurated as :Presidents of Johns Hopkins University, Johns Hopkins's first president on February 22, 1876, led the university to revolutionize higher education in the U.S. by integrating teaching and research. In 1900, Johns Hopkins became a founding member of the American Association of Universities. The university has led all Higher education in the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merck & Co
Merck & Co., Inc. is an American multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Rahway, New Jersey, and is named for Merck Group, founded in Germany in 1668, of whom it was once the American arm. The company does business as Merck Sharp & Dohme or MSD outside the United States and Canada. Merck & Co. was originally established as the American affiliate of Merck Group in 1891. Merck develops and produces medicines, vaccines, biologic therapies and animal health products. It has multiple blockbuster drugs or products each with 2020 revenues including cancer immunotherapy, anti-diabetic medication and vaccines against HPV and chickenpox. The company is ranked 71st on the 2022 ''Fortune'' 500 and 87th on the 2022 ''Forbes'' Global 2000, both based on 2021 revenues. Products The company develops medicines, vaccines, biologic therapies and animal health products. In 2020, the company had 6 blockbuster drugs or products, each with over $1 billion in revenue: ''Keytruda'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling as immunomodulating agents. Cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumour necrosis factors, but generally not hormones or growth factors (despite some overlap in the terminology). Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. They act through cell surface receptors and are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the balance between humoral and cell-based immune responses, and they regulate the maturation, growth, and res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten their anti-viral defenses. IFNs belong to the large class of proteins known as cytokines, molecules used for communication between cells to trigger the protective defenses of the immune system that help eradicate pathogens. Interferons are named for their ability to "interfere" with viral replication by protecting cells from virus infections. However, virus-encoded genetic elements have the ability to antagonize the IFN response contributing to viral pathogenesis and viral diseases. IFNs also have various other functions: they activate immune cells, such as natural killer cells and macrophages, and they increase host defenses by up-regulating antigen presentation by virtue of increasing the expression of major histocompatibility complex (M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
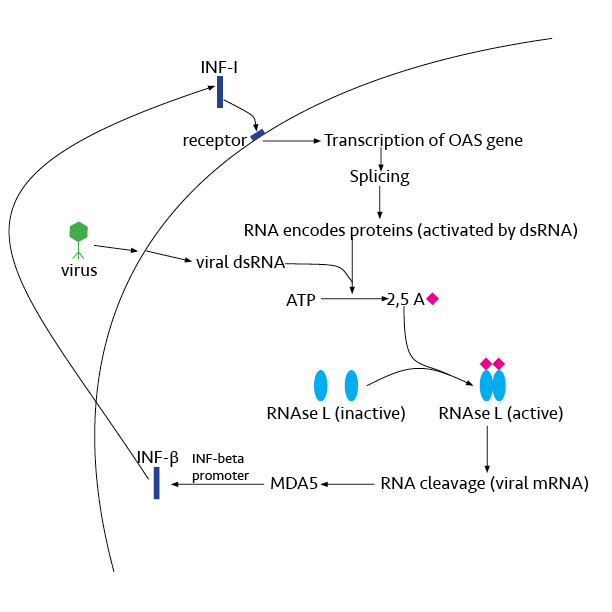
RNase L
Ribonuclease L or RNase L (for ''latent''), known sometimes as ribonuclease 4 or 2'-5' oligoadenylate synthetase-dependent ribonuclease — is an interferon (IFN)-induced ribonuclease which, upon activation, destroys all RNA within the cell (both cellular and viral). RNase L is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''RNASEL'' gene. This gene encodes a component of the interferon-regulated 2'-5'oligoadenylate (2'-5'A) system that functions in the antiviral and antiproliferative roles of interferons. RNase L is activated by dimerization, which occurs upon 2'-5'A binding, and results in cleavage of all RNA in the cell. This can lead to activation of MDA5, an RNA helicase involved in the production of interferons. Synthesis and activation RNase L is present in very minute quantities during the normal cell cycle. When interferon binds to cell receptors, it activates transcription of around 300 genes to bring about the antiviral state. Among the enzymes produced is RNase L, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Immunity
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Like the innate system, the adaptive immune system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components and destroys invading pathogens. Unlike the innate immune system, which is pre-programmed to react to common broad categories of pathogen, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to each particular pathogen the body has encountered. Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, and leads to an enhanced response to future encounters with that pathogen. Antibodies are a critical part of the adaptive immune system. Adaptive immunity can provide long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TLR 3
Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) also known as CD283 (cluster of differentiation 283) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TLR3'' gene. TLR3 is a member of the toll-like receptor family of pattern recognition receptors of the innate immune system. TLR3 recognizes double-stranded RNA in endosomes, which is a common feature of viral genomes internalised by macrophages and dendritic cells. Function TLR3 is a member of the toll-like receptor (TLR) family which plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. TLRs are highly conserved from Drosophila to humans and share structural and functional similarities. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns ( PAMPs) that are expressed on infectious agents, and mediate the production of cytokines necessary for the development of effective immunity. The various TLRs exhibit different patterns of expression. This receptor is most abundantly expressed in placenta and pancreas, and is rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Immunology
The ''Journal of Immunology'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed medical journal that publishes basic and clinical studies in all aspects of immunology. Established in 1916, it changed its name to ''Journal of Immunology, Virus Research and Experimental Chemotherapy'' from 1943 to 1949, then returned to the original ''Journal of Immunology'' in 1950. It is the official journal of the American Association of Immunologists. The editor-in-chief is Eugene M. Oltz. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 5.422. History The journal was established by Arthur Fernandez Coca (1875–1959) in 1916 as the official journal of the America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |